Introduction to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
The International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) is a common standard issued to make the financial statements understandable and comparable globally.
These standards are issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) with an objective to increase the transparency of published accounts and to assist investors in making economic decisions.
The standards are enforced by countries amending their local Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) to be compliant with the IFRS standards.
The standards issued prior to 2001 are referred to as International Accounting Standard (IAS) and those after 2001 are referred as IFRS. Collectively, these standards are referred to as IFRS and is applicable to all companies including banks.
IFRS implementation impacts the following areas:
- Presentation of accounts
- Accounting policies and procedures
- Legal documentation
- Looking at the value of financial assets and financial liabilities
- The way the entity’s business is conducted
IFRS9
The IFRS9 addresses the accounting for Financial Instruments with revised rules. This standard was issued in July 2014 and is effective since January 1, 2018.
A financial instrument is a contract that gives rise to a financial asset in one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument of another entity. Common financial instruments includes loans, bonds, equity shares, funds and so on.
The IFRS9 intends to make the accounting for financial instruments less complex through a number of significant changes from earlier standard, IAS 39.
The earlier standard relating to Financial Instruments - Recognition and Measurement under IAS 39 was considered complicated and subject to misinterpretations leading to inconsistency.
Financial institutions and companies were facing challenges in the application of these standards and hence were replaced with IFRS9.
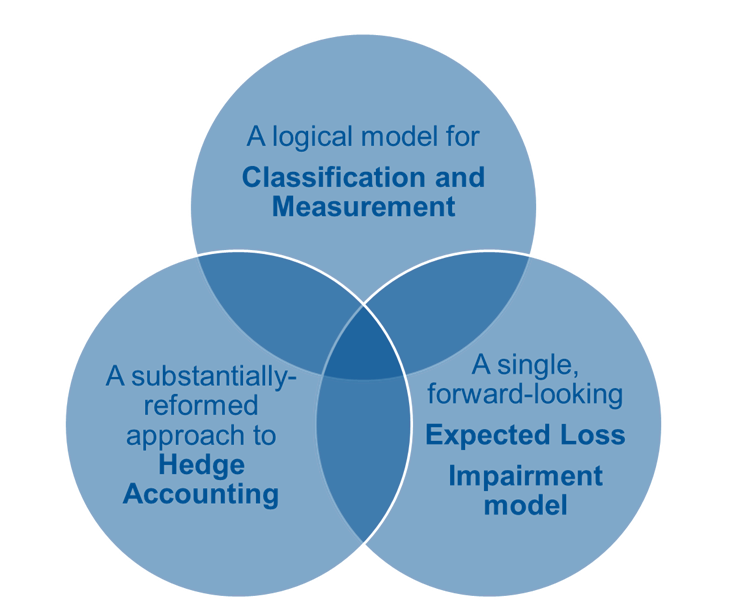
Following are the improvements introduced by IFRS 9:
- A logical model for classification and measurement
- A single, forward looking expected loss impairment model
- A substantially reformed approach to hedge accounting
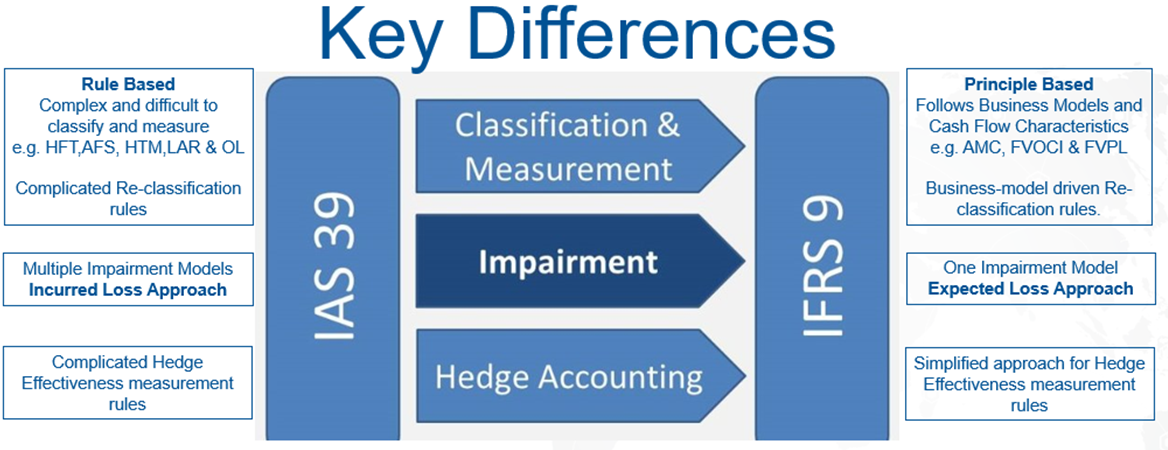
The main differences between the IAS39 and IFRS9 are given below:
The fully integrated architecture of IFRS solution is as below:
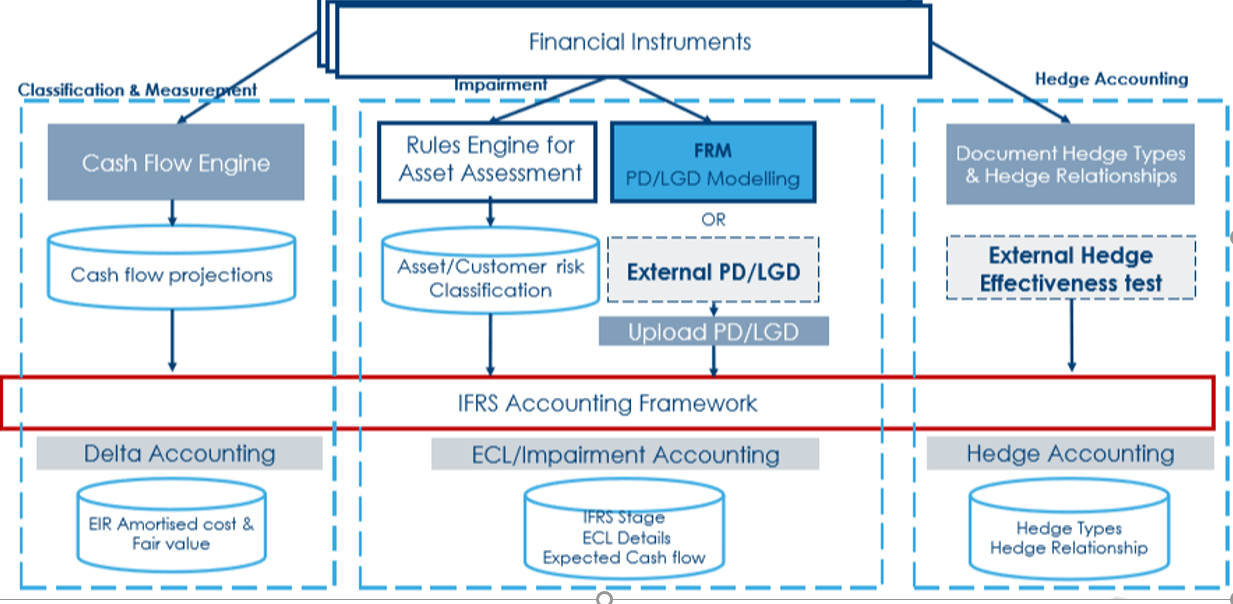
- The lending applications pass cash flows of the Financial Instruments to the cash flow engine to generate and store future cash flows.
- Based on the contractual cash flows of the contract, the system supports the calculation of Effective Interest Rate (EIR), Amortised cost (AMC), fair value of the contract.
- The future cashflows are discounted using the EIR to calculate the Net Present Value (NPV) of the contractual cashflows in the contract.
- The accounting framework allows to raise the accounting movements for the delta between the contract balances and the calculated value using the NPV method and is termed as Delta Accounting.
- The Provisioning (PV) module provides provisioning methodology and the classification is obtained based on the risk involved for the contract.
- The Rules Engine facilitates the overall functionality in assessing the risk and classifying the contracts.
- The impairment accounting is supported by IFRS9 (I9) module with the accounting rules based on the Expected Loss approach.
- The Expected Credit Loss Model (ECL) Model includes the Probability of Default (PD) and Loss given Default (LGD) values for calculating the expected cash flows from the contractual cash flows to arrive at the ECL.
- The system does not calculate the PD and LGD values but provides only the framework for uploading these values, either from the PD and LGD modelling within Temenos Financial Risk Management or banks themselves can provide these values for ECL calculations.
