Introduction to IAS 39
International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) issued standards to address the Accounting of Financial Instruments in IAS 39 to address the needs arising out of globalisation of financial markets and its associated complexities. This aims to recognise all the financial assets and liabilities on the balance sheet (including derivatives that was previously held as off balance sheet) and move closer to full fair value accounting for these assets and liabilities.
IAS39 is a standardised set of rules for the accounting and reporting of financial assets and liabilities.
IAS 39 is introduced as a global standard and aims to:
- Replace the various local GAAP regulations
- Provide clarity and confidence for investors
- Evaluate the true financial risk of a company
IAS39 can be broken down into the following elements:
- Recognition and classification of assets and liabilities
- Measurement
- Impairment
- Hedge Accounting
IAS 39 – Accounting Framework Solution
This framework provides IAS 39 as a standard in Temenos Transact products. IAS39 provides the following main functionalities by using Temenos Transact applications:
- Classify assets and liabilities
- Recognise profit and loss through Amortised Cost (AMC)
- Recognise profit and loss using Fair Value (FV)
- Produce Disclosure values of the contracts
- Run multiple accounting GAAPs
The IA module used for the IAS 39 compliance has a flexible accounting framework, which allows the users to generate the accounting entries according to their specific requirements. Additionally, it allows accounting entries to be raised with different GAAP types, which are identified by the position type in the entry, so that entries can be excluded for the same line definitions but can be classified based on GAAP types.
The design of IAS39 allows for the capture of all the cashflows into the EB.CASHFLOW file. Using this data, the Effective Interest Rate (EIR) is calculated. Amortised Cost (AMC) and/or the Fair Value (FV) are calculated using the cashflow data and the EIR and/or market rates.
These calculated amounts are adjusted by actual cost balances (LIVEDB and accrued interest) already stored to give amounts to be posted. The amounts can be posted to Profit or Loss (P/L), Internal Accounts or Central Reporting File (CRF) as specified by the bank.
Multi-GAAP reporting is obtained through the usage of the POSITION.TYPE. Temenos Transact can report financial accounting based on these position types.
The ability to exclude zero lines from the general ledger is taken to the level where the option to include or exclude line details can be based on high-level settings such as POSITION.TYPE.
The accounting core can create and maintain entries based on the position of a set of accounts, p/l codes and reports setup for the reporting system(s).
Existing key financial files such as EB.CONTRACT.BALANCES and EB.CASHFLOW enable the system to record details of the underlying system to the level of the position types allowing an audit trail for the entries raised.
The interaction with IFRS of the Temenos Transact modules is closely integrated for some, whilst for other modules there is an element of accounting suitable for IFRS reporting as a subset of the standard reporting mechanism of Temenos Transact.
Standard Reporting modules
Modules that have in-built accounting for handling specialised reporting features, such as IFRS are:
In case of a Forex trade, both sides of the deal are revalued against local currency using the forward exchange rates with two sets of revaluation postings being made for a cross currency deal.
To comply with IFRS requirements, a set of net revaluation entries are required for each deal.
- For forward deal types, an NPV calculation is applied to this net revalued amount.
- For spot deal types, no NPV calculation is required.
The NPV calculation is performed on the net local amount obtained from revaluation of both sides using a specified yield curve.
There are four possible situations:
- A single-currency Spot contract
- Book the one spot revaluation (no NPV is needed for spot)
- A cross-currency Spot contract
- Calculate the NET Spot revaluation and book this net Spot revaluation (no NPV is needed for spot).
- A single-currency Forward contract
- Calculate the NPV on the one forward revaluation amount and then book this NPV.
- A cross-currency Forward contract
- Calculate the NET for forward revaluation amount and then calculate the NPV on the amount.
The securities revaluation processing allows use of different asset types to separately recognise profit and loss generated based on the following:
- Change in market price
- Foreign exchange rate movement
These options are defined in the own-book portfolio record.
IFRS-linked modules
Modules that are directly linked with the IFRS reporting system are:
- Arrangements (AA)
- All in one Accounts (AZ)
- Loans and Deposits
- Money Market
- Syndicated Loans
To update EB.CASHFLOW for IFRS, two fields in AZ.PRODUCT.PARAMETER and four fields in AZ.ACCOUNT are set.
The values entered in the Ias Classification and Ias Subtype fields of AZ.PRODUCT.PARAMETER defaults in AZ.ACCOUNT. However, the user can overwrite the defaulted values with user defined values. These fields are optional fields.
When an AZ.ACCOUNT record is authorised, an EB.CASHFLOW record with same ID as that of AZ.ACCOUNT is updated with all the present and future cash flows including principal component, interest, tax, charges and so on.
The cash flows of principal and interest for the same date are updated as a consolidated amount, whereas charges and taxes are updated as an independent component.
Credit card is exempted as cash flows cannot be predicted.
Contracts entered in the LD module have a few pivotal fields to link them into creating IFRS accounting adjustments. When the deals are authorised, the requisite information (present and future cashflows including principal component, interest, tax charges and so on) is updated centrally in the core system file, EB.CASHFLOW. Once the accounting routines are processed, EB.CONTRACT.BALANCES, IFRS.ACCT.BALANCES and optional IFRS.ACCOUNTING.DETAILS files are also updated.
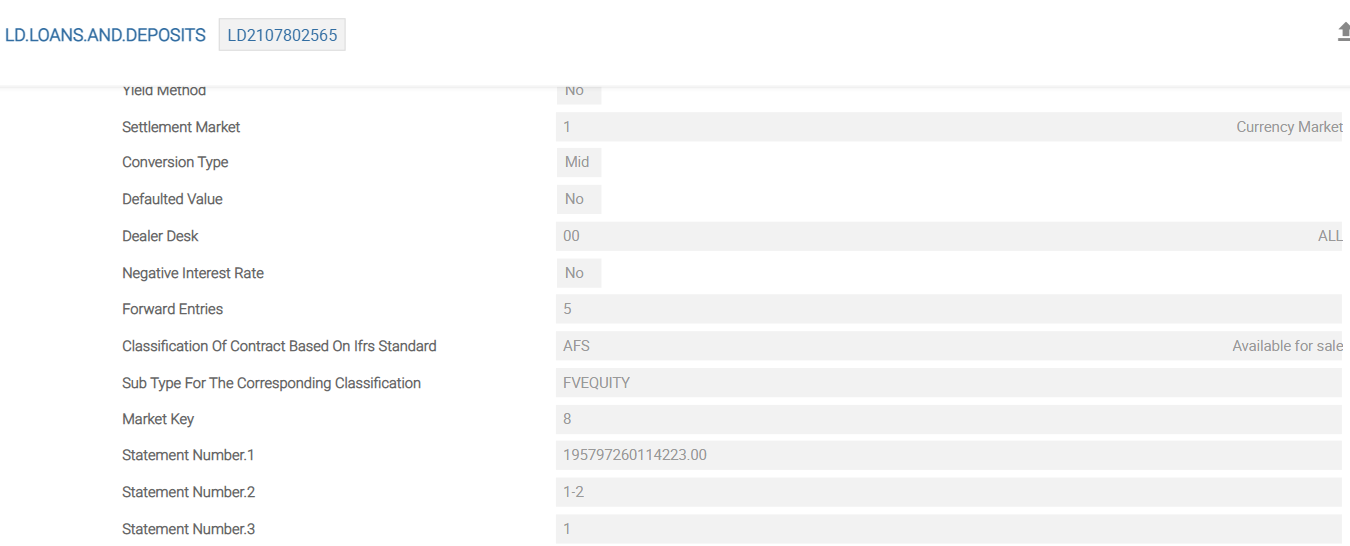
The following fields are entered into the LD contract in the example shown. The following is the EB.CASHFLOW record created for this contract.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Ias Classification | Links to the classification table |
| Ias Subtype | Links to IFRS.SUB.TYPE |
| Market Key | Either a fixed rate or a link to PERIODIC.INTEREST |
| Market Margin | Margin to be applied to the rate from Market Key |
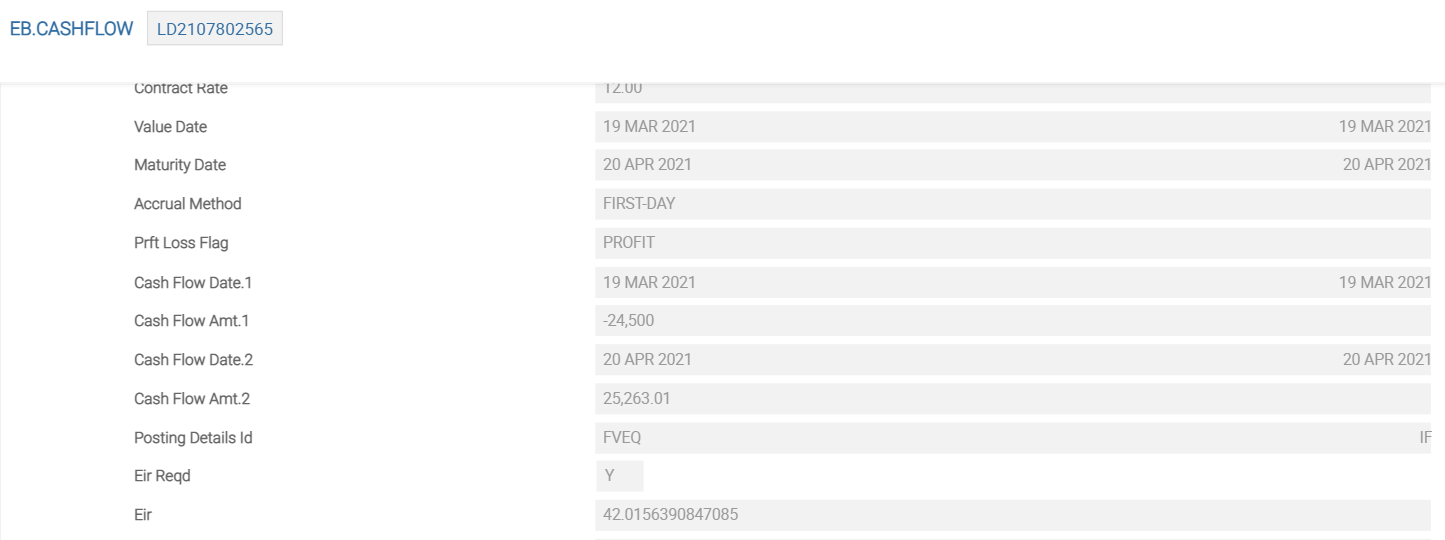
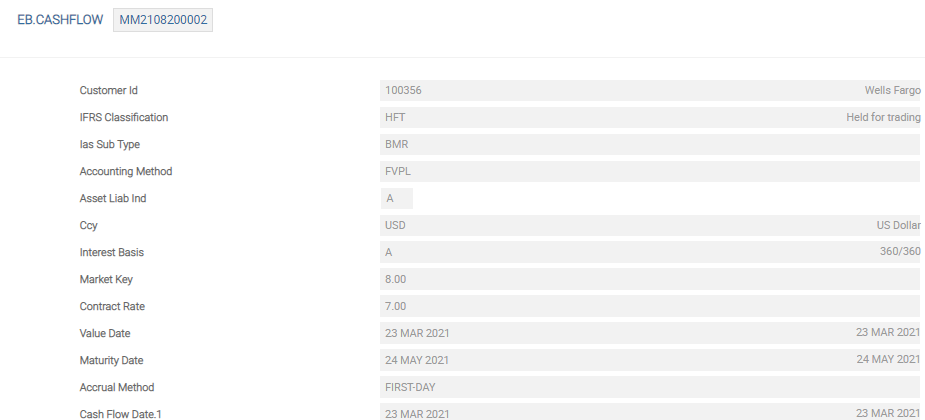
Contracts entered in the MM module have a few pivotal fields to link them into creating IFRS accounting adjustments. When the deals are authorised, the required information (present and future cashflows including principal component, interest, tax charges and so on) is updated centrally in the core system file, EB.CASHFLOW. Once the accounting routines have processed these, the EB.CONTRACT.BALANCES, IFRS.ACCT.BALANCES and optional IFRS.ACCOUNTING.DETAILS files are also updated.
