Introduction to Delivery
This topic explains the Delivery (DE) module that manages the flow of all messages from Temenos Transact, such as confirmations, payments and advices which gives full control over formatting and language of presentation to the users. Messages are generated automatically, as soon as the transaction is complete or when a scheduled event occurs.
All messages may be either printed or sent through electronic carrier systems, such as SWIFT, Telex and the like.
Messages from external carrier systems are received by the delivery system and formats (if necessary) according to the user-determined requirements. Then, printed output containing the incoming information is produced. For example, after authorisation the payment messages are passed in the Funds Transfer (FT) module, which updates the accounts and it's related information.
The delivery process is fully automated, but the users may take control over many aspects of message management. Temenos Transact has the facility to inspect, control the message queues and use graphical enquiries to view the queue status. Once the messages are in queue, the individual messages may be displayed, amended or re-routed.
The DE module is classified as:
- Base functionality – Covers the setup and usage of delivery across the business applications in Temenos Transact.
- Message creation functionality – Covers the setup and usage of applications under the DE module, which are not explicitly linked to any other Temenos Transact application that generate the delivery messages for various purposes.
Base Functionality
Message Creation Functionality
Product Configuration
This section details the configuration setup required for the DE module.
SF is the product code for SWIFT messages (available from R13). With this product code, SWIFT messages are formatted only if the SF product is installed. If SF is not installed, then the messages will go to repair status. This is applicable for incoming and outgoing SWIFT messages.
The DE.PARM application holds a number of parameters to control the processing of messages in the DE module. This application contains a single record (SYSTEM.STATUS). With the replacement of formatting and ad hoc processing accompanied by the new delivery services, the settings in DE.PARM may not be applicable.
The following are the types of data on DE.PARM:
- Parameters that allow the operator to shut down the carrier control modules, the inward and outward formatting modules. The shut down can be:
- Urgent (after the message being processed).
- Normal (when all queues have been processed).
- Parameters that can be used to optimise the performance of all carrier control, inward and outward formatting modules. The options are:
- After processing all urgent messages, a specified number of priority messages and a specified number of normal messages are processed, before returning to check whether there are any other urgent messages to be processed.
Making these numbers larger increases the efficiency of the system, but causes slight delays in the processing of urgent messages.- A wait time can be specified. This is the time that the carrier control and formatting modules will wait, between finishing the processing of all their queues and searching them again for input.
A longer wait time gives other users a faster response, but causes slight delays to messages. - Fields are defined in the way the delivery system is installed.
- The Cet Time Diff field defines the local time difference from the Central European Time (CET). This is used in the conversion of SWIFT messages and added after the time.
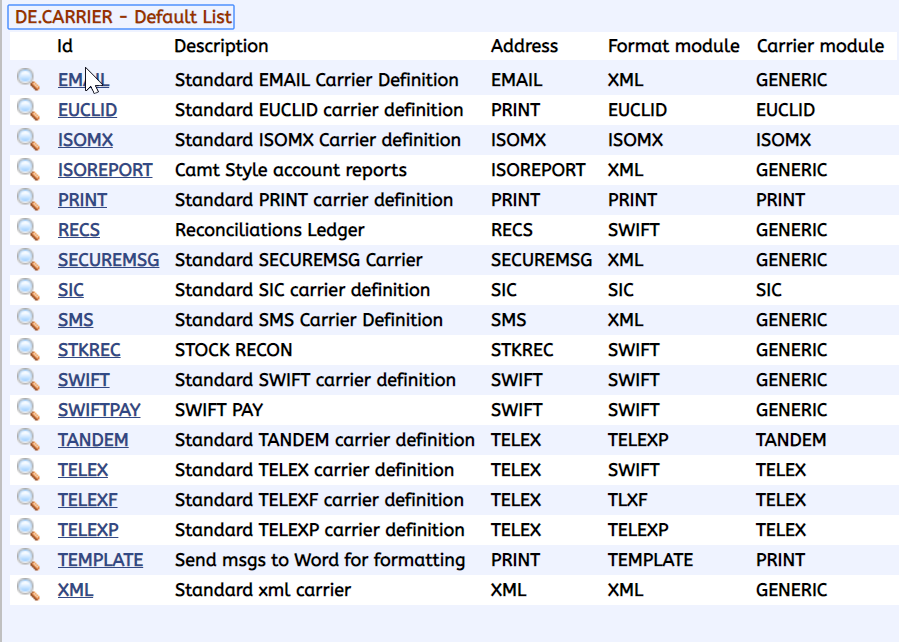
The DE.CARRIER application contains the details of all carriers available in the DE module. The bank need not amend this application, unless new interfaces are required to be linked to the delivery system. The user must specify the carrier in the DE.PARM application, to enable the carriers specified in DE.CARRIER. The ID of DE.CARRIER is the name of the carrier, as used in DE.PRODUCT.
