Introduction to Loan Loss Provisioning
Provisioning is the fund that a bank sets aside to cover potential losses on loans. Provisioning involves the following steps:
- Classification of debts under the same risk characteristics
- Actual Calculation and posting the provision amount
- Manual posting when required
An asset with a low risk requires a lesser loan provision compared to an asset with higher risk. Thus, the amount of loan loss provision is calculated as a percentage of the loan balance based upon the perceived risk of the asset.
To process provisioning, asset must be classified according to its credit risk characteristics. Provisioning regulations are divided into two categories:
- The regulations of the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), which is referred as IFRS Impairment.
- Non-IFRS complies with the local regulations. This is referred as Standard Provisioning.
Read the IAS 39 User Guide, for more information on impairment under the Incurred Loss Model.
Read the IFRS9 User Guide for more information on Impairment under the Expected Loss Model.
PV module was created as a separate module in Temenos Transact for provisioning. It is also a prerequisite to use the PV functionality along with the International Accounting Standards for IFRS impairment and provisioning.
The PV module enables the following functionality:
- IFRS Impairment Model – Impairment of assets under IFRS9 (requires IA & I9 Module) based on the Expected Loss Model.
- IFRS Collective and Manual impairment requires the IA Module.
- Standard provisioning of assets.
The provisioning module supports the following important activities:
- Classification of assets based on perceived risk
- Calculation of provision
- Manual adjustment of classification and provision amount
- Posting of the provision amount
Product Configuration
The following image shows the key components of the PV module.
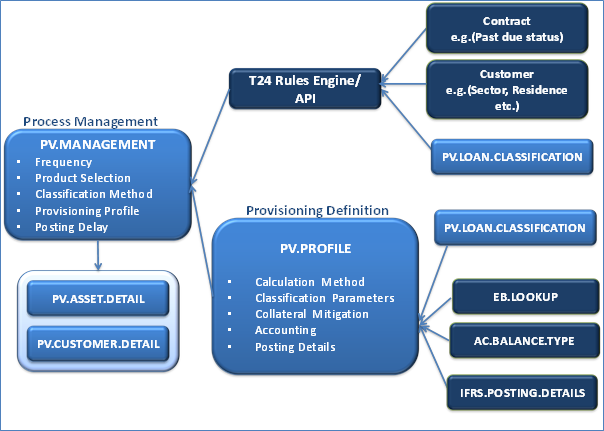
The configuration for standard provisioning must be in the following order:
- Parameters for Classification of Assets
- Parameters for Calculation of Provision
- Parameters for Posting of Provision
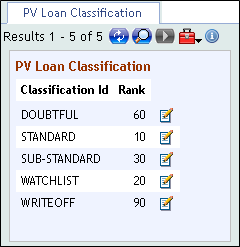
PV.LOAN.CLASSIFICATION)
The PV.LOAN.CLASSIFICATION id is the risk classification that indicates the risk level of the contract or the customer and will be used to allocate the percentage for provision. A risk classification will be assigned to the contract and customer by the classification process.
The rank is a unique number that indicates the risk level for each risk classification. This is used by the system to determine which classification is worst. Risk classification is defined according to the rank given. The table below provides an example of the list of risk classifications that can be created in the PV.LOAN.CLASSIFICATION table.
There are no global standards that define the classification of assets under credit risks. The criteria and rules for classifications may differ across countries or banks; hence a flexible mechanism is required to handle different rules and criteria for asset classification. The following two methods can be used to classify the credit risk in the PV module:
- Use the Temenos Transact rules engine.
- Write a local routine (API) which can be plugged into the PV module.
The Temenos Transact rules engine is used to establish the rules for classification and to determine the classification code (that is, PV.LOAN.CLASSIFICATION) to be assigned to each individual asset. To configure the rule or rules for classification, one or more contexts must be passed to the engine as these will contain the necessary criteria for classification. These criteria can be created from contract or arrangement and customer. For example, these may include:
- The days past due (this may be held in the contract or arrangement record)
- The debtor assessment , which can be a subjective rating (it may be held in the customer record)
- To establish rules in Temenos Transact Rules Engine, following parameters are required:
EB.CONTEXTRULE DESIGNEREB.RULESEB.RULES.VERSIONEB.RULE.GATEWAY
For more details on how to set up theTemenos Transact Rules Engine, read the user guide.