- Hedge Accounting is optional under IFRS 9 and is supported by IH module.
- States the Hedge Types (Fair value/Cash flow/Investments).
- Documents the hedge relationship.
- Define Accounting rules based on types of Hedge.
- Framework for generating hedge accounting entries.
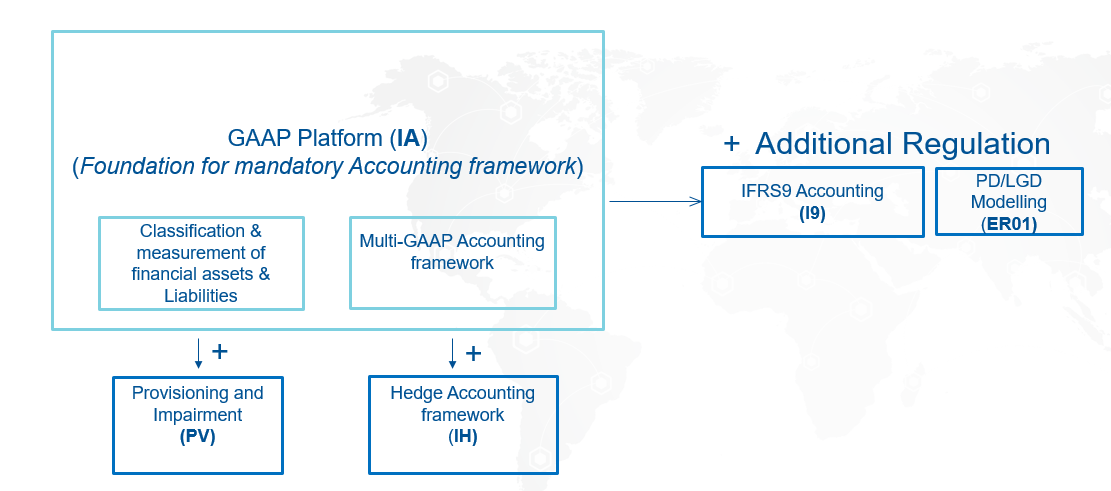
The IFRS9 solution is a combination of IA, PV and I9 modules as displayed below :
Product Configuration
The IFRS9 compliance on financial instruments is achieved by configuring the following parameter tables.
- PV configuration
- IFRS9 configuration and
- PD/LGD parameters
The following tables are configured in the PV module for classifying the contracts in the following order.
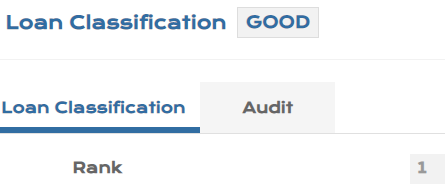
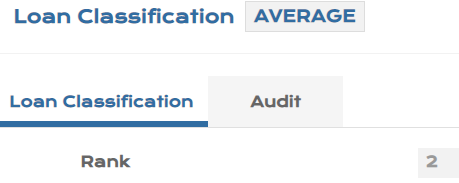
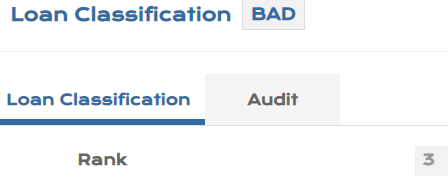
This application defines possible Classification indicating the level of risk.
- Record Id is any Alphanumeric Id.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Rank | A unique ranking is maintained for the classification defined (contract level). |
| Stage | PV.LOAN.CLASSIFICATION can be linked to the stages under IFRS 9 configuration. |
The screenshots of PV.LOAN.CLASSIFICATION that can be defined for classification are shown below
This application defines the parameters and method for the appropriate provision calculation for each loan based upon the classification applicable for a contract.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Prov Calc | Indicates the provision amount calculation method. Should be set as IFRS for impairment calculation using IFRS cashflows. |
| Source Balance | Holds the balance used to calculate the provision amount
which can be an individual balance or a virtual balance (AC.BALANCE.TYPE)
record. This field is used to calculate provisions in case of collective impairments or undrawn commitments. |
| Class | A multi-value set of fields that specify the provisioning percentage to be applied to a contract, based on its classification in PV.LOAN.CLASSIFICATION. |
| Accounting | Indicates whether the calculated provision amount is to be accounted for.
|
| Ccf Cut Off | Specifies the percentage to be excluded to derive the Exposure Amount. |
| Prob of Deft | A multi-value field that holds the Probability of Default value. |
| Loss Given Deft | Allows the Loss Given Default at the individual product or range of product level. |
| Posting Details | A mandatory field that holds a valid IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS record for raising accounting entries. The position type should be IF for IFRS. |
| Segment | Holds a valid record of PV.RISK.SEGMENT. If the risk segment of the contract matches this field, then the segment and classification details are considered for the contract |
| Seg Prov Calc | Specifies the type of calculation to be followed for the segment to derive the provision amount. |
| Seg Ccf Cut Off | Specifies the percentage to be excluded in order to derive the Exposure Amount at the segment level. |
The screenshot of PV.PROFILE is displayed below:
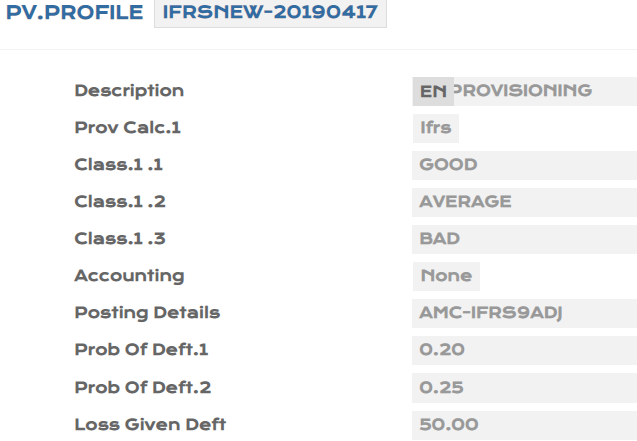
This application defines the frequency for Classification, Provision Calculation process, and selection of records to be processed.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Job Frequency | Defines the frequency to run the Provisioning Process for calculation and posting. |
| Posting Timing | Indicates when posting is to be done. |
| Posting Delay | Defines the number of days to delay posting after the classification process. |
| Profile ID | The mapped PV.PROFILE ID that indicates the classification and provisioning calculations. |
| Class Level |
Defines the classification that is used for provisioning
|
| Product | Defines the selection criteria of contracts for each Product giving the starting and ending category. |
| Class Rule | Determines the classification to assign to contract through the Rules Engine is to be defined. Using this field, banks can define their own rules for classification of contracts. |
| Class API | Calculates the classification of the loan through an API and is mutually exclusive with Class Rule. Banks can have their own APIs and define different rules for different products. |
| Class Frequency | Defines the frequency upon which contracts are classified. This frequency takes precedence if defined to perform classification job. |
| Calc Post Freq | Specifies the recurrence pattern for calculating and posting the provision. |
A sample record of PV.MANAGEMENT for Arrangement Architecture (AA) loans is shown below
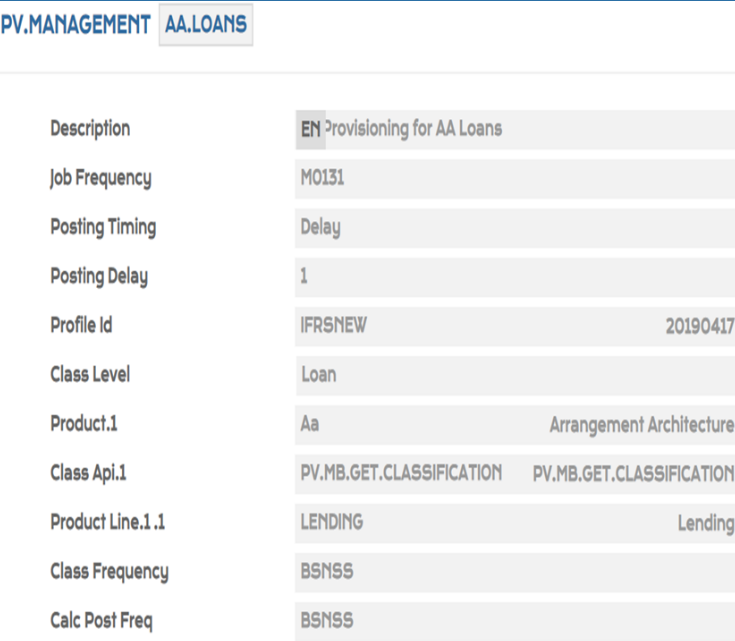
Read the documentation on PV module for more information.