Each record contains:
- The address type to be used for the carrier (that is, when accessing DE.ADDRESS).
- The formatting rules (defined in DE.FORMAT.CARRIER).
- The carrier module (for example, SWIFT).
If the carrier module is GENERIC, the interface must be specified. The interface must reference a record in DE.INTERFACE, which contains the details of the protocol for all generic interfaces (non-generic interface details are stored in DE.PARM). When the record is authorised, formatting and carrier applications are created (if they are not existing already).
The Apply Address Rules field in DE.CARRIER, enables the bank to define for each carrier if that carrier is allowed for validation of the address rules or not. The available options in this field are Yes or Null and the default value is Null.
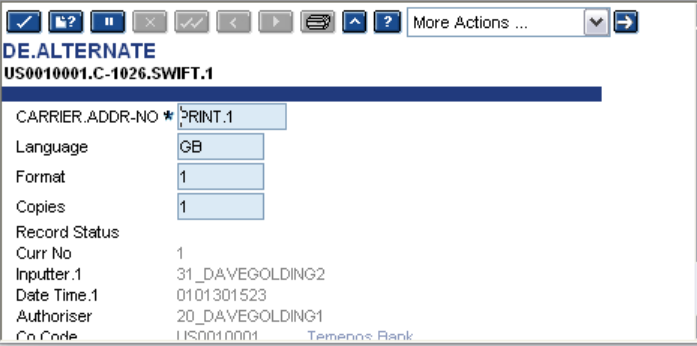
The DE.ALTERNATE application contains the alternative carriers or addresses to be used, if a message is to be rerouted. For example, a customer may normally have all their messages sent to a particular telex number, but that telex number might be out of order, so all their messages are to be sent to an alternative telex number.
The DE.ALTERNATE application is accessed, if the Msg Disposition field in the inward and outward DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER applications are set to REROUTE.
When a message is passed through formatting and if the Msg Disposition field is set to REROUTE, the DE.ALTERNATE application is accessed for the carrier, address number, language and format. It then copies the message which is to be sent. The ID of this application is as follows:
- Company code followed by ’.’
- C-customer number followed by ’.’ or A-account number followed by ’.’
- Carrier followed by ’.’
- Address number (that is, nnnnn as per DE.ADDRESS)
For example, US0010001.C-1026.SWIFT.1
When this application is accessed, only a record at the same level as the DE.PRODUCT record originally read will be accessed. Therefore, if the DE.PRODUCT record originally read was at customer level, then the DE.ALTERNATE application will be accessed at customer level. If an appropriate record cannot be found, the message will go into repair with a corresponding error message.
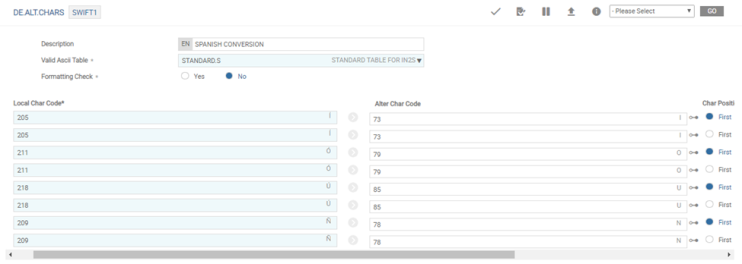
The DE.ALT.CHARS application holds the character mappings for the replacement of language specific characters to SWIFT acceptable characters.
If a field is defined as a language based field and the data captured is in the French, the system allows standard French characters such as á,è,é,Ç, if the date captured is in the German characters, then it allows ü,ß. When the system uses such information in the SWIFT messages, it converts it to SWIFT acceptable characters.
The system provides a default set of known characters and the alternative replacements. In addition, it provides an option to amend the application, if the user wants to add more characters.