EB.LOOKUP:
EB.LOOKUP is a generic template to hold all the lookups for data access service. The user can define EB.LOOKUP and use them as drop-down lists in applications without creating separate tables for each field. The ID of this file will be in the format virtual table name*real.key.
For standard provisioning, different provision percentages can be applied to different types of balance. A virtual table PV.PROVISION.TYPE, with the following records may be defined as:
- PV.PROVISION.TYPE*TOTALPVPRINCIPAL for Principal
- PV.PROVISION.TYPE*TOTALPVINTEREST for Interest
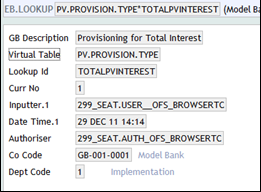
The following screenshot shows EB.LOOKUP record details:
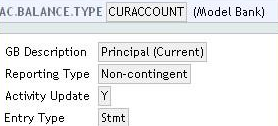
AC.BALANCE.TYPE:
The source balance must be defined for each provision type. Source balance is the balance used for provision calculation. It is the link to the AC.BALANCE.TYPE application.
It may include a single financial component used in AA.ARRANGEMENT as shown below:
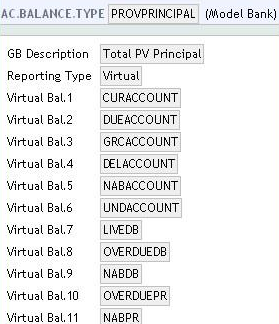
If the source balance includes more than one financial component, then the AC.BALANCE.TYPE record may hold the list of the existing AC.BALANCE.TYPE records and asset types from reporting (RE.TYPES) such as LIVEDB
The following screenshot shows the AC.BALANCE.TYPE record for the source balance for principal balance. It includes existing AC.BALANCE.TYPE records and non-AA asset types.
The provision profile (PV.PROFILE) contains definitions of the type of calculation to be performed, the base balance type for provision calculation and provision percentage applicable for the respective balance type and risk classification.
A contract can follow only one type of calculation by default, unless a multi-GAAP provisioning setup is provided.
Read the Multi-GAAP Provisioning user guide for more information.
The PV.PROFILE table works as per the date. An additional reference table (PV.PROFILE.XREF) contains a list of the dates held for the provision profile.
The Class field in PV.PROFILE application, which refers to the risk classification, must be defined in ascending order of rank.
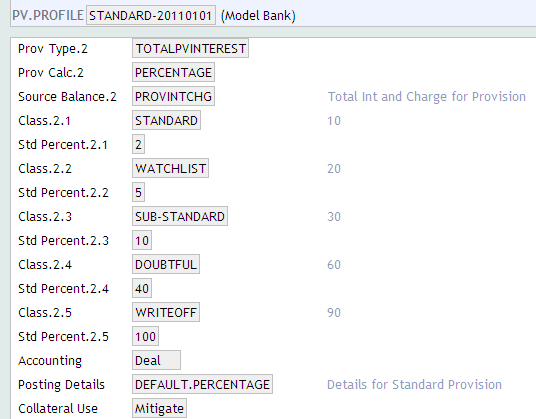
The Prov Calc field in the PV.PROFILE application is used define the provision calculation method. Provision can be calculated using any of the following methods:
- IFRS – Impairment calculation under IFRS.
- PERCENTAGE – For standard provisioning calculation.
- API – For specific local requirement that requires a local routine to perform the calculation.
A contract can follow only one type of calculation, hence either the IFRS, Standard Provision Percentage or an API is allowed.
The Source Balance field allows a valid AC.BALANCE.TYPE record or valid ASSET.TYPE. The Collateral Use field is allowed if the provision calculation is not IFRS, but is allowed for Standard Provisioning. The posting details input must exist in the IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS application and is mandatory if there is any value in the Prov Calc field.
For each classification defined in PV.LOAN.CLASSIFICATION, user can define the associated percentages required for the calculation of provision. The following percentages are used for the provisioning calculation based on the calculation method:
- Percentage (standard provisioning)
- Std Percent – This is the standard percentage to apply to the Balance.
- IFRS
- PD – Probability of default (probability that the contract may default).