Once the PV configuration is complete, the following parameter tables need to be configured for IFRS9 compliance in the following order:
This parameter table defines the rules for the regulation. The record ID must be the name of the regulation, that is, IFRS. The screenshot below displays the parameter.
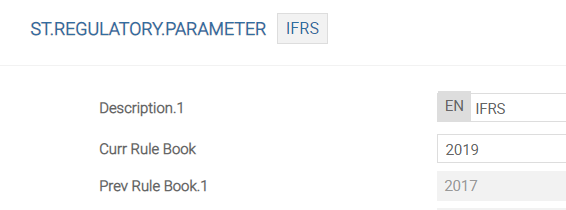
The following table explains the fields in the above screenshot.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Description | Indicates the name assigned for the regulation. |
| Curr Rule Book | Holds the year of release of the regulation. |
| Prev Rule Book | Displays the previous releases of the regulation. When the Curr Rule Book field is changed, the system automatically updates this field with its previous values. |
This table refers to the business models or classification of financial assets and liability according to the IFRS regulation.
IFRS9 requires a strict classification of financial assets and liabilities according to their purpose.
The IAS.CLASSIFICATION table is used to describe the business model. The business model classification is extremely important as it defines various accounting and measurement rules to be applied.
The following records are released in Temenos Transactbased on the Business Models under IFRS9, such as AMC, FVOCI and FVPL, where the users are allowed to view these records and are not allowed to input or amend them.
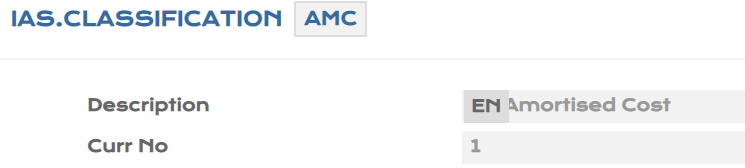
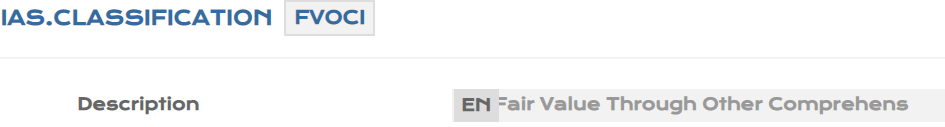
This is a COMPANY LEVEL table, which governs the rules for IFRS 9 regulation.
The PARAMETER table with the Stages and their corresponding loan classifications are shown below:

This table stores the accounting methods to be applied for different kinds of contracts based on the classification of assets and liabilities. Users can configure this table based on their requirements.
The Id for this record can be any alpha-numeric free text.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Acct Head Type | Forms part of a multi-value set to specify the asset types. By multi-valuing the Acct Head Type field, different values can be defined for each accounting head–AMORTISED, AMORTISED STAGE 1, AMORTISED STAGE 2, DISCLOSURE, IMPAIR AMORTISED and so on. |
| NPV Method | Forms part of a multi-value set to specify if the Net Present Value (NPV) calculation is required based on the IAS.CLASSIFICATION and the accounting method specified. If NPV calculation is not required, an option to include an external routine to calculate the amount is given through the Calc Rtn field. Input of either of these two fields is mandatory. |
| NPV Rate | Specifies the rate type applicable to the calculation, which can be either an EIR rate or a MARKET rate. The value in this field can be entered only if the specified NPV Method is set to Yes. |
| Posting Reqd | Provides an option to the bank to decide whether the values need to be only calculated or posted as well. This is applicable to methods like DISCLOSURE.
All the contracts stated at AMC are valued at a market rate on the reporting date for the purpose of disclosure in order to state them at fair value. The fair value amount so calculated is not required to be posted but is only supposed to be disclosed. |
| Adjust Entry | Indicates whether the entry to be posted is an adjustment to what has already been posted on the contract. This is allowed only for contracts classified under fairvalue through equity |
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Bal to Exld | Defines the balance or asset types to be excluded from Temenos Transact balances. This functionality is available only for AC.BALANCE.TYPE records with Reporting Type set to VIRTUAL. |
| Hybrid Acct Type | Indicates the hybrid method of IFRS accounting, where the contract is measured based on fairvalue, using the Market Key on the first day of a loan disbursement. On subsequent days, the loan is measured using the amortised cost method. |
| Impair Int Bal Type | Defines the asset types under which accrual entries are raised for different applications. Allows a valid record from AC.BALANCE.TYPE with Reporting Type set to VIRTUAL. |
The following screenshot displays the AC.BALANCE.TYPE.
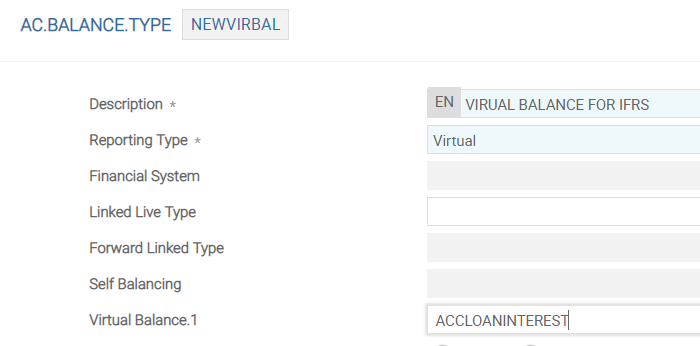
In the following example, the accounting heads AMORTISED has the AC.BALANCE.TYPE record NEWVIRBAL entered into the Bal To Exld field . All normal accounting heads uniformly follow a single Temenos Transact balance.
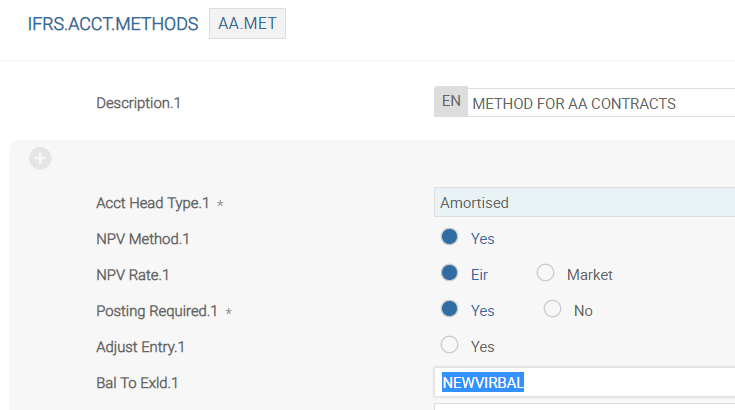
The above screenshot shows the Bal To Exld field in the IFRS.ACCT.METHODS table.
- When the Bal To Exld field is populated for the AMORTISED accounting head and left blank for other Acct Head Types, the system defaults the Bal To Exld field from AMORTISED to the other normal accounting heads.
- An error is displayed if the user enters a different AC.BALANCE.TYPE record.
The Acct Head Types under AMC is shown in the table below.
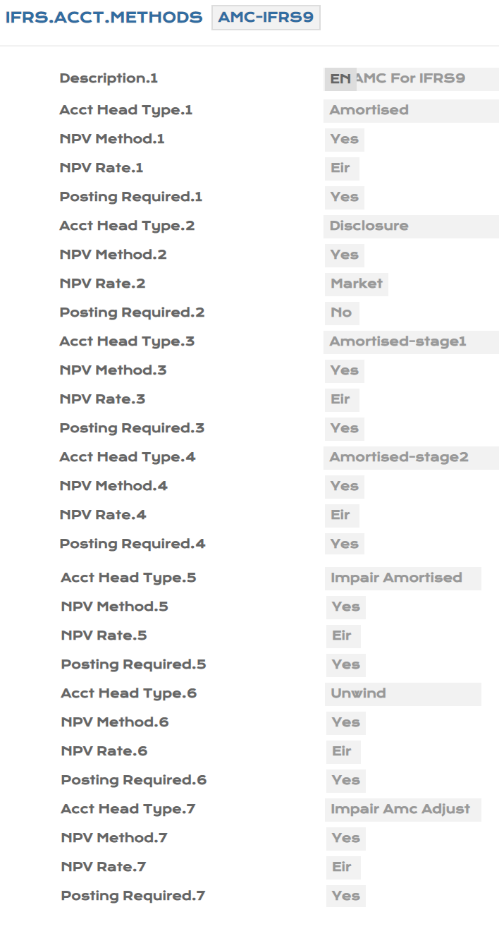
This table stores the details relating to the way the accounting entries are generated in order to make the contracts compatible with IFRS9 requirements. This displays as a separate table so that the user can configure based on their requirements.