The ID of this application must be a meaningful ID that must be relevant to any validation or conversion and used in carrier’s formatting of the message. A single language specific character may be replaced by null, one or more characters.
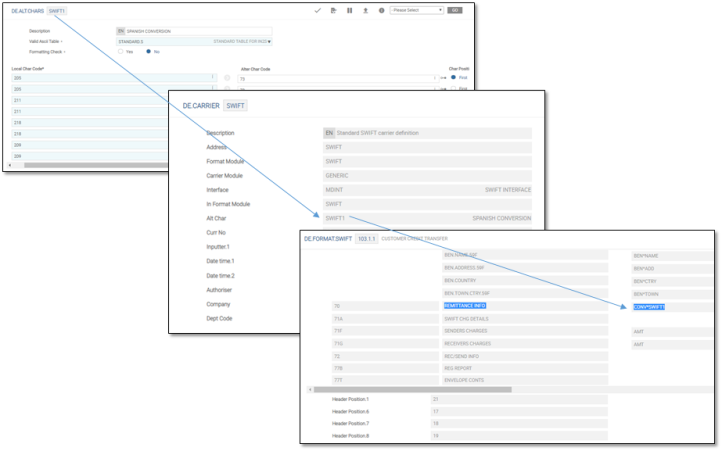
The ASCII.VALUES application must be configured to ensure that the character sets are allowed. It is possible to define invalid characters and their replacement values by message format types.
- SWIFT message types - ‘è’ is not allowed for this message type and should be replaced with ‘e’.
- CAMT message types - ‘è’ is not allowed for this message type and need not be replaced, whereas ‘â’ is not allowed and should be replaced with ‘a’.
Conversion is achieved by attaching CONV*DE.ALT.CHARS to the field as shown in the below screenshots.
The product information in the DE.PRODUCT application is used by formatting process when expanding the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records for the copies required for the message. Product information consists of status (normal, hold or delete), carrier or delivery address, version of the format to be used and how many copies should be made.
After the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records has been expanded, the DE.PRODUCT record is not read again for this message, even if the message is resubmitted and is placed again on the dun-formatted queue. Therefore, if language, format or copies are to be changed after the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records has been expanded, the message must be re-routed.
The DE.PRODUCT records may be specified for:
- A particular company.
- A customer.
- An account.
And each of the DE.PRODUCT records may be specified for:
- All message types.
- Specific message types.
- All banking applications.
- A specific application.
During formatting, the DE.PRODUCT is read for the most specific record, matching the details on the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records. If the most specific record is not found, the DE.PRODUCT is read again until a more general record is found. The ID of the DE.PRODUCT application consist of one or more following components in the sequence given below:
- Company code followed by ’.’
- C-customer number followed by ’.’ or A-account number followed by ’.’ (this is not present for company level records)
- Message type or ALL followed by ’.’
- Application or ’ALL’ or xxyy, where xx is the Application code and yy is the Funds Transfer (FT) product code.
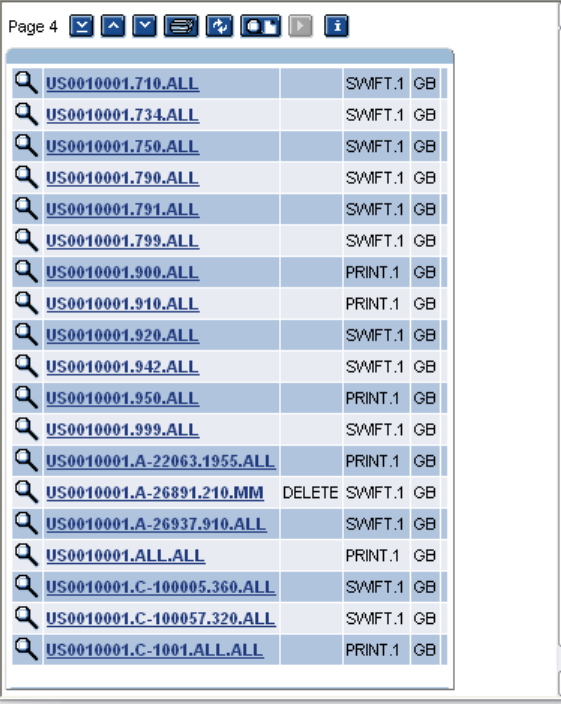
A sample of portfolio specific DE.PRODUCT records:
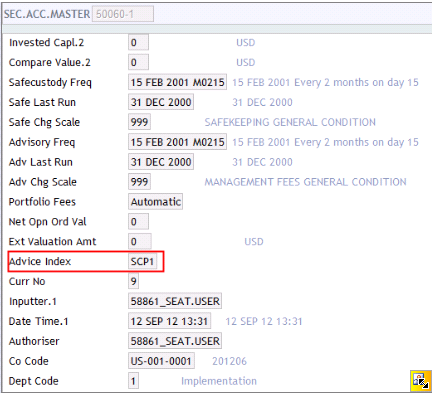
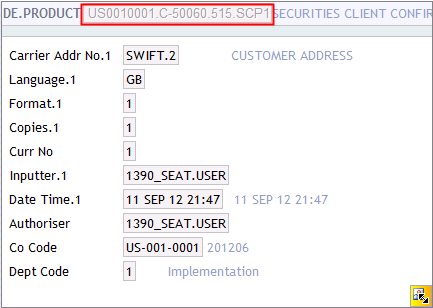
The records in the DE.PRODUCT application is searched in the following order:
- All fields used to find the records in the DE.PRODUCT are stored in the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records. Therefore, by using the fields available and by searching the DE.PRODUCT (in the above order), it is possible to find out which DE.PRODUCT record has been used to expand the multi-value set in the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records.