- LGD – Loss given default(the percentage loss if there is a default).
- LIP – Loss identification period (the period between the loss event and when the bank acquires information about or is notified about it). This is used only for the Incurred Loss Model.
Each provision type has an associated Source Balance, which indicates where the balance for that provision type is picked up. This is a valid AC.BALANCE.TYPE id that defines a list of virtual types for arrangement contracts and asset type for other contracts.
For standard provisioning, it is possible to mitigate the collateral from the provision amount. This functionality is available if the Collateral Use field is set to MITIGATE in the PV.PROFILE.
The Collateral.Use field is not allowed if the provision calculation method is IFRS.
The Accounting entries are raised at deal level as defined in the Accounting field, that is, accounting entries are raised for each contract. The parameters required to generate these entries are set-up in the IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS table and the link to IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS is defined in the Posting Details field.
The Posting Details field is mandatory and must be a valid key to the IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS table.
For IFRS impairment, IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS relating to the contract is used as held in EB.CASHFLOW.
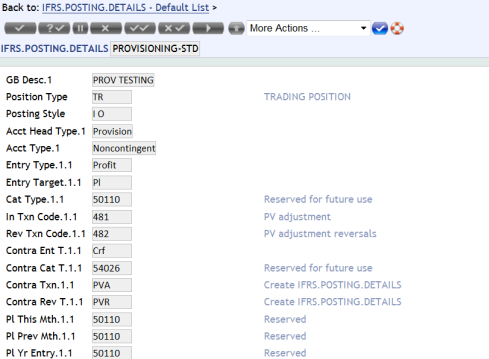
IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS
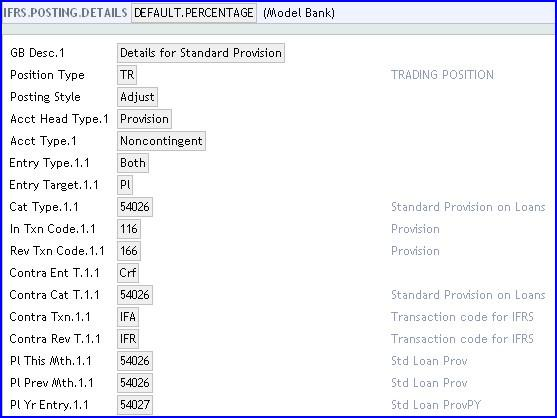
The IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS table stores details relating to the way accounting entries are generated to make the contracts compatible with the IFRS requirements. These are also used for provisioning. Different records are required for IFRS and standard provisioning because different Position Type is used for each one.
The following screenshot shows the default record for standard provisioning with the Position Type updated as TR:
The default record for IFRS has Position Type updated as IF, as shown below.
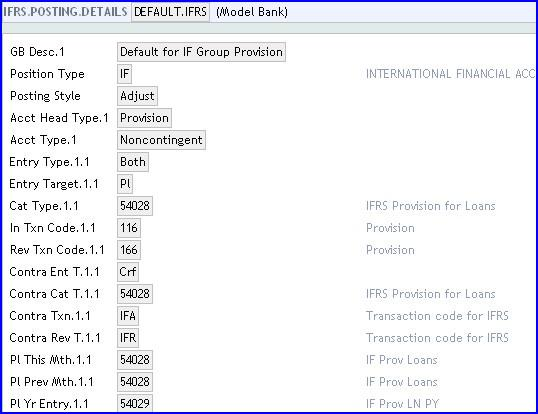
The Acct Head Type field value, Provision, must be added into the existing IFRS.ACCT.METHODS and IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS records that are linked to the IFRS.SUB.TYPE record for IFRS impairment.
Defining Different PL Categories for Profit and Loss:
- The Entry Type field is specifically defined as profit and loss, with categories pertaining to each type, in order to differentiate between profit and loss in provisioning.
- Specific categories and transaction codes can be mentioned for both entry types.
- This is applicable for both standard and IFRS provisioning.