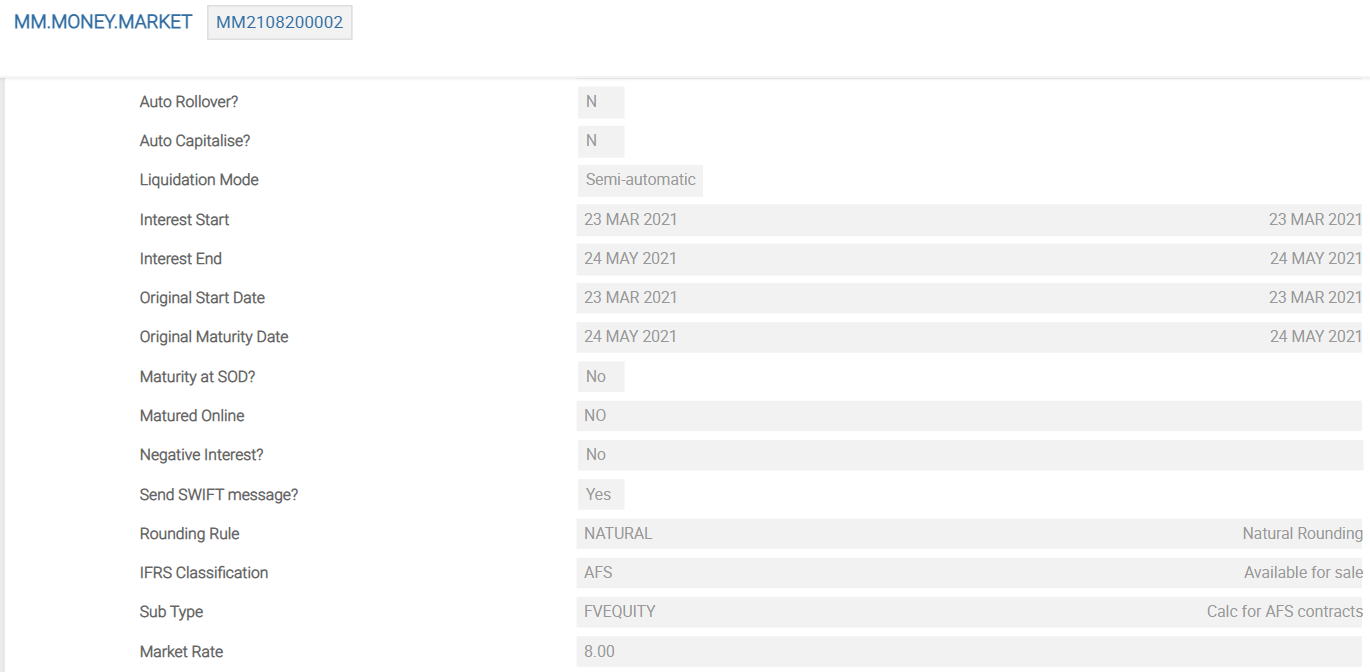
The following is the EB.CASHFLOW record created from the MM example contract.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Ias Classification | Links to the classification table |
| Ias Subtype | Links to IFRS.SUB.TYPE |
| Market Key | Either a fixed rate or a link to PERIODIC.INTEREST |
| Market Margin | Margin to be applied to the rate from Market Key |
Asset contracts entered in the SL module have a few pivotal fields to link them into creating IFRS accounting adjustments. When the deals are authorised, the required information (present and future cashflows including principal component, interest, tax charges and so on) is updated centrally in the core system file, EB.CASHFLOW. Once the accounting routines have processed these, EB.CONTRACT.BALANCES, IFRS.ACCT.BALANCES and optional IFRS.ACCOUNTING.DETAILS files are also updated.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Ias Classification | Links to the classification table |
| Ias Subtype | Links to IFRS.SUB.TYPE |
| Market Key | Either a fixed rate or a link to PERIODIC.INTEREST |
| Market Margin | Margin to be applied to the rate from Market Key |
Impairment of Securities Contract
Under IFRS regulations, the accounting of any asset, either bond or loan, which goes into default can potentially change. The revaluation of the gains and losses (with reference to securities held by Available for Sale (AFS) portfolios) is posted to equity (internal accounts) instead of PL for AFS portfolios.
However, when a security is identified as impaired, the current loss booked in equity is reversed and booked to P&L.
It is possible to:
- Identify the security that is impaired and record the reason for impairment
- For each AFS portfolio that has a position in the security, reverse the current loss from the internal account and posted to an impairment category
- Cancel impairments which result in reversal of PL and post back to equity
- Post subsequent losses for impaired securities to impairment PL, instead of to equity
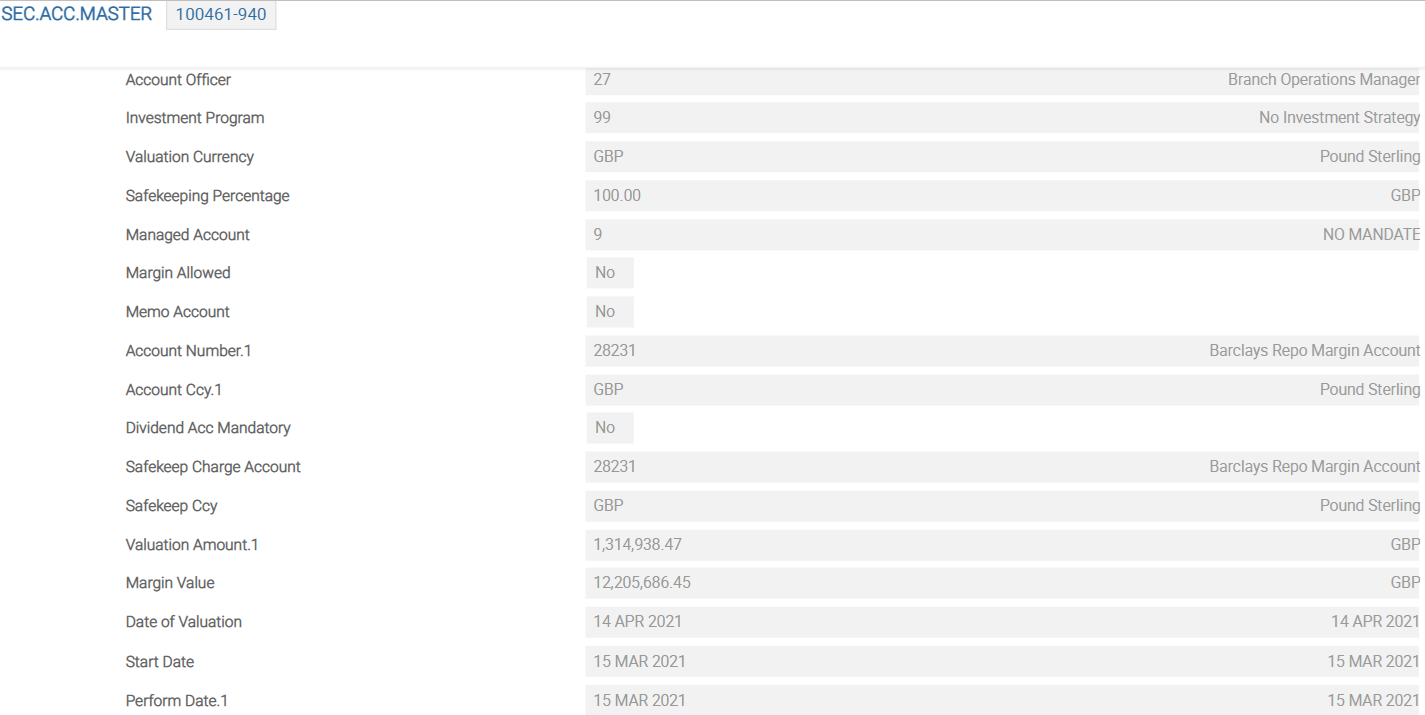
Configuring IAS 39
To classify assets and liabilities according to IFRS standards, the following primary parameter tables are considered for processing.