- The multi-value set on the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records are expanded according to the fields in the DE.PRODUCT record. For example, if the DE.PRODUCT record says that, one copy should be sent by SWIFT and one by print. The DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records are updated accordingly. The following fields in the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER are updated from the DE.PRODUCT record:
- Carrier Addr No
- Format
- Msg Language
- Msg Priority
- Msg Status
- Msg Disposition
- If the DE.PRODUCT record says that a particular carrier should send two copies, these copies are split on the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records into two multi-value sets.
- If a single message should be sent to multiple customers, the Mdr Customer field in the DE.PRODUCT application (a multi-value set) can be used to specify additional customers to whom the copies of the message needs to be sent. This can be specified for customer or account level records and for print carrier only.
- The language on the DE.PRODUCT record is not used to update the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records, if the DE.PRODUCT record used was a company level record, since the language passed from the application is more specific.
- For a particular message type, if copies are not allowed, that is, copies is set to NO in the DE.MESSAGE, then only the first copy of the message specified in the DE.PRODUCT record is used to update the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records.
- The DE.PRODUCT record can also be used to hold the messages or to delete the messages, using the Status field.
The DE.ADDRESS application contains the names and addresses of a bank customers, and also the details of each company within the banking organisation. The basic postal address of each customer is automatically updated, when the address is changed through customer maintenance (CUSTOMER application). A record is created in the DE.ADDRESS application with ID as COMPANY ’.C-’ CUSTOMER ’.PRINT.00001’
The address on this record cannot be updated through the DE.ADDRESS application, but must be updated through CUSTOMER application. The SWIFT IDs, telex numbers and alternative print addresses are also held in DE.ADDRESS. These records may be input and amended through the DE.ADDRESS. The ID of this records is COMPANY ’.C-’ CUSTOMER ’.XXXXXX.N’, where, XXXXXX is a valid carrier defined in DE.CARRIER (for example, SWIFT, TELEX) and N is the address number. The address number is in the range 00001 to 99999.
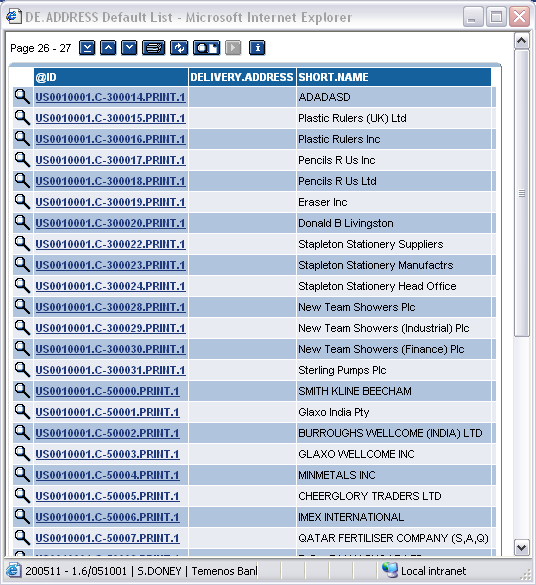
During formatting, after the DE.PRODUCT record has been read, DE.ADDRESS is read for each copy of the message in the multi-value set in the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records. The ID of DE.ADDRESS application consists of the fields in the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records, using the carrier address from the DE.CARRIER and the address number held in the Carrier Addr No field. If the ADDRESS record is not found in DE.ADDRESS, the message will go into repair.