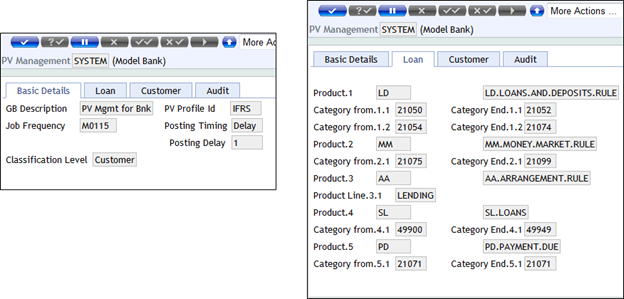
PV.MANAGEMENT
Provision Management (PV.MANAGEMENT) defines when the provisioning process should be triggered, what products are subject to assessment, the rules used to determine the classification and the provision calculation. The system allows multiple PV Management records to be created, thus allowing different classification and provisioning rules for different groups of products. For example, commercial loans may be treated differently to personal loans.
It allows the users to define the parameters that controls the provisioning process. These parameters include the following:
- Frequency to run the provisioning process (this keeps track of the next classification date, which triggers the provisioning process).
- The number of days to delay the posting after the classification process.
- Selection criteria of contracts for each product.
- The level of classification ( classification at the contract level or worst classification for the customer).
- Classification rule (Temenos Transact rules engine) or API.
- Link to provisioning profile.
There are two process setups that are allowed in the system:
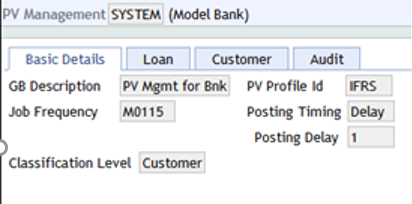
- A single
PV.MANAGEMENTrecord,SYSTEM,is allowed for each lead company. It can also be shared within a multi-company environment. The provisioning management record is linked to one provisioning profile.
The following screenshot shows an example of the PV.MANAGEMENT record:
- Multiple
PV.MANAGEMENTrecords can be defined for individual products. This allows the bank to set up classification and calculation rules per product. In the following example, records have been created for LD commercial loans and LD personal loans. A product category may only be specified in onePV.MANAGEMENTrecord. ThePV.MGMT.PRODUCT.LISTis an internal table, which holds the list of category Range/Product Group/Product Line defined for an application inPV.MANAGEMENT.
Individual PV.MANAGEMENT records cannot be entered if a SYSTEM record is already created in the PV.MANAGEMENT application. The existing SYSTEM record needs to be reversed before entering new records.
The following screenshot shows the PV.MANAGEMENT record for commercial and personal loans:
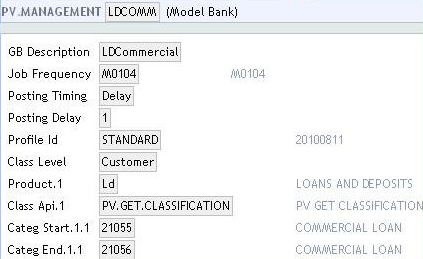
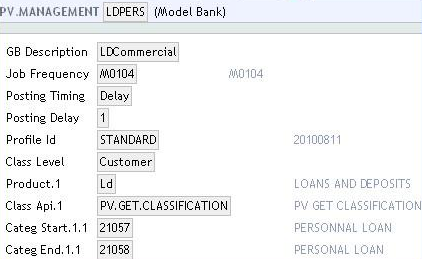
Frequency
The frequency is the date that triggers the classification process. The following screenshot shows the Job Frequency updated as MO115 in the SYSTEM record. Thus the next processing date is the 15th of the following month if current date is greater than 15th.
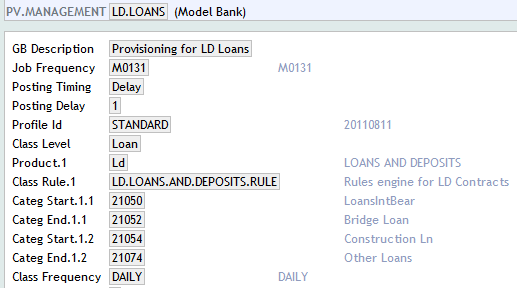
Using the Class Frequency field, user can set the classification frequency to be different from the calculation and posting frequencies. If this field is set, it can be used to calculate the Next Class Date. The Next Calc Date and Next Post Date continue to use the Frequency field to determine their frequencies. In the following example (screenshot), the frequency for classification has been set to DAILY in the Class Frequency field.