ID of the records is free text to link to the contracts at IAS.CLASSIFICATION or IFRS.SUBTYPE level.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Position Type | Updates with value IF on validation of a record. User input is not allowed. |
| Posting Style | Specifies the posting style to be adopted. Accepted values are IO or ADJUST. |
| Acct Head Type | This field is part of a multi-value set of fields to specify the asset types. As a multi-value field, different values can be defined for each accounting head–AMORTISED, AMORTISED STAGE 1, AMORTISED STAGE 2, DISCLOSURE, IMPAIR AMORTISED and so on. |
| Acct Type | Specifies whether the posting is to happen to the CONTINGENT or NONCONTINGENT base. |
| Sub Acct Head Type | This field is part of the associated multi-value set of fields for Acct Head Type – Amortised. It can accept the AA properties for CHARGE. |
| Entry Type | Specifies the type of the entry. This can have different categories to post the Profit and Loss amounts. Has options Profit, Loss and Both. |
| Entry Target | Specifies whether the entry needs to be raised to Internal Accounts, PL categories or the CRF base. The allowed options are:
|
Users can define the category used for posting along with the transaction codes and reversal transaction codes used for generation of entries.
A sample record for the Category and transaction codes to be defined for every Acct Head Type field is displayed below:
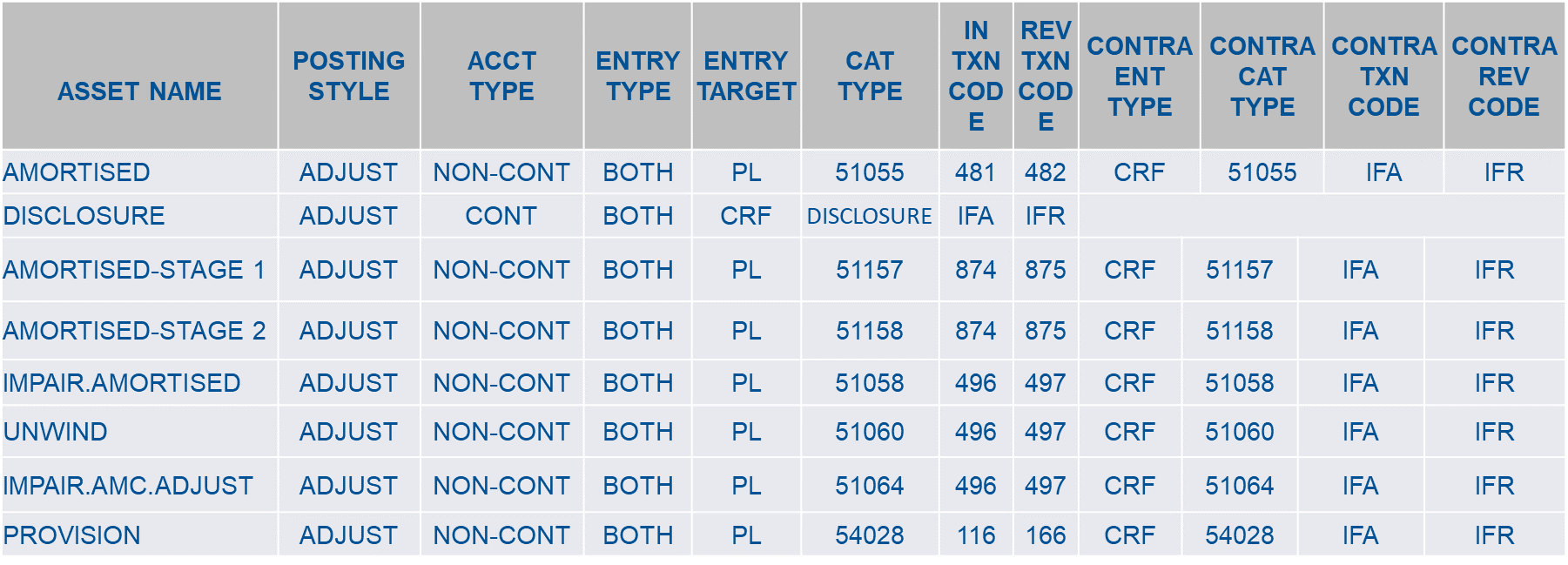
A sample record of IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS for an AMC business model is displayed below:

This table contains the details relating to IFRS.ACCT.METHODS and IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS along with details relating to the amendments to the cash flows and EIR, if any. Record ID is free text.
The following table details the fields and description.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Descrit | Defines the sub-type. |
| Accounting Method | Displays the ID of IFRS.ACCT.METHODS that stores the accounting methods to be applied on contracts based on the classification. |
| Posting Details | Displays the ID of IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS that stores the details relating to the generation of accounting entries. |
| Def Recalc Method | Defaults the recalculation method during cash flow changes for the contracts. Options allowed are either CARRY.COST, EIR or QUANTITATIVE TEST. |
| Event Type | Defines the IFRS.EVENT.TYPE. |
| Recalc Method | Defines the recalculation method opted for event wise. The options are CARRY.COST, EIR or QUANTITATIVE TEST. |
| Term | Indicates the option to determine EIR and AMC. The options are
The difference between the SHORT and EXPECTED is that with Short, after the end of the period, the interest rate fixing generates another cashflow for the next rate fixing period and recalculate the EIR whereas with the option of ‘Expected’ life of the contract, after the end of the period the system stops IFRS9 processing. |
An example IFRS.SUB.TYPE for AMC is shown below:
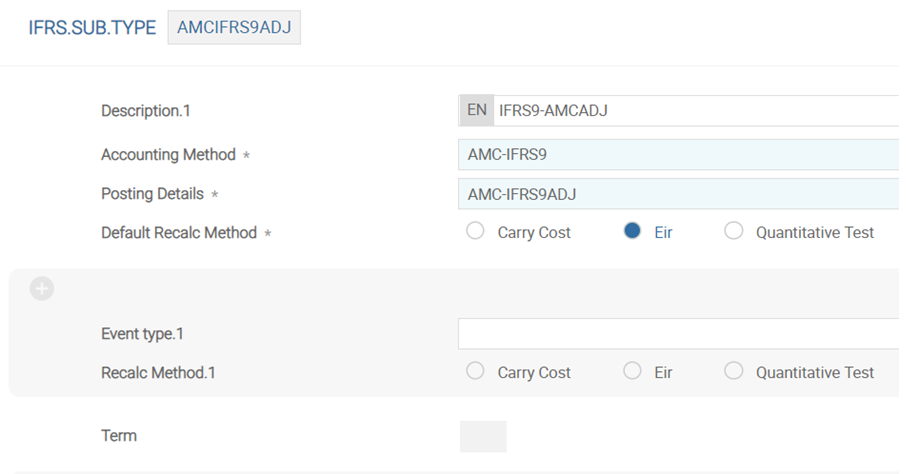
This application defines accounting frequency for subtypes of different companies. ID is the Company name and under each company, for each IFRS Subtype, the accounting frequency can be defined.
The following table defines each field available in this application.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Ifrs Sub Type | Displays set of subtypes. |
| Acct Freq | Denotes the frequency at which the specified subtype is processed. Each subtype must have its own frequency setting. However, it can be different for different subtypes. |
| Upd Acct Dtls | Provides the option to update the system maintained table IFRS.ACCOUNTING.DETAILS. Options are Yes or No. |
| Split Delta | Provides the option to split the amortised amount with the respective fees and cost. |
The below screenshot displays the IFRS.SUB.TYPE with its corresponding frequency set.

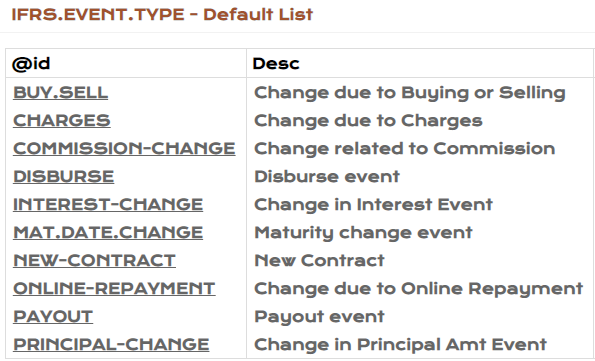
This application stores various events that can occur over the life of a contract, which can amend the cash flows pertaining to it. The default list is as below:
Once the PV configuration and the IFRS parameter tables are configured, other tables relating to PD and LGD parameters are entered since their values are included in the ECL calculations.