The address in the DE.ADDRESS is appropriate to the carrier ID used to update the To Address field in the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records. It is possible to hold all printed output for this address by setting the Hold Output field to Yes.
The message goes through delivery process in the normal way, but instead of being printed, it is written to the HOLD.CONTROL table. When up to date messages are required for the customer, it can be printed using the PRINT.CUST.OUTPUT application.
A multi-value Address field is available in DE.ADDRESS. When the customer’s main address is updated, the DE.ADDRESS PRINT.1 record is updated by copying the address lines from the CUSTOMER record to the DE.ADDRESS PRINT.1 record. For all other DE.ADDRESS records, the Address multi-value field is manually inputted.
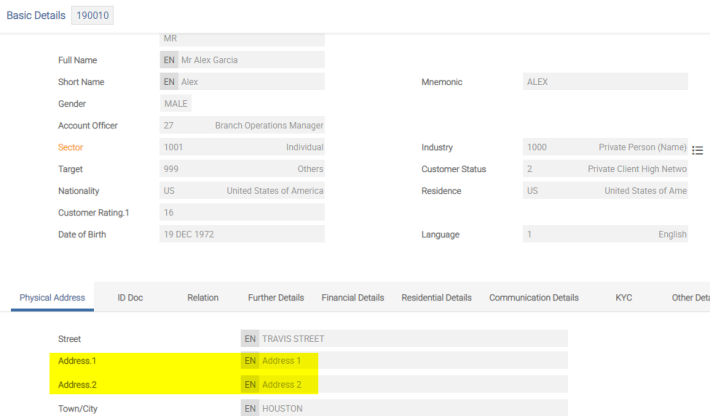
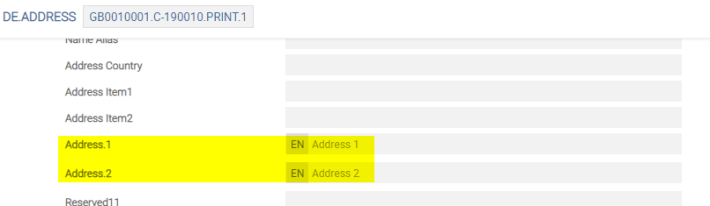
Additional address line details are added using the following fields:
- The Address Type field identifies the nature of the postal address (that is, the postal office (PO) box, home). These values are defined in the EB.LOOKUP application.
- The Address Purpose field represents the purpose of an address (that is, communication to customer, communication to in care of party)
- The Building Number field represents the number that identifies the position of a building in the street.
- The Building Name field identifies the name of the building and entrance.
- The Flat Number field represents the number that identifies the apartment and unit that have other dwellings above or below, often with shared access and common areas.
- The Po Box Number field identifies PO box number.
- The Country Subdivision field identifies a subdivision of a country, such as, state, region or county.
- The Title field holds the title for the customer name.
- The Salutation field represents the greeting used for communication with the customer.
- The Address Validated By field represents the party or service, which confirms that it is a valid or real address.
- The Idd Prefix Phone field represents an international call prefix or dial out code.
As the priority of a message can only be N, the DE.DISP.CONTROL application is used to change the status of a message. Disposition checks are done after the carrier is identified at the transaction level itself. If the messages are marked as HOLD or DELETE or REROUTE, the appropriate applications are updated as mentioned below:
- If HOLD, the DE.O.HOLD.KEY application is updated.
- If DELETE, the DE.O.HEADER is deleted.
- If REROUTE, the message is put into the DE.ALTERNATE application.
On releasing the DE.O.HEADER from HOLD, the held records are moved into the appropriate carrier activation applications. The DE.DISP.TIMECHECK service process the messages marked as HOLD until a particular time.