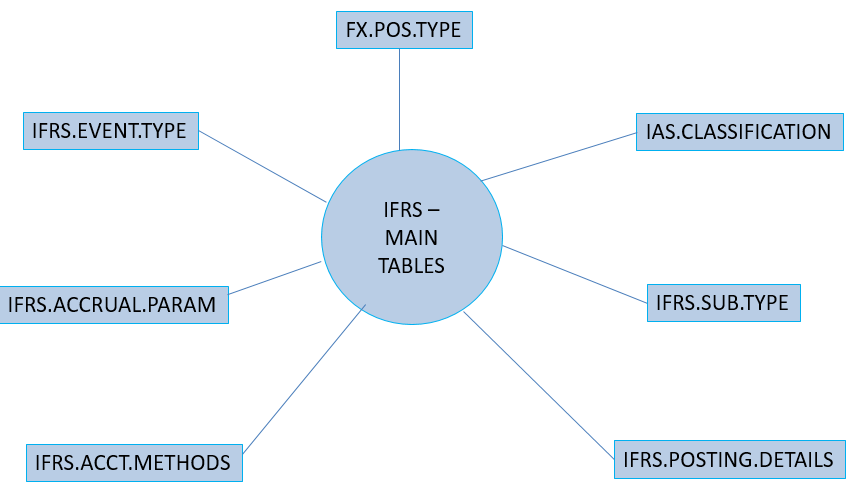
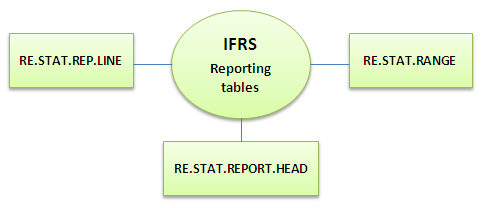
The secondary tables associated with IAS 39 are given below.
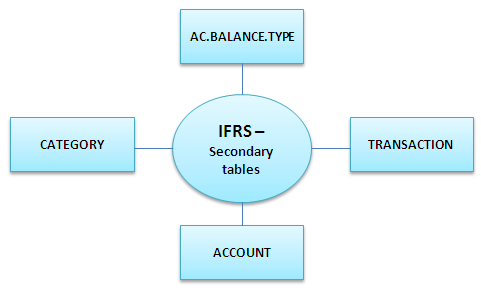
The chart below shows the reporting tables associated with IAS 39.
IFRS.EVENT.TYPE
This table stores the various events that can occur over the life of a contract, which can amend the cash flows pertaining to it. The values in this table are hard-coded and has a default list.
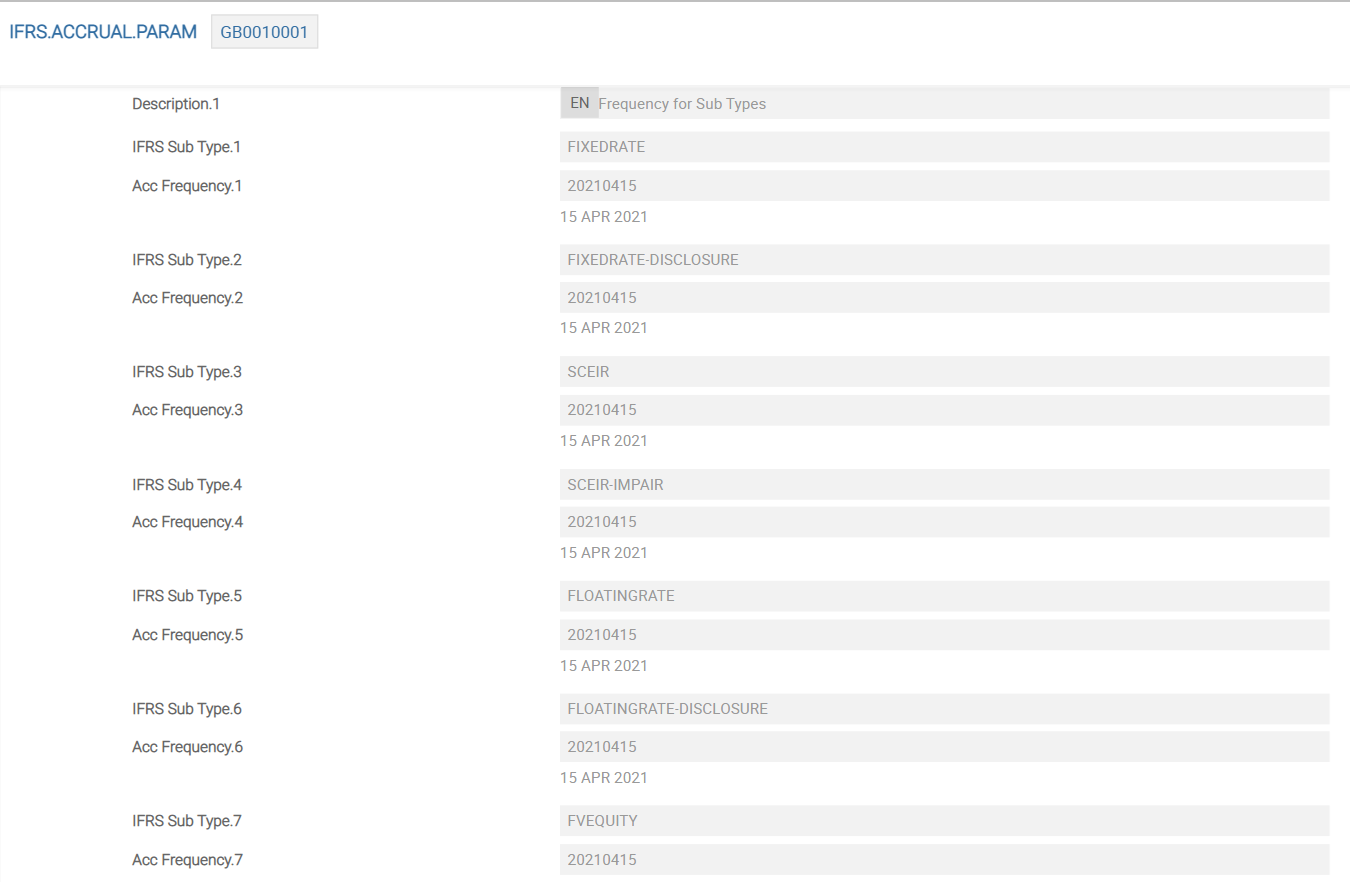
IFRS.ACCRUAL.PARAM
This is one of the important tables in IFRS and the absence of any records on it effectively means that IFRS accounting does not take place. Each Ifrs Sub Type must have its own frequency setting, and where required, the DISCLOSURE part of a sub-type can have its own unique setting to override its parent sub-type.
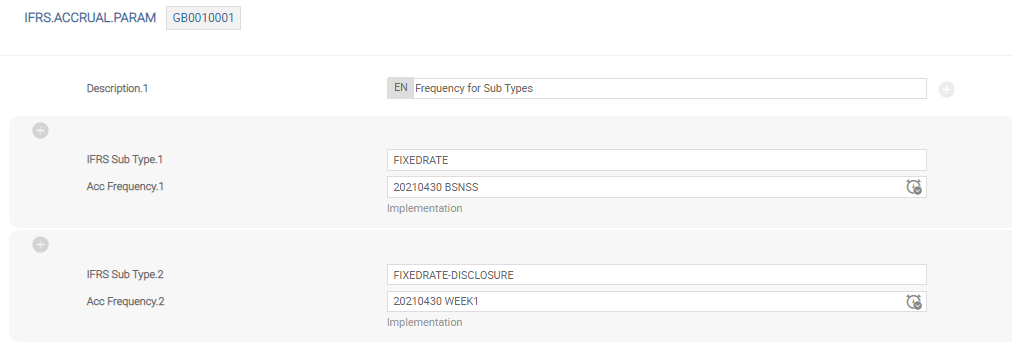
The above screenshot shows an example of IFRS.ACCRUAL.PARAM.
As given in the example, the FIXEDRATE subtype is set to a business day accrual, but for illustration purposes, FIXEDRATE-DISCLOSURE is set as weekly.
When adding new subtypes, it is important to add a frequency in this table.
IFRS.ACCT.METHODS
IFRS.ACCT.METHODS stores the accounting methods to be applied for different kinds of contracts based on the classification of assets and liabilities. This is kept as a separate table so that the users can do the setup based on their requirements.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Asset Type | A multi-value set that specifies one of the following asset types:
|
| Npv Method | A multi-value set, specifies if the Net Present Value (NPV) calculation is required based on the Ias Classification and the accounting method specified. If NPV calculation is not required, an option to include an external routine to calculate the amount is given using the Calc Rtn field. |
| Npv Rate | A multi-value set that specifies the rate type applicable to the calculation, which can be an EIR rate or a MARKET rate. This field can be entered only if the specified Npv Method is set to Yes. |
| Posting Reqd | A multi-value set to enable the bank whether the values need to be only calculated or posted as well. This is possibly applicable to methods like DISCLOSURE. |
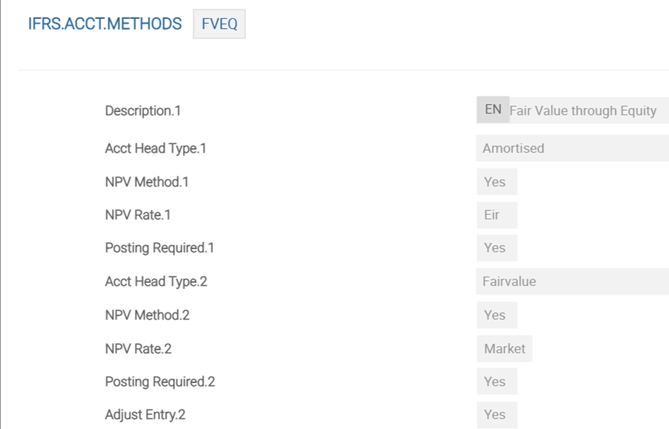
The above screenshot shows the IFRS.ACCT.METHODS table for FVEQ Accounting Head.
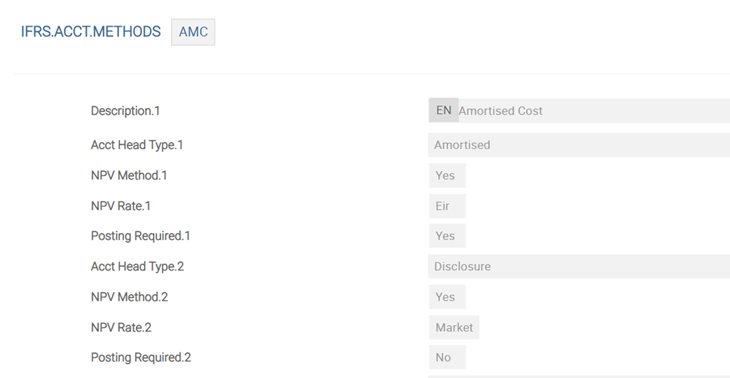
The above screenshot shows the IFRS.ACCT.METHODS table for AMC Accounting Head.