Temenos Transact does not do any calculation of the PD/LGD values but provides the framework for uploading them. These PD/LGD values can be uploaded either from the PD/LGD modelling within the Temenos Financial Risk Management or their local tables.
The Probability of Default (PD) is defined as the Probability that the obligor will default within a given time horizon. There can be a minimum of two PD values or Point-in-Time (PIT) PD values.
The multivalued field Prob of Deft is used to store the Probability of Default with minimum two PDs. The system uses the first PD as 12M PD for stage 1 contracts and the second PD as Lifetime PD for stage 2 or 3 contracts.
A multivalued field Prob of Deft is made available wherein yearly PDs are allowed to be input for a contract year wise till its maturity period. The system uses the PD defined for the corresponding periods and arrive at the ECL provisioning during IFRS processing.
LGD is defined as the percentage loss incurred relative to the Exposure at Default.
It provides the loss that a bank is bound to incur when a default occurs. This normally is based on the type of Loan or Collateral and is worked out by the Credit Risk Department of a Financial Institution.
Read the Reporting property class for more information.
Customers have the flexibility to define the PD or LGD values at various levels according to their requirement. The uploading of PD and LGD values are available at four levels. They are:
- Through an Application Program Interface (API) in IFRS.PARAMETER
- At Contract level
- At Customer level
- At Product level
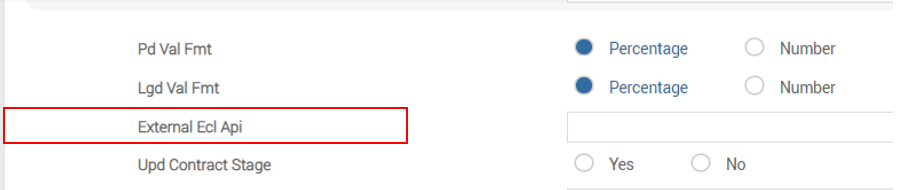
The screenshot below displays the External Ecl Api field in IFRS.PARAMETER.
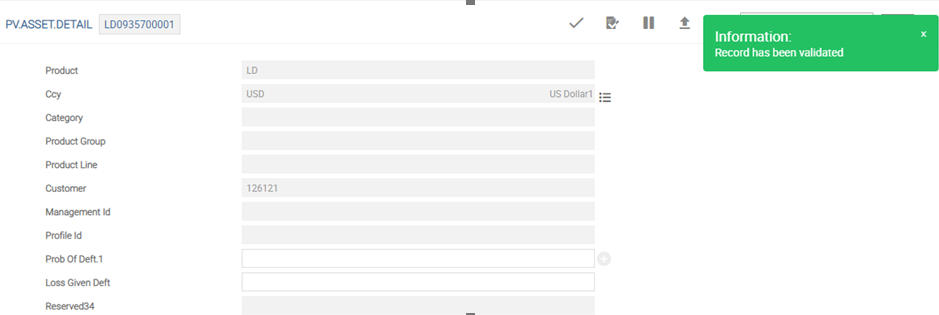
The following screenshot displays the multivalued fields Prob of Deft and Loss Given Deft – optional at contract level in PV.ASSET.DETAIL.
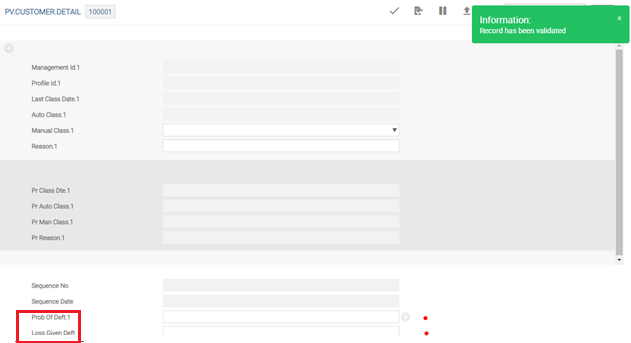
The following screenshot displays the multi-valued fields Prob of Deft and Loss Given Deft - optional - at customer level in PV.CUSTOMER.DETAIL.
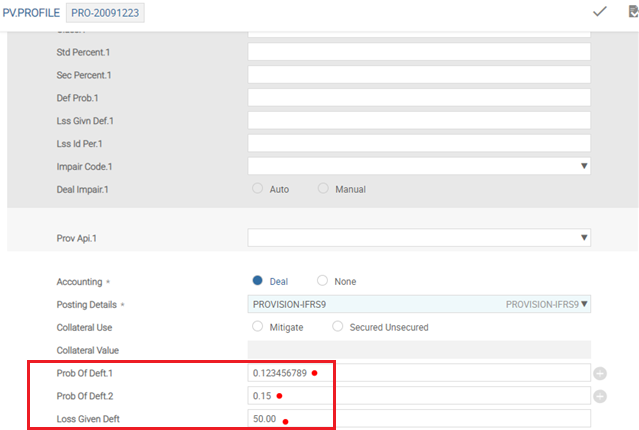
The below screenshot displays the multi-valued fields Prob of Deft and Loss Given Deft - Default - at product level in PV.PROFILE.
To accommodate Probability of Default (PD) or Loss Given Default (LGD) at various levels, the system allows manual inputs in the following tables.
- PV.ASSET.DETAIL
- PV.CUSTOMER.DETAIL
- PV.PROFILE
The system performs Expected Credit Loss (ECL) calculations using the appropriate PD and LGD values recorded at different levels depending on the stages.
For Stage 1 contracts, 12M ECL is calculated using the first PD and LGD, and for Stage 2 and 3 contracts, lifetime ECL is calculated.
Order of Priority
The ECL calculator selects the PD/LGD values in the following order:
- If an API is defined in the IFRS.PARAMETER
- If PD/LGD is defined in PV.ASSET.DETAIL
- If PD/LGD is defined in PV.CUSTOMER.DETAIL
- If PD/LGD is defined at the product Level, the ECL calculator,
- Picks the risk level to be applied for contract - if the classification is at the LOAN level, get the risk level from PV.ASSET.DETAIL, and if the classification is CUSTOMER, get the worst risk level for customer from PV.CUSTOMER.DETAIL.
- Picks the corresponding PD/LGD defined for the risk level from PV.PROFILE for defined group of products.
The PV.PROFILE link is assigned to the PV.MANAGEMENT where the group of product is defined for collective impairments.
- List of Product Category
- List of Product.Group/Product.Line
PV.PROFILE allows one PD and LGD by Product, Segment and Risk classification for IFRS provisioning.
An option with IFRS in the Seg Prov Calc allows IFRS provisioning at the segment level similar to that of standard provisioning.
The provision process is as follows:
- The list of risk segments is defined in the PV.RISK.SEGMENT table.
- The borrowers are assigned a risk segment based on the criteria specified through the Rules Engine or local API in PV.MANAGEMENT.
- The risk segment is recorded under the Auto Risk Segment field in PV.ASSET.DETAIL.
- One PD and LGD can be specified by Product, Segment and Risk classification.
Order of Priority
If one PD and LGD by Product, Segment and Risk classification is available in PV.PROFILE, then the order of priority in retrieving the PD and LGD for the ECL calculation is as follows:
- By Product, Segment and Risk Classification.
- If not specified at that level, then the default level is by Product and Risk classification.
Read the Standard Provisioning section for more information.
An example of ECL calculations at various levels is shown below:
- Input a customer and create an account for the customer.
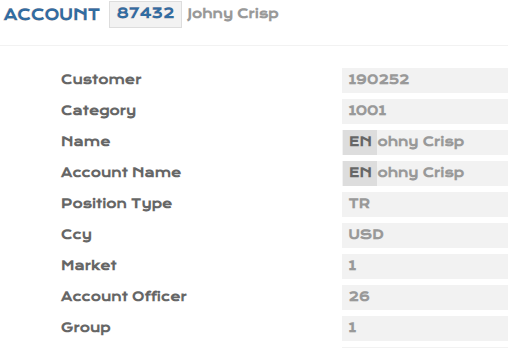
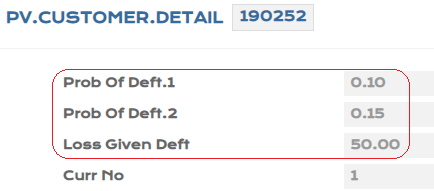
- For the customer created, update the PV.CUSTOMER.DETAIL with PD1 - 0.10% ,PD2 -0.15%, LGD - 50% manually.