If this field is not entered, then the classification frequency is determined using the Frequency.
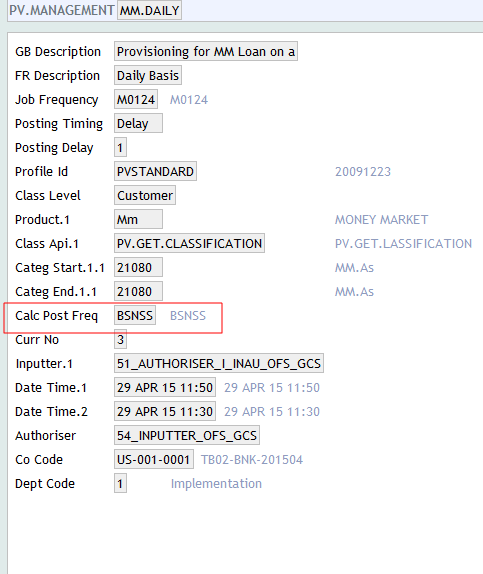
The Job Frequency field also determines the time when the calculation and the posting processes are triggered. The calculation and posting processes can also be triggered on every business day by setting the Calc Post Freq field in the PV.MANAGEMENT record, corresponding to the types of product.
This overrides the frequency defined under Job Frequency for the calculation and posting processes.
The following screenshot shows that Calc Post Freq is set to BSNSS, which means that the calculation and posting is triggered on every business day. The frequency defined under the Job Frequency applies to the classification process.
Provisioning Profile:
The link to the provisioning profile (PV.PROFILE) is defined here, it indicates that the calculation method to be used for the Provision is as per defined in the PV.PROFILE record, here the link is to the PV.PROFILE record ‘IFRS’. The PV.MANAGEMENT record can be linked to only one PV.PROFILE record. Only a single Provision Profile is allowed; hence the Provision percentages for a specific classification is applied to all contracts falling under that classification. For example the Standard Percentage for “Doubtful” is 40%, then a provision percentage of 40% is applied to all contracts with classification 'Doubtful' irrespective of the types of product.
Posting Delay:
The only value allowed in Posting Timing field is DELAY. This field indicates that there is a delay between the calculation and the posting of provision. The window between calculation and posting is defined as number of days in the Posting Delay field. This window allows for any changes that may affect the provision amount to be posted.
In the above example, the posting delay is 1 day, which means that posting is done one day after the classification and calculation process is triggered. In this case, a recalculation takes place prior to the posting.

Classification Level:
The following classification level indicates the classification to be considered when calculating the provision:
- If the Class Level is set to LOAN, the classification assigned to the contract is used.
- If the Class Level is set to CUSTOMER, the worst classification for the customer is considered.
Selection of Contracts:
The contracts selected for the provisioning process are defined under each respective Product (AA, AC, LD, MM, SL, BL, MG, MD, LI and PD allowed).
For the Product field in this record, the associated Category code range(s) are only valid for non-AA products such as LD, SL etc. The AA product accepts either the product line (PRODUCT.LINE) or one or more product groups (PRODUCT.GRP).
Classification Rule:
The classification rules must be defined for each product. It can be a link to the Temenos Transact Rules Engine in field Class Rule or by using an API as defined in Class Api field. The value in Class Rule must be a valid Id to the EB.RULE.GATEWAY table.
PV.ASSET.DETAIL
The provision asset detail application (PV.ASSET.DETAIL) holds current and historical details pertaining to the automatic classification and provisioning of an asset.
The user can also manually override the auto classification or a provision amount for that contract.
PV.ASSET.DETAIL is updated during online authorisation of a record and also during COB processing. Initial creation of the PV.ASSET.DETAIL record occurs when the classification details are passed during the execution of the PV.CLASSIFICATION job described in the COB processing section of this document.
The contract Id passed is also the key to the EB.CONTRACT.BALANCES record.
Any PV.ASSET.DETAIL record is updated with the product. For records emanating from an AA contract both PRODUCT.GROUP and PRODUCT.LINE are updated. For other contracts, the CATEGORY is updated instead.