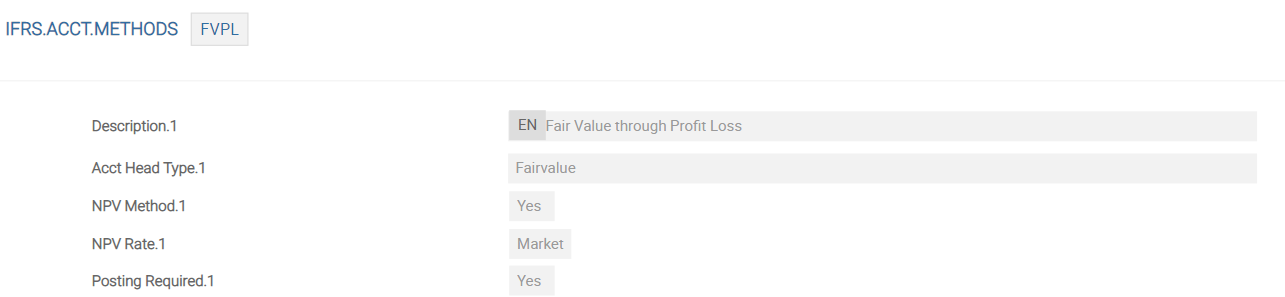
The above screenshot shows the IFRS.ACCT.METHODS table for FVPL Accounting Head.
The Adjust Entry field, a multi-value set, indicates whether the entry to be posted is an adjustment to what is already posted on the contract. It can be entered only when the accounting method is FVEQUITY (FVEQ). For accounting methods such as AMC, FVPL or DISCLOSURE, input to this field is not required. An error is produced if the FVEQUITY record is not set up with Asset Type of AMORTISED and FAIRVALUE.
The BAL TO EXLD field in IFRS.ACCT.METHODS defines the balance or asset types to be excluded from Temenos Transact balances. This functionality is available only for AC.BALANCE.TYPE records with Reporting Type set to Virtual.
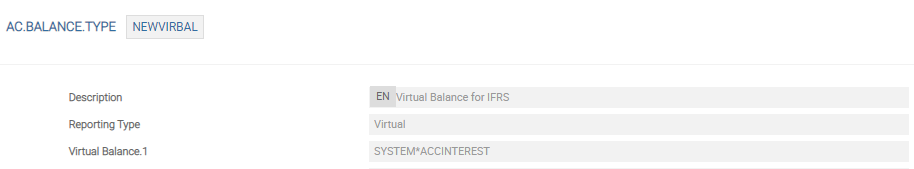
In the following example, AMORTISED, FAIRVALUE and DISCLOSURE accounting heads have the same AC.BALANCE.TYPE record and NEWVIRBAL is entered into BAL TO EXLD field. All normal accounting heads uniformly follow a single Temenos Transact balance.
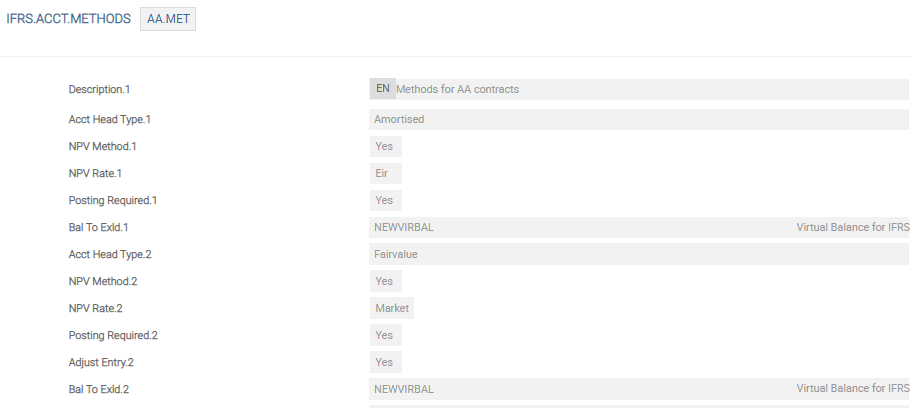
The above screenshot is an example of IFRS.ACCT.METHODS.
When the BAL TO EXLD field is populated for AMORTISED accounting head and left blank for FAIRVALUE or DISCLOSURE, the system defaults the BAL TO EXLD from AMORTISED to the other normal accounting heads. If any one normal accounting head has value in BAL TO EXLD, then the rest should be defaulted if not entered.
An error is displayed if a user inputs a different AC.BALANCE.TYPE record for AMORTISED, FAIRVALUE and DISCLOSURE.
The same logic applies to the impairment accounting heads and has a common BAL TO EXLD value:
- IMPAIR.AMORTISED
- UNWIND
- IMPAIR.AMC.ADJUST
- AMORTISED.UNDER.IMP
- IMPAIR.FAIRVALUE
- IMPAIR.FV.ADJ.INC
- IMPAIR.FV.ADJ.DEC
Any value, which is different, invokes an error.
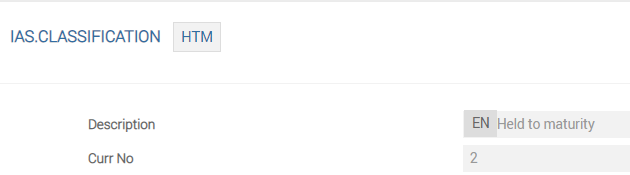
IAS.CLASSIFICATION
IAS39 requires a strict classification of financial assets and liabilities according to their purpose. This classification is extremely important as it defines various accounting and measurement rules to be applied. The following records are released in Core Banking.


IFRS.SUB.TYPE
IFRS.SUB.TYPE provides the details relating to the amendments to the cash flows and EIR (if any). Each record connects the details from the IFRS.ACCT.METHODS and IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS settings and, just as importantly, is the record, which is linked to the underlying deals or contracts.
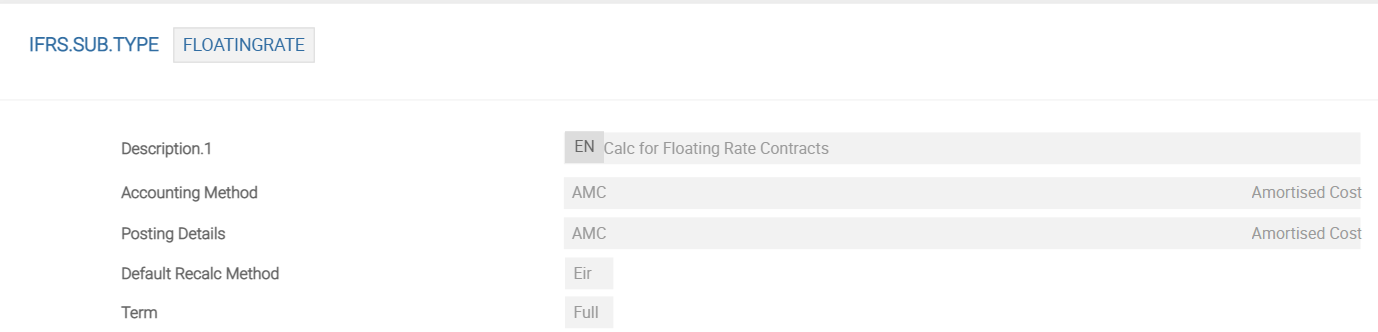
The above screenshot is an example of IFRS.SUB.TYPE - FLOATINGRATE.
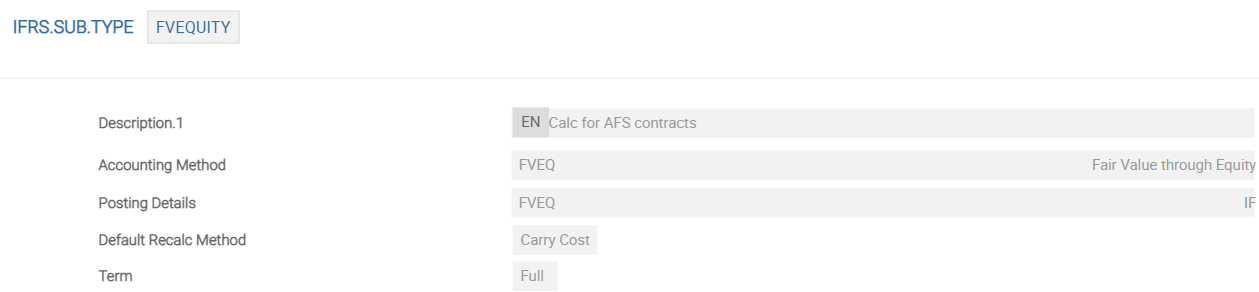
The above screenshot is an example of IFRS.SUB.TYPE - FVEQUITY.
When a contract is created and the IFRS parameters are defined, the cash flow details are passed to the cash flow engine. Cash flow engine calculates the EIR and updates the EB.CASHFLOW with the cash flow and EIR details during End-Of-Day process.
It is possible to define whether the:
- Full contractual life is to be used for the calculation of EIR
- Short term is to be used (This applies for contract under a floating rate, with a periodic interest rate change).
- Expected life of the contract (for AA contracts only)
The difference between the Short and Expected is given as follows:
- For short, after the end of the period, the interest rate fixing generates another cashflow for the next rate fixing period and recalculates the EIR
- For Expected, after the end of the period, the system stops IFRS processing.
This definition can be defined in the Term field in the IFRS.SUB.TYPE application.
IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS
IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS stores the details relating to the way the accounting entries are generated to make the contracts compatible with the IFRS requirements.
ID of the records is free text to link to the contracts at IAS.CLASSIFICATION or IFRS.SUB.TYPE level.