The DE.DISP.CONTROL application is used to specify special conditions for which particular processing is required. If the conditions are satisfied, the requirements specified in DE.DISP.CONTROL overrides all other the requirements. The only condition is that, it cannot override restrictions such as deleting messages for message types, which cannot be deleted (that is, Delete field in DE.MESSAGE application is set to NO) or the copies of messages being generated for message types that do not allow copies (Copies field in the DE.MESSAGE application is set to NO).
The DE.DISP.CONTROL application can be used in the following scenarios:
- All messages for a particular carrier must be rerouted (the DE.ALTERNATE application is accessed to find the new carrier).
- Print a copy of all messages, which have a message type of 100 and for Customer 254 or 256.
The above is achieved by setting up the conditions on which the message status is set. Alternatively, a user-defined routine can be specified to check complex conditions, the routine passes back whether the conditions were matched or not. The routine name is placed in the Field Name field and must be prefixed by @ character. The routine is passed with the current DE.O.HEADER record in argument one, the OPERAND in argument two and the CONDITION in argument three.
The return argument is argument four and should evaluate to true (1) or false (0 or null). The routine should be specified as EXAMPLE.NAME (HEADER.REC, OPERAND, CONDITION, RETURN.FLAG).
Records are added to the DE.DISP.CONTROL application with a numeric ID. When the transaction is entered and passes the formatting stage, DE.DISP.CONTROL application is examined in numerical order until a record is found with satisfying conditions or until no further records are found in the DE.DISP.CONTROL application. Thus, if a message matches the conditions specified in DE.DISP.CONTROL records 10 and 50, only record 10 will be applied to the message. Therefore, it is important to be cautious when entering records in the DE.DISP.CONTROL application, to assign the ID according to the importance of the record.
Conditions can be specified in the DE.DISP.CONTROL record to compare the fields in the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records to certain values.
In the DE.DISP.CONTROL application, the messages that match the conditions specified can be updated with specific status. This is entered in the Status field and the field can be set as:
- HOLD
- HOLD hh:mm
- WAIT hh:mm
- RELEASE
- DELETE
- RESUBMIT
- REROUTE or
The HOLD status can also be used with the Hold Until Date field, by either specifying an exact date or entering VAL to set the hold date according the days’ delivery for the currency.
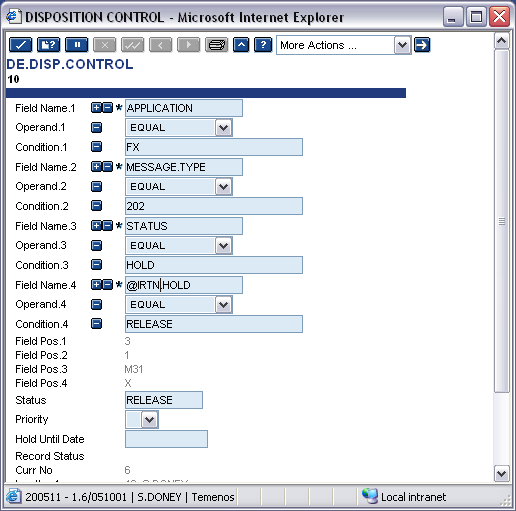
When a new or amended DE.DISP.CONTROL record is authorised, the Msg Disposition or Msg Status field in the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records for each message that has been successfully formatted but not sent (messages not in the repair queue) is amended, if the information in the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records match the conditions defined in that DE.DISP.CONTROL record. This involves examining numerous queues and application in the delivery system and could take some considerable time.
However, if the Delivery Operator does not require the DE.DISP.CONTROL record to be applied to messages already formatted, but only requires them to be applied to newly generated messages, the Disposition Control field in the DE.PARM application can be set to N before the DE.DISP.CONTROL record is authorised, then it must be reset to Y after the record is authorised.
The DE.DISP.CONTROL records are also applied to messages that are created by the delivery system during formatting, unless the Disposition Control field in DE.PARM is set to N. The following status affects the records with a disposition of Formatted:
- HOLD
- WAIT
- DELETE
- RESUBMIT
- REROUTE
They operate subsequently while formatting the records that are set to Formatted. The WAIT hh:mm status is translated to HOLD hh:mm, when the DE.DISP.CONTROL record is applied.
The RELEASE status affects the records in HOLD status and operates subsequently during formatting. The PRINT status prints an image of the formatted messages, regardless of the carrier used to send the message. It produces a printed copy of a SWIFT message (if the message was originally sent by SWIFT). If the original message was sent out by print, the image has ’** COPY ** COPY ** COPY **’ printed at the bottom of each.