- Create a facility for USD 500,000 with participant bank being 999999 (own bank) for full value.
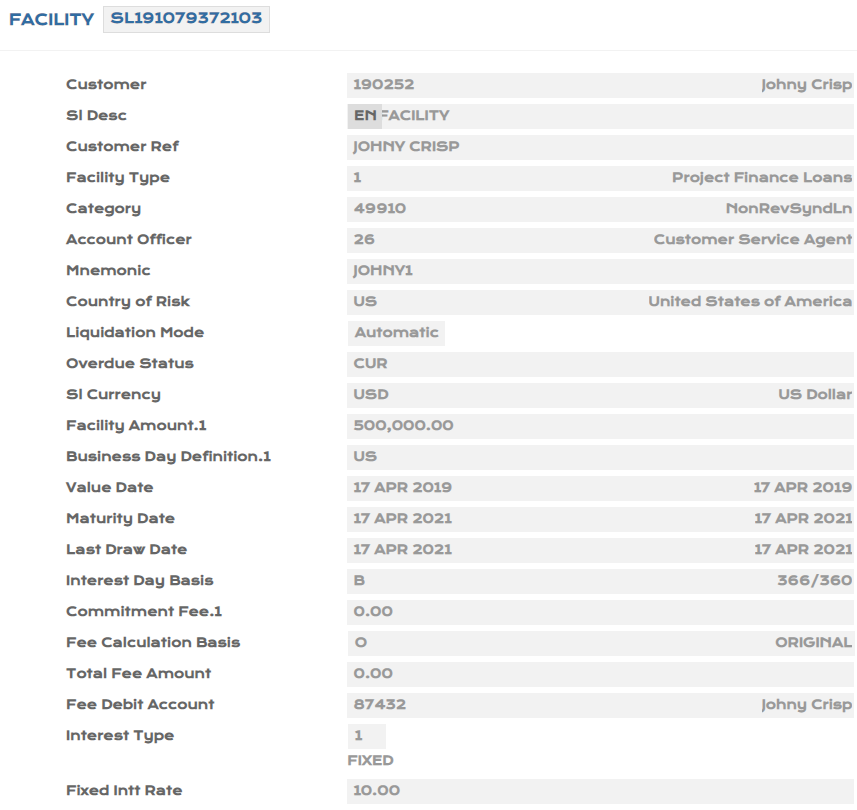
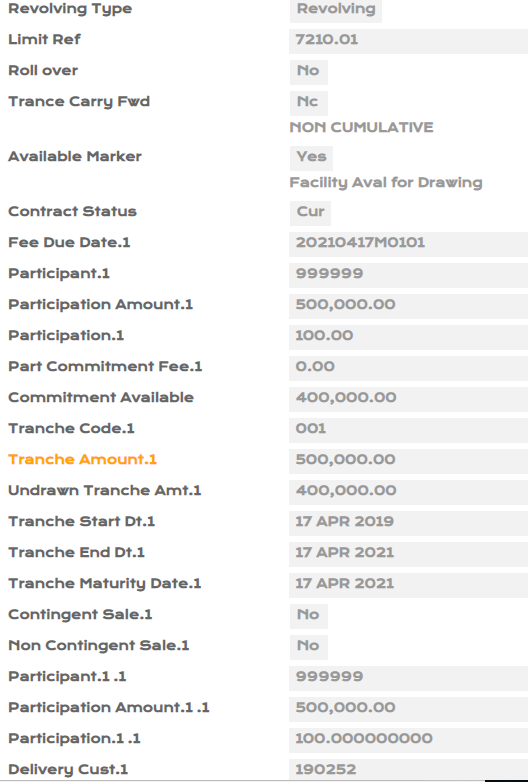
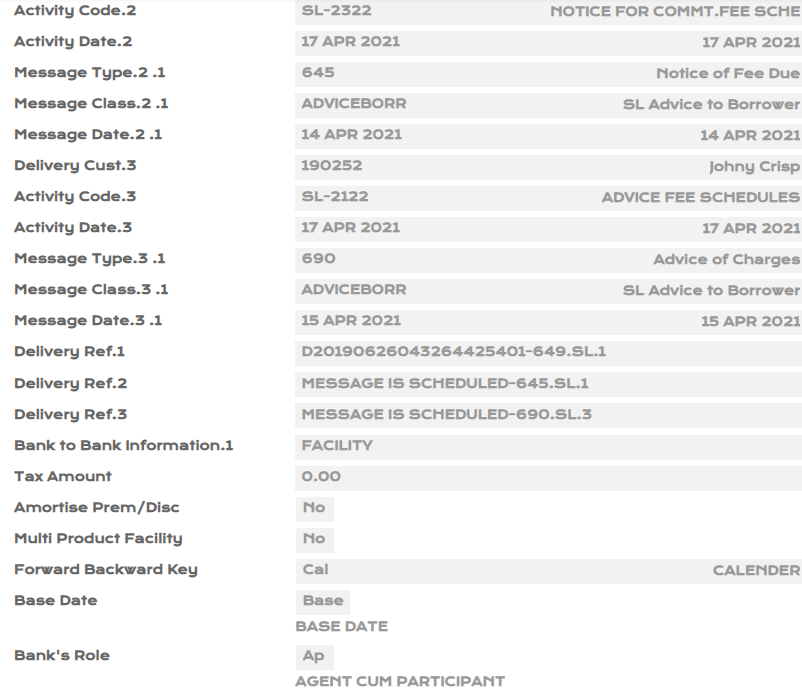
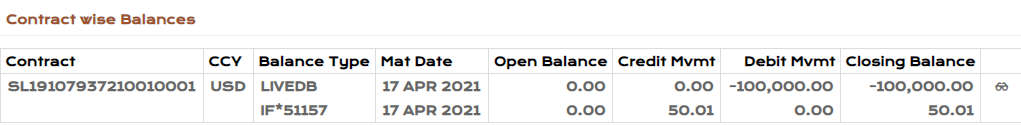
- Create an Syndicated Lending (SL) loan contract for two years using category as 49910 with the following details :
- Loan Amount: USD 100,000 and Interest Rate - 10% , Interest payable on the last day of every month.
- Use Amortised Cost business model (Adjustment type) for the loan under International Accounting Standard Classification
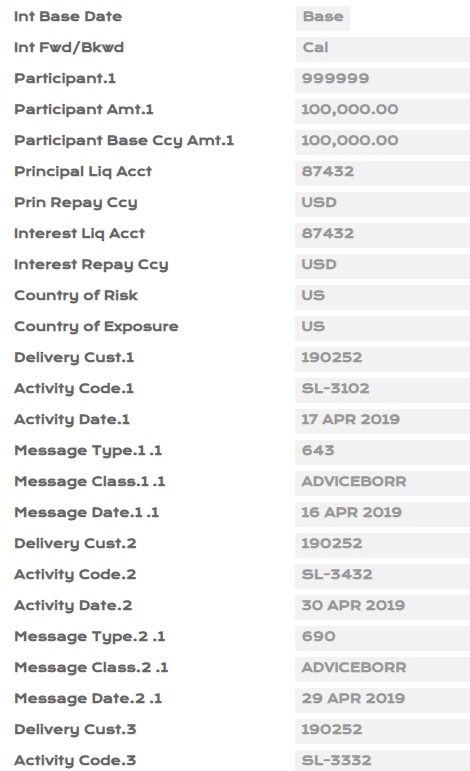
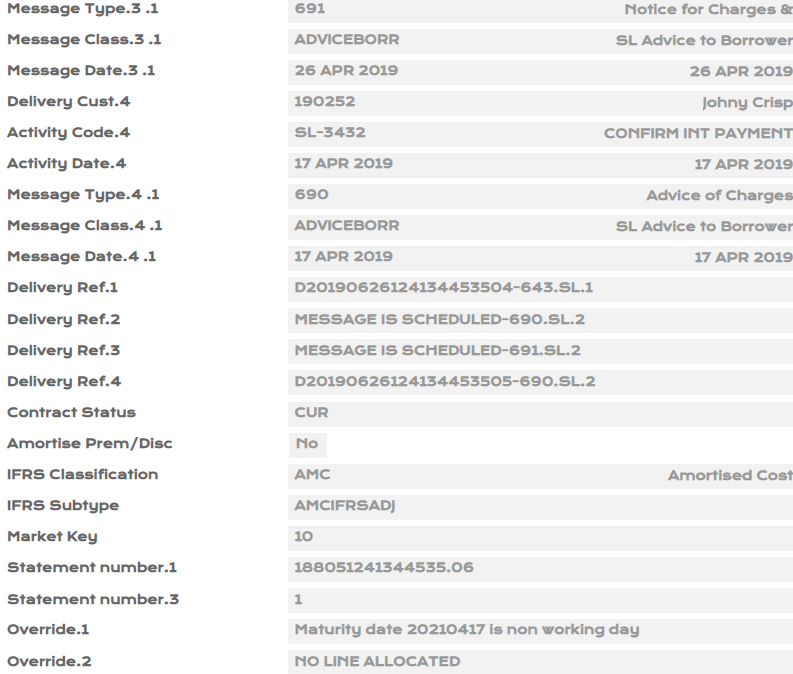
- Upon authorisation of SL loan, view EB.CASHFLOW, IFRS.ACCT.BALANCES and IFRS.ACCOUNTING.DETAILS.