The broad concept of the settings is split into the following categories:
| Categories | Description |
|---|---|
| Posting Style | I.O (reverse and re-book) or ADJUST (adds or subtracts to existing amounts) and applies to all the asset name subsets |
| Asset Name(s) | The asset name(s) the record relates to Amortised, Disclosure and Fairvalue |
| Account Type | Contingent or non-contingent |
| Entry Type | Profit only, Loss only or both (for amortised only both) |
| Entry Target | ACCOUNT, PL or CRF (internal account, CATEG.ENTRY or RE.CONSOL.SPEC.ENTRY) |
| Contra Entry Target | ACCOUNT or CRF (internal account or RE.CONSOL.SPEC.ENTRY) |
This is kept as a separate table so that the user can do the setup based on their specific requirements.
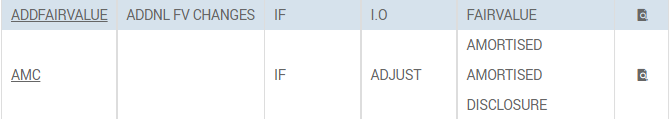
FX.POS.TYPE
FX.POS.TYPE is used to split the position and accounting of the bank into logical divisions. This application is mandatory when using a GAAP or IFRS financial reporting. Although prefixed by FX, the table is in common usage in Temenos Transact and is referred to by CATEGORY, ACCOUNT and many accounting or position parameter files.
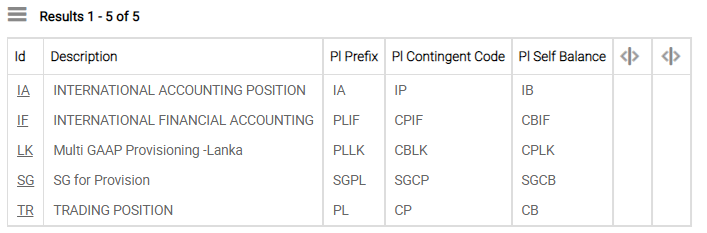
The above screenshot shows the different GAAPs defined.
When used for GAAP reporting, it is recommended that the two digit ID is set to the same ID used by the country (that is IN for India).
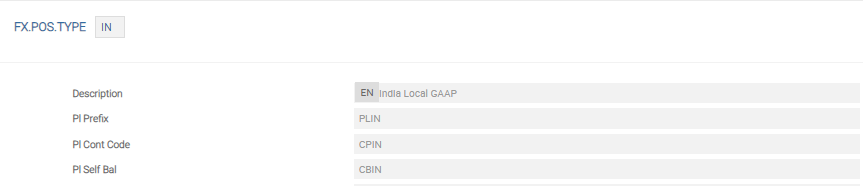
The TR record is the original and default record used by Temenos Transact and it must be present. The IF record is the one used for IFRS reporting and must be present if IFRS reporting is required.
In normal usage, the ID of the table is used but for contingent and self-balancing an extended ID identifier is needed. It is recommended that the following style of values is followed:
- For P/L, add the PL prefix to the position type, for example PLIF.
- For Contingent P/L add CP prefix to the position type, for example CPIF.
- For self-balancing P/L add CB prefix to the position type, for example CBIF.
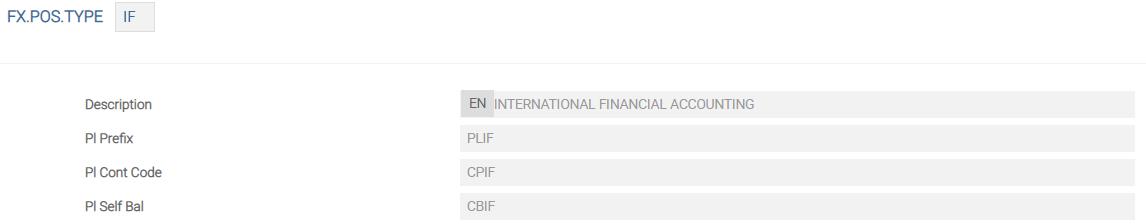
Otherwise, it is achieved by default by taking the first character of the ID and adding 'P' for contingents and 'B' for self-balancing. Alternatively, the user can define their own values of up to four digits for each of these.
RE.PL.PREFIXES is a system control file, which stores a cross-reference of all the prefixes and prevents the duplication of any user or system defined values.The following tables should be configured in the sequence for impairment processing:
IFRS.IMPAIRMENT.CODEIFRS.ACCRUAL.PARAMsetup for impairmentIFRS.ACCT.METHODS- AMCIFRS.POSTING.DETAILS- AMCIFRS.ACCT.METHODS - FVEQIFRS.POSTING.DETAILS - FVEQ- Collateral setup for Impairment
IFRS.ACCRUAL.PARAM setup for Impairment
The screenshot shows an example of IFRS.ACCRUAL.PARAM record which is set up with the impairment details.
For each Ifrs Sub Type, there must be a multi value in this record XXX-IMPAIR (XXX is the Ifrs Sub Type). The following screenshot shows a sample record SCEIR–IMPAIR.
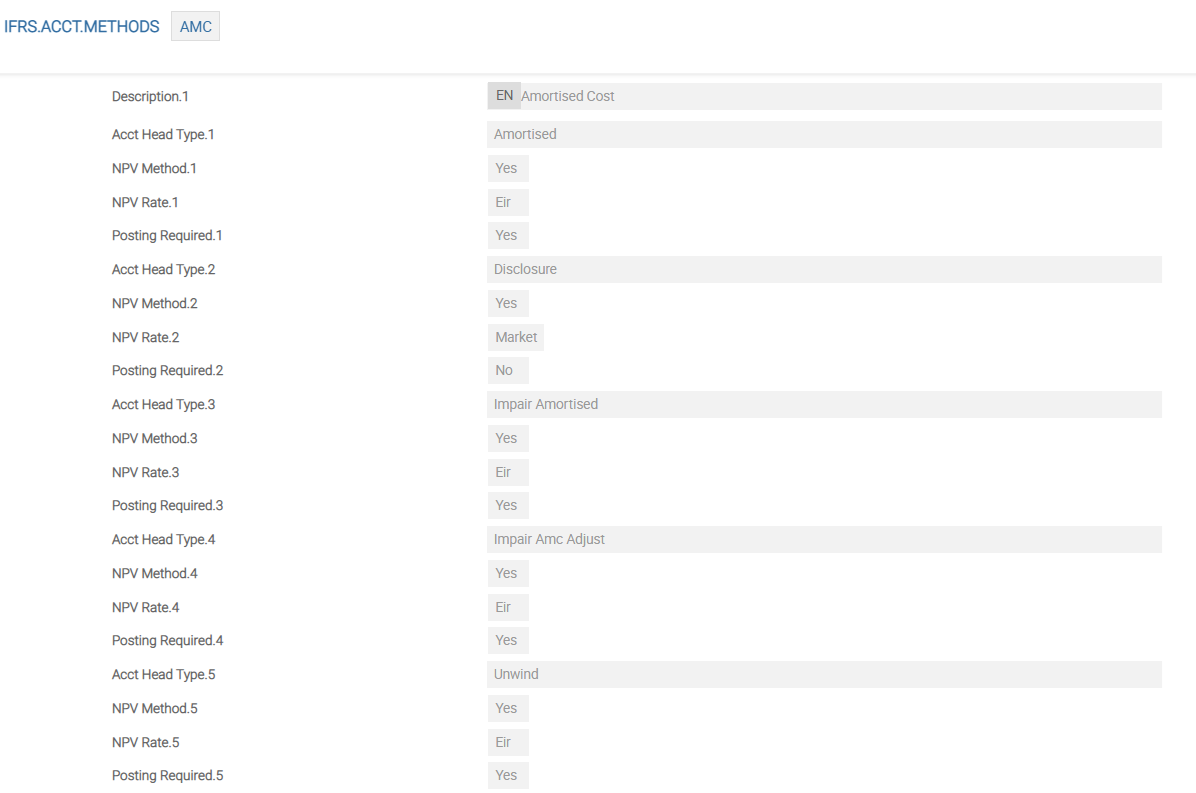
IFRS.ACCT.METHODS – AMC
For impairment, the following additional Asset Types are required to define the accounting methods for impairment. These should be added to the IFRS.ACCT.METHODS record AMC. The following are also shown in the example screenshot:
- IMPAIR.AMORTISED − The impairment loss of contracts valued at Amortised.
- UNWIND − The unwinding of the carrying amount of an impaired contract.
- IMPAIR.AMC.ADJUST − The adjustment to the impairment loss for an impaired contract valued at AMC.