The following screenshot shows the PV.ASSET.DETAIL record for LD product:
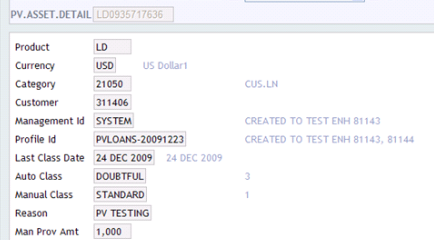
Identifiers for related PV.MANAGEMENT and PV.PROFILE records are also updated here together with classification details.
The Manual Class field must contain the Id of a valid PV.LOAN.CLASSIFICATION record. An example of manual input to PV.ASSET.DETAIL is shown below.
Input to Manual Class, Reason, and the Man Prov Amt fields.
The provisioning details differ slightly based on the method used for calculation:
- IFRS
- The last calculation Date
- The base amount used for calculation
- The calculated provision amount
- Standard Provisioning
- The last calculation date
- the provision Type
- The associated base amount
- The associated collateral amount
- The calculated provision amount
User can manually override the automatic classification or the calculated provision amount for contract by inputting the classification or provision amount.
The PV.ASSET.DETAIL record also holds some static information such as:
- Product, Currency, Customer, Category for non-AA contracts and product. Group or product line for AA contracts.
- Identifiers for related
PV.MANAGEMENTandPV.PROFILErecords are also updated.
Any update to the classification or calculation details cause the existing details to be moved to the previous classification or calculation details.
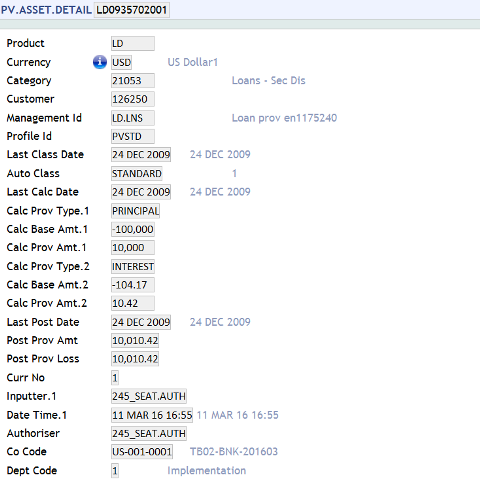
PV.ASSET.DETAIL and the oldest 17 multi-value fields are moved to the PV.ASSET.DETAIL.HIST table.Calculated provision amount and the provision loss amount is displayed in PV.ASSET.DETAIL and PV.ASSET.DETAIL.HIST in order to determine the profit and loss amounts in specific.
The following screenshot shows the calculated provision amount and the provision loss amount updated in the PV.ASSET.DETAIL.
PV.CUSTOMER.DETAIL
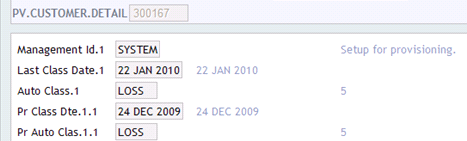
The provision customer detail application (PV.CUSTOMER.DETAIL) holds current and historical details pertaining to the automatic classification for a customer. The classification held will be the worst classification from the selected contracts for the customer. PV.CUSTOMER.DETAIL record may be updated by the classification of multiple selections of records for one Customer.
User can also manually override the automatic classification for a customer by inputting a classification. Manual Class field must be entered with a valid PV.LOAN.CLASSIFICATION record. Updates to this application causes existing classification details to be moved to previous classification fields before the record is written using the customer ID. PV.CUSTOMER.DETAIL contains identifiers for related PV.MANAGEMENT and PV.PROFILE records.
The updates to the PV.CUSTOMER.DETAIL application, which excludes non-manual processing of records, are updated on the same day if the classification passed is worse than the existing one. This record shows the previous, last classification and classification dates.
Illustrating Model Parameters
This section covers the following Model parameters.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
PV.LOAN.CLASSIFICATION
|
This application holds the possible classification to define the level of risk. A unique numeric ranking is given for each classification. For example, Rank 1 is classified as Standard. |
PV.PROFILE
|
|
PV.MANAGEMENT
|
This application allows the user to define the following:
|
PV.ASSET.DETAIL
|
|
PV.CUSTOMER.DETAIL
|
|
Illustrating Model Products
Model Products are not applicable for this module.
In this topic