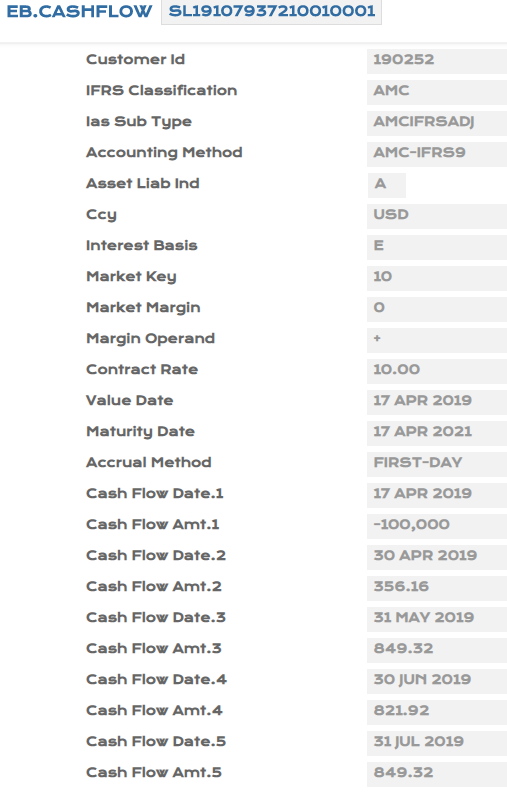
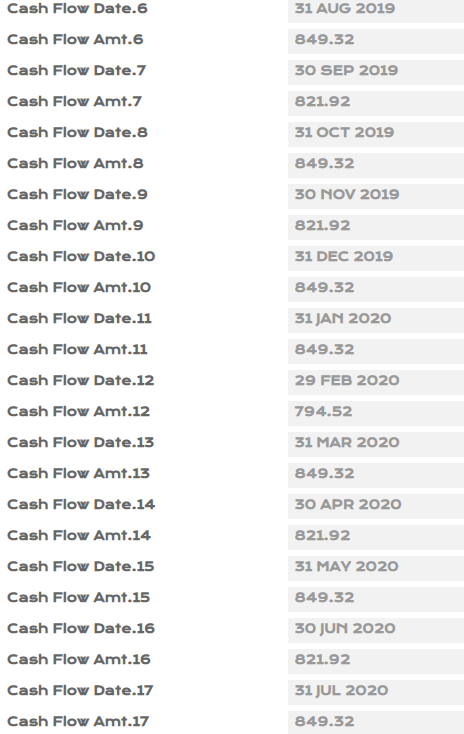
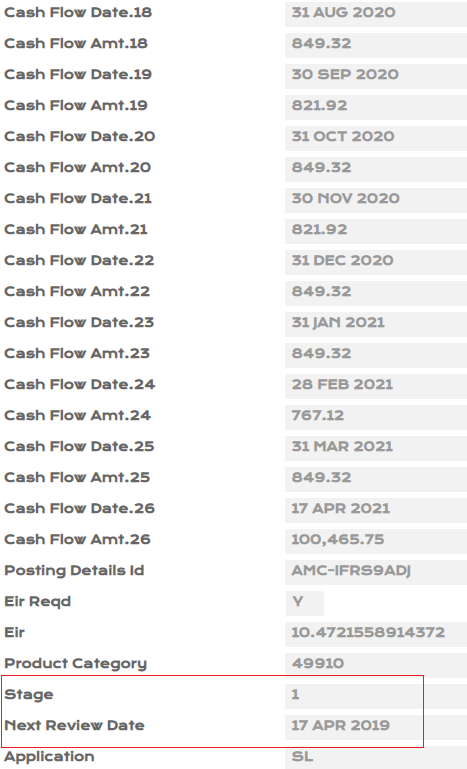
- Input PD1 - 0.15%, PD2 - 0.20%, LGD - 50% manually for the loan created in PV.ASSET.DETAIL.
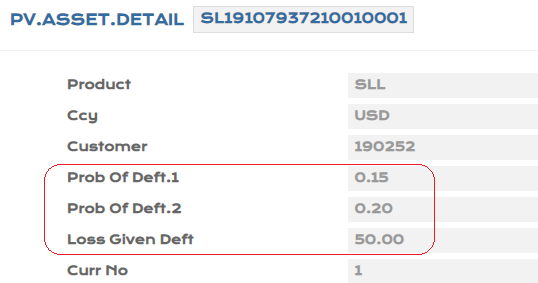
- For online ECL calculation, the system picks up the PD/LGD values from PV.CUSTOMER.DETAIL.
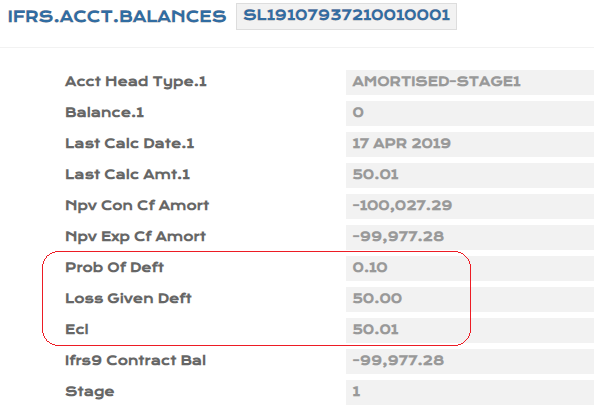
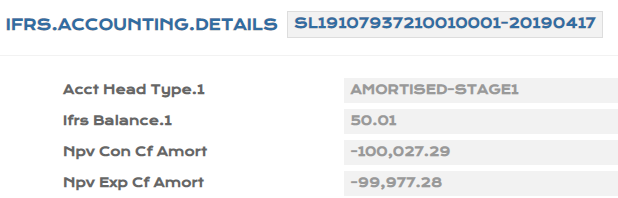
- After Close of Business, the ECL calculation is based on PD,LGD from PV.ASSET.DETAIL being the higher order of priority.