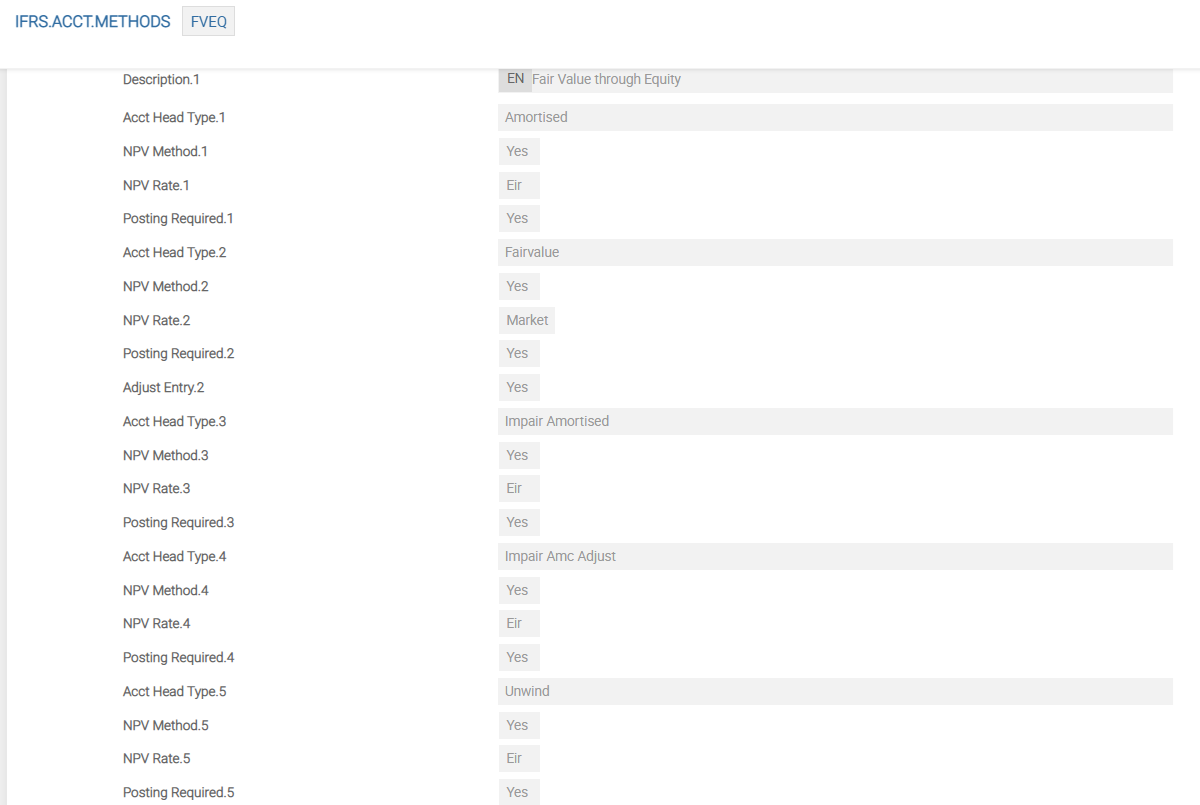
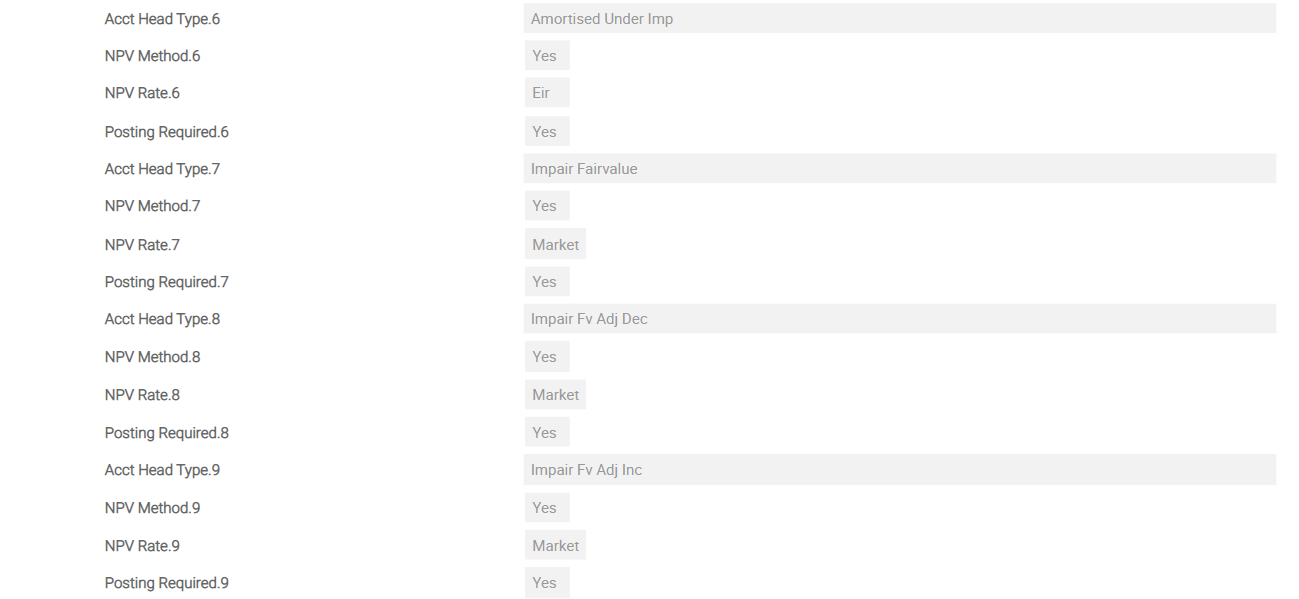
IFRS.ACCT.METHODS – FVEQ
For impairment, the following additional Asset Types are required to define the accounting methods for impairment. These should be added to the IFRS.ACCT.METHODS record 'FVEQ'. The values are:
- IMPAIR.AMORTISED
- UNWIND
- IMPAIR.AMC.ADJUST
- AMORTISED.UNDER.IMP
- IMPAIR.FAIRVALUE
- IMPAIR.FV.ADJ.INC
- IMPAIR.FV.ADJ.DEC
These Accounting Heads are explained in the Configuration section, below the IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS.
IFRS.IMPAIRMENT.CODE
IAS 39 suggests a list of acceptable objective impairment evidence. The IFRS.IMPAIRMENT.CODE defines and captures the various codes, which can be used for impairment evidence. Within Temenos Transact, the following records are released, however new records can be created as required:
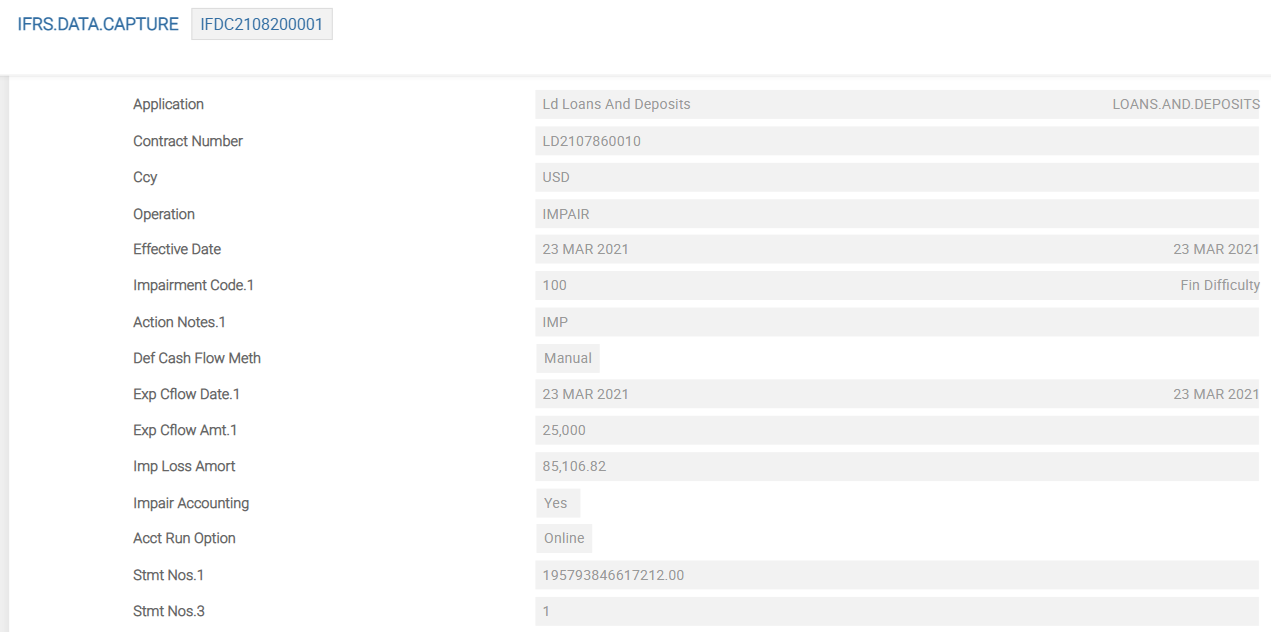
The Impairment Code field is entered in the IFRS.DATA.CAPTURE record.
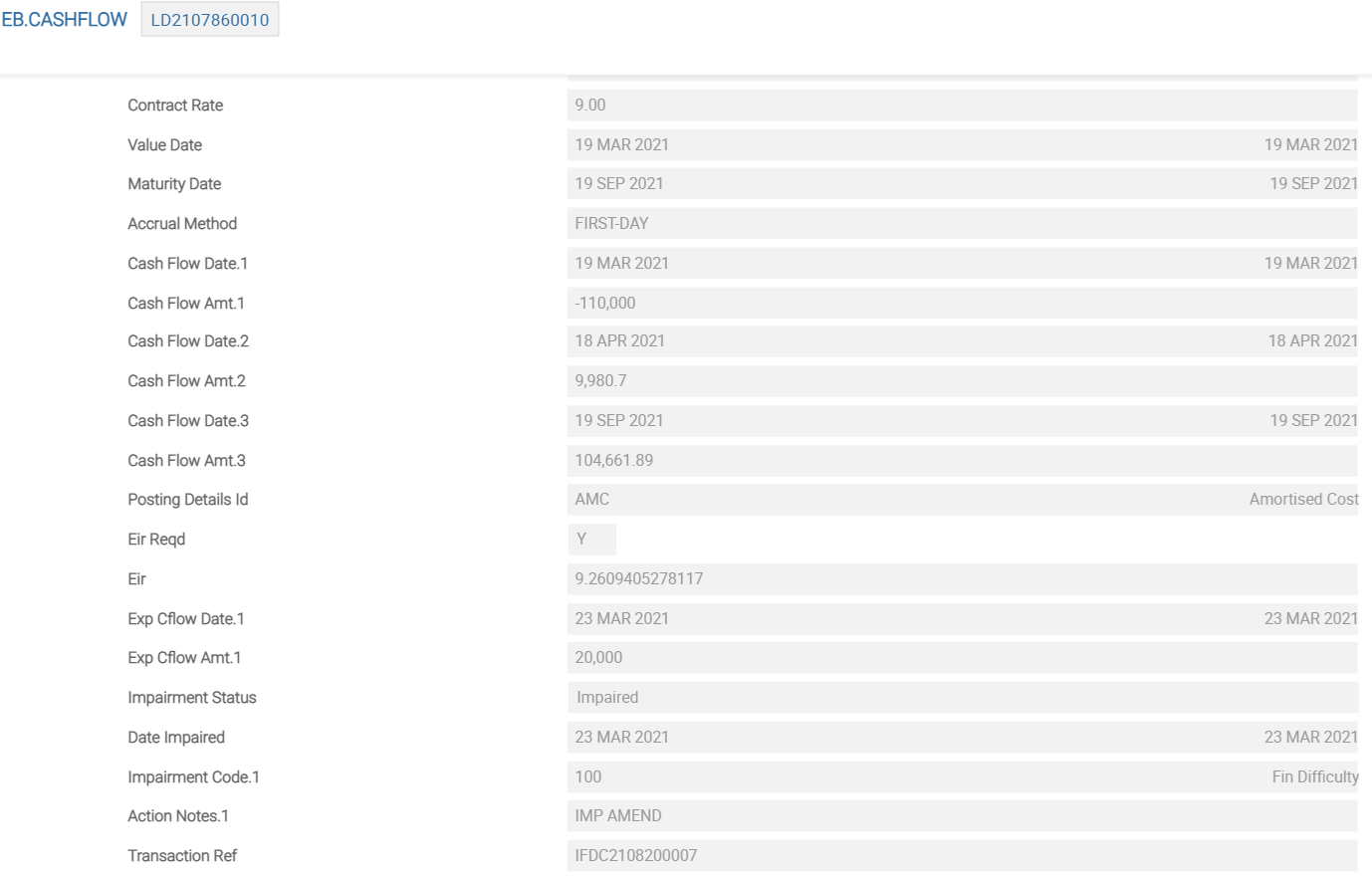
Once the IFRS.DATA.CAPTURE record is authorised, the related EB.CASHFLOW record is automatically updated by the system with the impairment code.
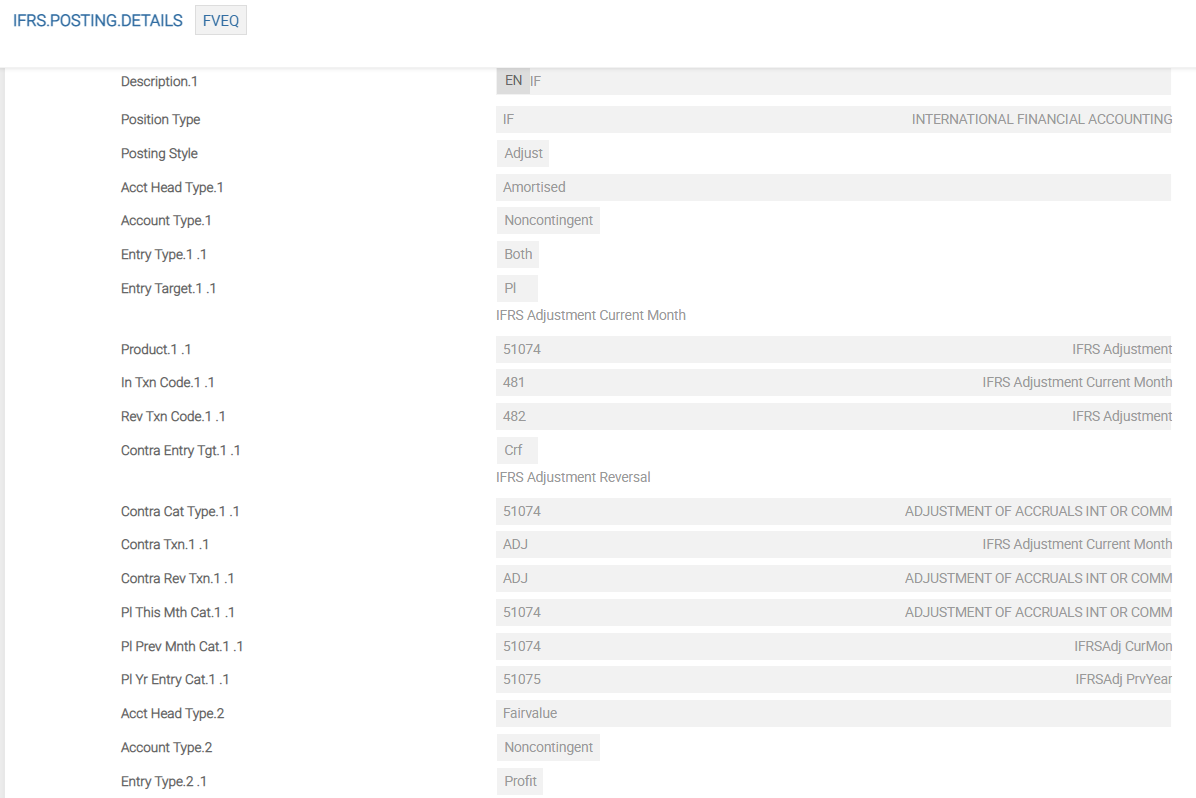
IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS – AMC
For impairment, the following additional Asset Types are required to define the accounting methods. These should be added to the IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS record AMC.
- IMPAIR.AMORTISED
- UNWIND
- IMPAIR.AMC.ADJUST
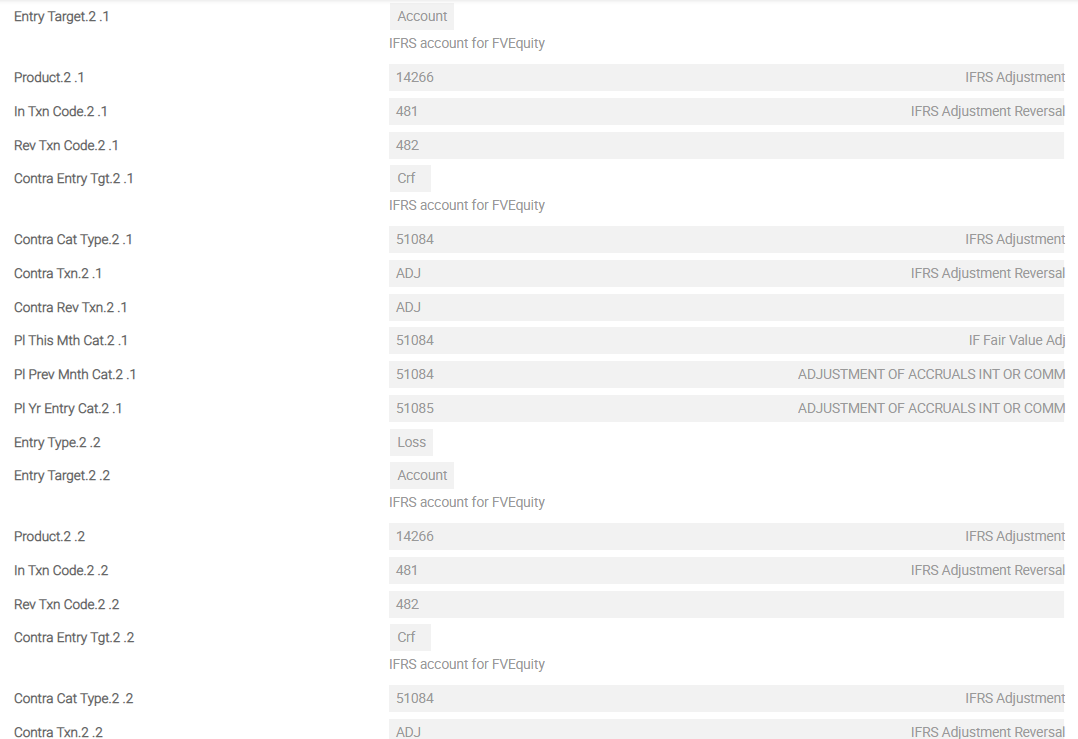
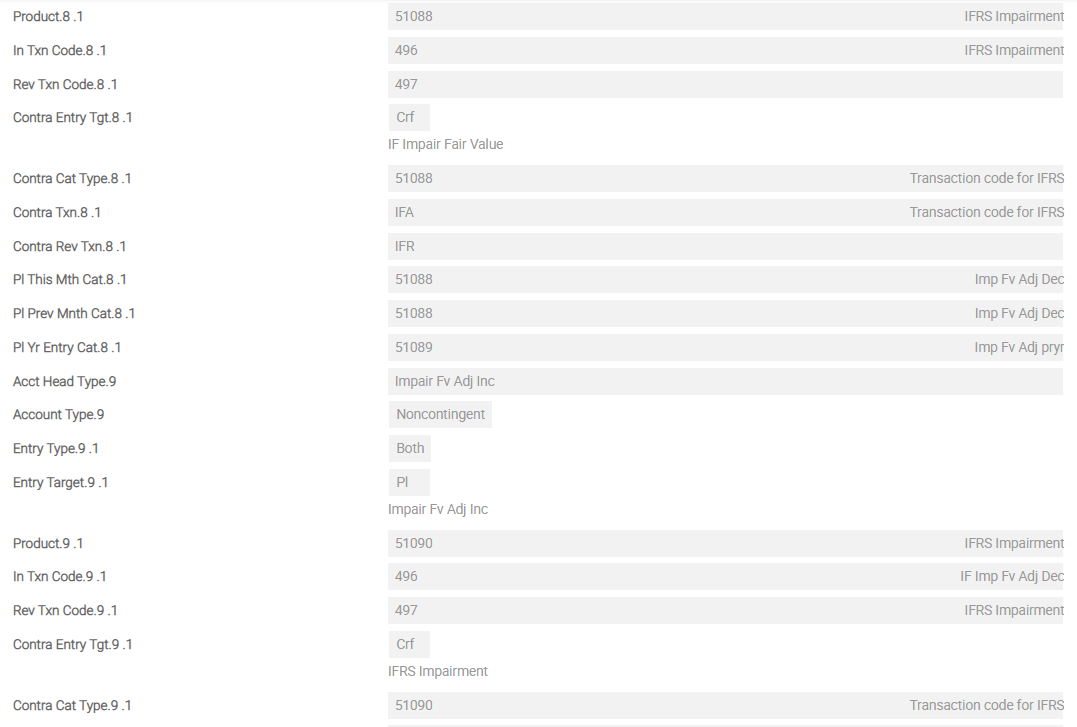
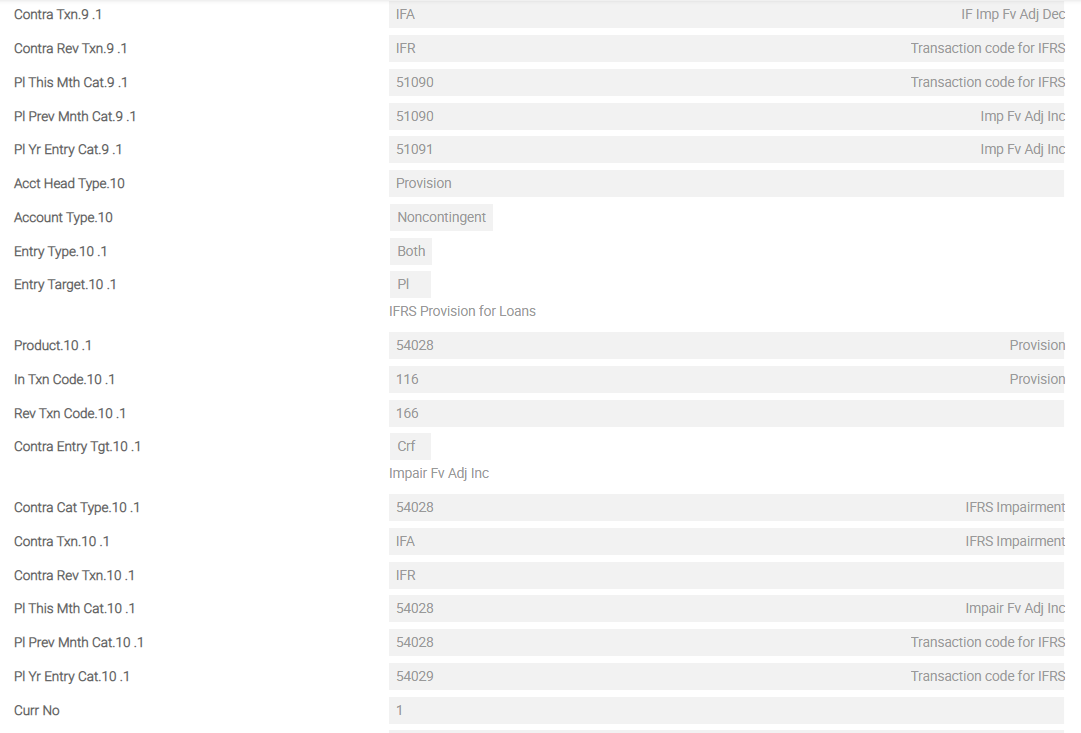
IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS – FVEQ
For impairment, the following additional Asset Types are required to define the accounting methods. These should be added to the IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS record AMC.