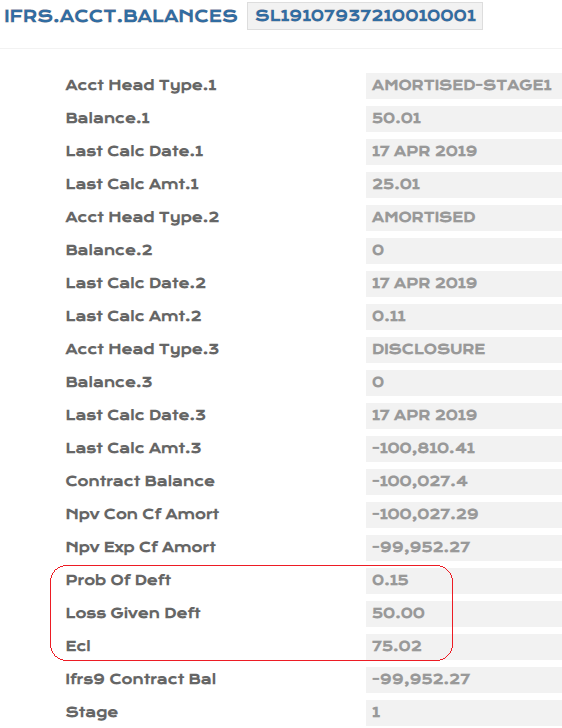
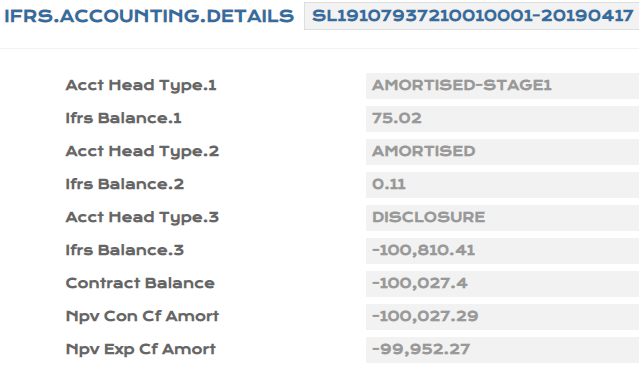
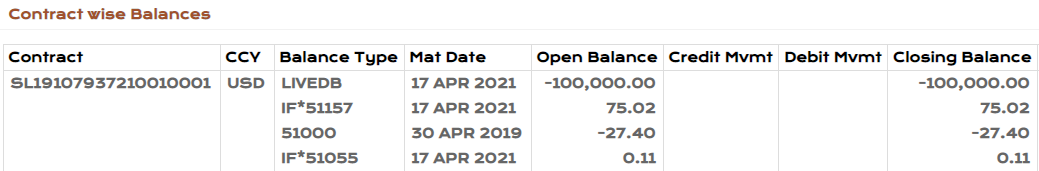
The Probability of Default (PD) and Loss Given Default (LGD) values that are applied in the Expected Credit Loss (ECL) calculations can be uploaded at every individual record level or for group of records.
To consume the PD and LGD values in bulk, the system initiates an EB.FILE.UPLOAD process. In the example below, the EB.FILE.UPLOAD process is for two existing customer records, 100100 and 12345.
Perform the following to steps to bulk upload:
- Create an excel file with customer record id’s and respective PD values for upload and save the excel file in .csv format.
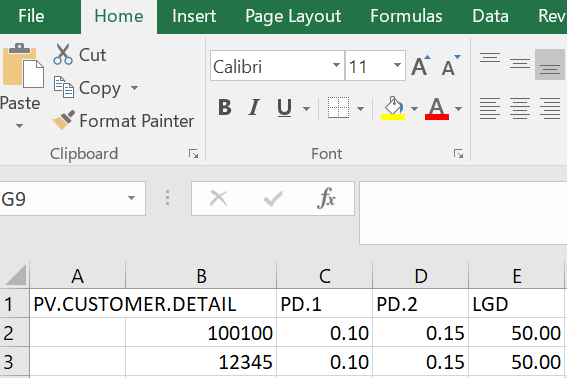
- Upload this file path in TC Upload Path field in EB.FILE.UPLOAD.PARAM table.
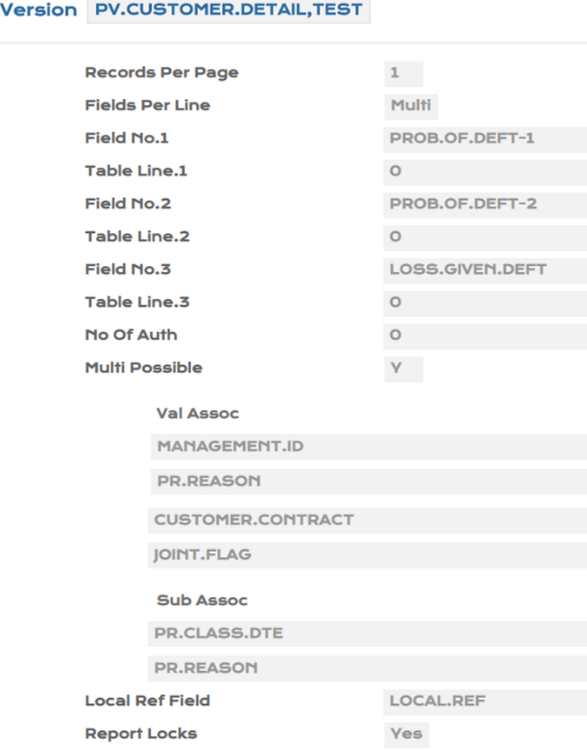
- Create a version for zero authorisation.
- Create an EB.FILE.UPLOAD.TYPE record, to include the versions created.
- Define the Upload DIR field where system updates the files uploaded. Extension of file upload to be mentioned as csv
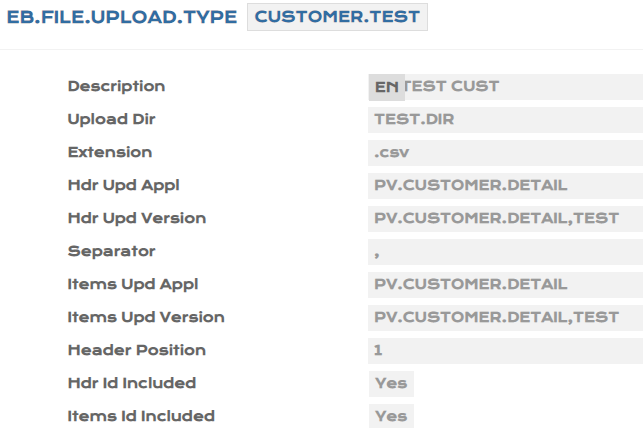
- Create an EB.FILE.UPLOAD record to upload the .csv file created, which holds the customer record id’s with the respective PD values.
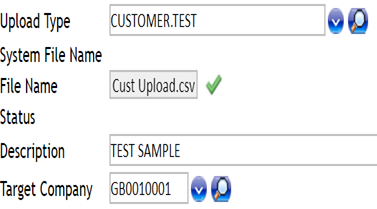
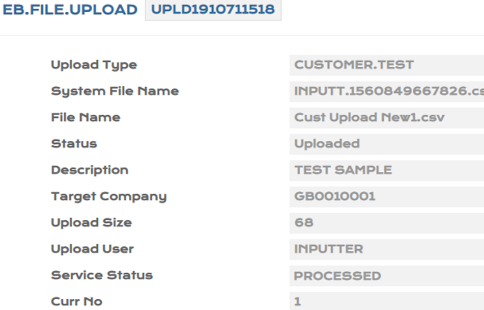
- Run the BNK/T24.UPLOAD.PROCESS service.
- Before upload
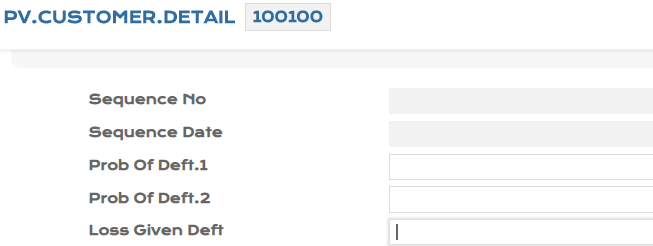
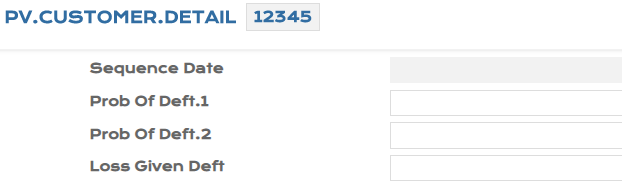
- After upload
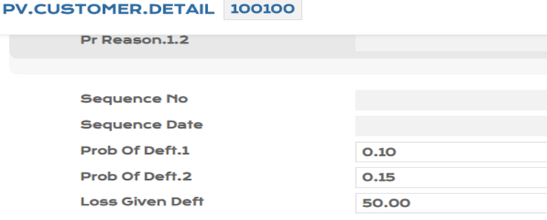
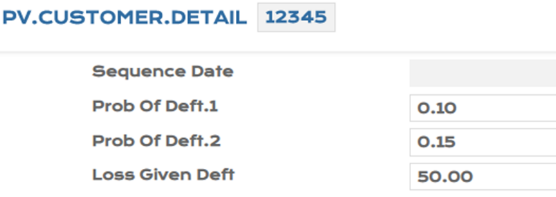
Illustrating Model Parameters
Parameters configured in Model Bank are detailed below:
Illustrating Model Products
Model Products are not applicable for this module.
In this topic