- IMPAIR.AMORTISED
- UNWIND
- IMPAIR.AMC.ADJUST
- AMORTISED.UNDER.IMP
- IMPAIR.FAIRVALUE
- IMPAIR.FV.ADJ.INC
- IMPAIR.FV.ADJ.DEC
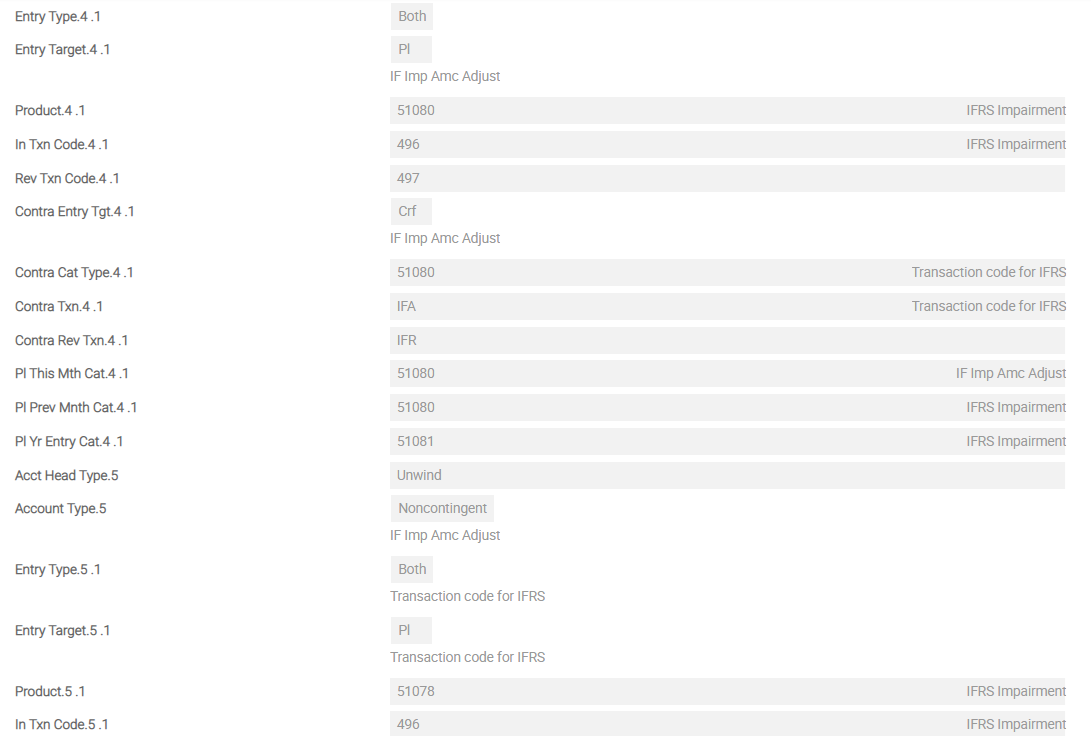
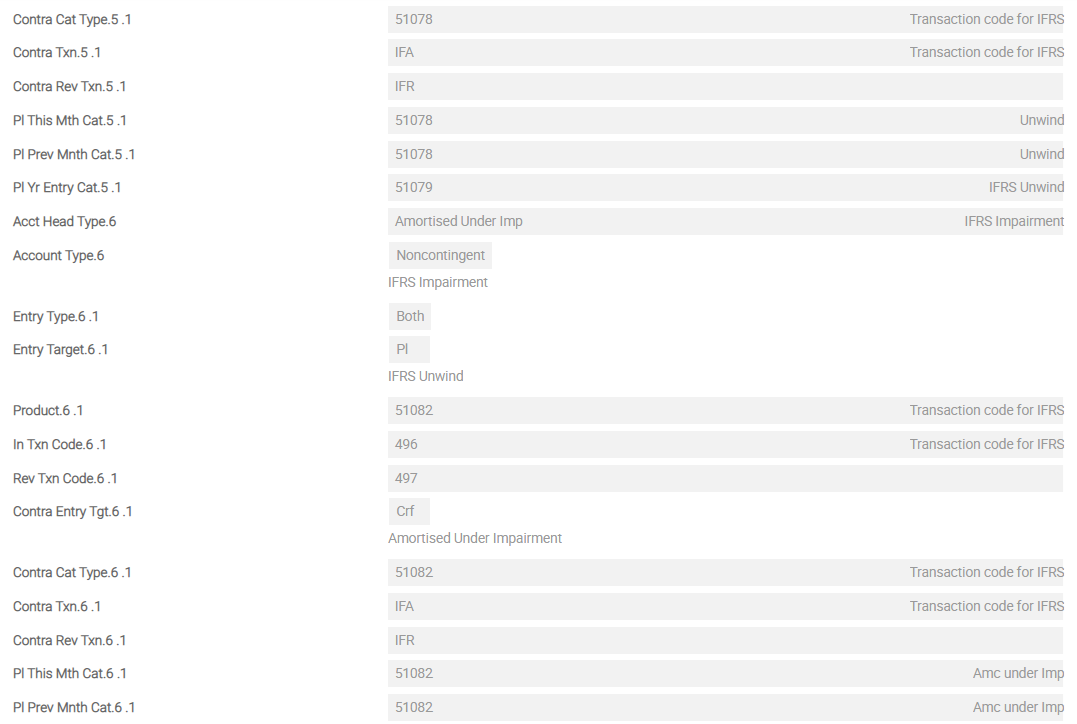
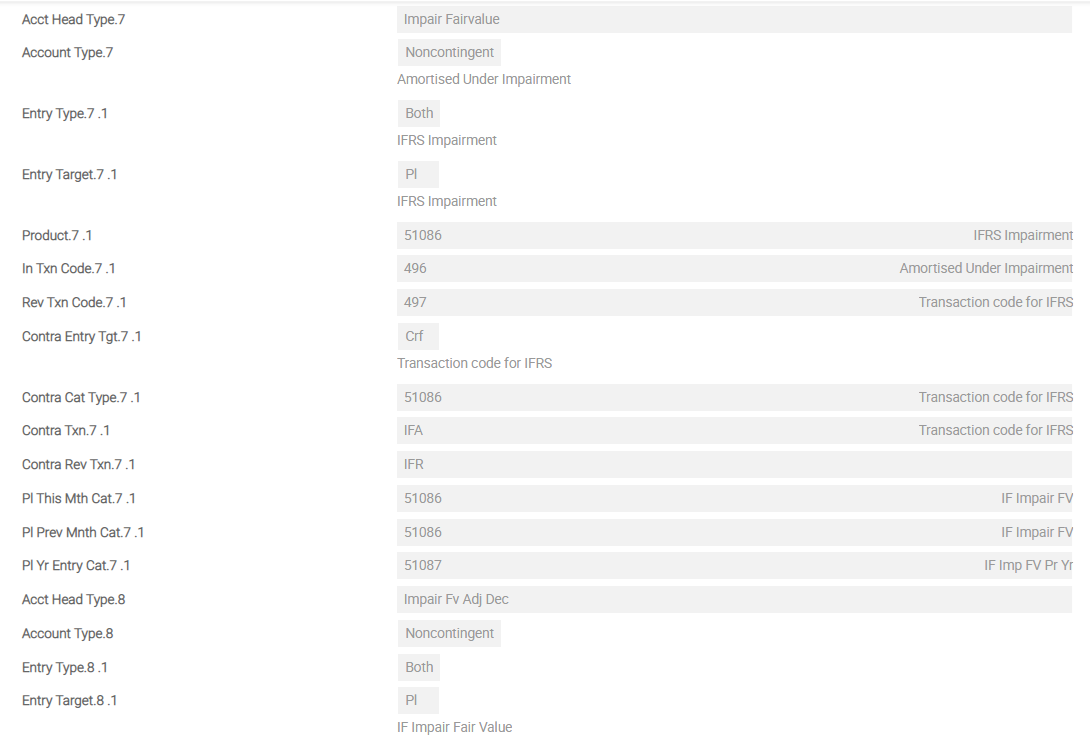
The screenshots below show a single screen of IFRS.POSTING.DETAILS for FVEQ. This example shows the sequence of Asset Types from first Asset Type until eighth Asset Type for FVEQ in detail.

Illustrating Model Parameters
The high-level configurations available in the Model Bank are given below:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
IAS.PARAMETER |
|
IAS.CLASSIFICATION
|
|
Product-Level Parameter Setup
The following parameters must be set up for each product:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
IAS.APPLICATION.PARAM
|
|
IAS.RATE.TYPE
|
|
IAS.AMOUNT.TYPE
|
|
IAS.PRODUCT.CONDITION
|
|
IAS.PRODUCT.GROUP
|
|
Illustrating Model Products
Model Products are not applicable for this module.
In this topic