Each DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records that is changed has the ID of the DE.DISP.CONTROL record, placed in the appropriate Disposition No field in the each copy of message affected. This ensures a less important DE.DISP.CONTROL record which does not subsequently change it. Records with lower IDs take precedence over higher IDs, for example, 10 takes precedence over 100.
The record should be reversed when the conditions no longer apply. Run the DE.DISP.CONTROL application using the DE.DISP.TIMECHECK record in TSA.SERVICE.
The DE.INTERFACE application contains the details of the protocols for all interfaces which use the Generic Delivery interface. The protocols for interfaces written prior to the introduction of the Generic Delivery interface are either stored in DE.PARM or are hard-coded in the program. The sequence numbers for existing interfaces are stored in the F.LOCKING application. This application need not be amended unless a new interface is being developed.
Minimum validations are done in the fields of the DE.INTERFACE application. This is to allow maximum flexibility when new interfaces are written. The ID of the application is the interface, as defined in the Interface field in the DE.CARRIER application.
Archival of Delivery Messages
The Delivery messages can be archived using the Transact Standard archival or Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) archival.
The DL module must be installed for the user to initiate the archival service to archive the delivery messages to a Read-only (RO) database. Otherwise, the user moves the data records to the $ARC file using the Standard archival method. The user defines Retention Period in ARCHIVE for the DELIVERY.IN and DELIVERY.OUT records for the inward delivery messages and outward delivery messages, respectively. If the delivery message date in DE.I.HEADER (for Inward message) and DE.O.HEADER (for Outward message) cross Retention Period, it is archived.
The user must execute the following services as a pre-requisite for initiating the generic archival service to archive the delivery message in the Transact Standard archival process.
| Services | Description |
|---|---|
| DE.EOP.INWARD and DE.EOP.OUTWARD | These services analyse the DE.O.HEADER and DE.I.HEADER entries respectively to identify the records that are processed completely. These services select the DE.I.HEADER and DE.O.HEADER records, moving the records from DE.I.HEADER to DE.I.HEADER.ARCH and DE.O.HEADER to DE.O.HEADER.ARCH respectively. |
| DE.MM.CLEAR.HANDOFF | This service deletes the DE.O.HANDOFF records where DE.O.HEADER is previously removed. This service selects all the DE.O.HANDOFF records to identify the records to be deleted. |
| Delivery Inward and Delivery Outward Archiving | These services archive the records from DE.I.HEADER.ARCH and DE.O.HEADER.ARCH respectively along with related table records.
|
However, when the DL module is installed, the DLM archival processing logic consolidates the processing performed by the pre-requisite services mentioned above. The generic archival service execution is sufficient to perform the delivery archival based on the DELIVERY.IN and DELIVERY.OUT records configured in ARCHIVE.
Sample screenshots of the ARCHIVE application for the delivery messages are shown below.
ARCHIVE> DELIVERY.INARCHIVE> DELIVERY.OUT


When Retention Period ends and the user runs the archival service, the files mentioned in Arc Filename are archived.
Read Archiving for more details regarding Transact Standard archival process. Read Data Life Cycle Management for more details regarding DLM Archiving process.
Illustration Model Parameters
This section covers the Model Parameters required for the Delivery module.
| S.No | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tracker Status Reason
|
Allows users to define the status code and status reason which is used to update the status of the incoming MT103 payment in the SWIFT Confirmation tracker. |
| 2. | DE.MESSAGE.HEADER
|
Allows users to define the message headers, which are used for various type of messages. For each header, it stores the version, set of Business and Generic Metadata, which must be pushed as part of the data event with the payload. |
| 3. | DE.BUSINESS.SERVICE.RULES
|
Allows users to create business service rules for delivery messages based on domain, message name id, business application, application context field, application context value, start date, end date, business service and status. When a Delivery Message is handed off to Delivery, it considers the supplied value if the Business Application supplies the Business Service. Otherwise, it determines the Business Service based on the DE.BUSINESS.SERVICE.RULES application setup. |
| 4. | DE.DELIVERY.RESPONSES
|
Stores the incoming replies received for the outward interact MX messages (Ack/Nack/DLN) sent through delivery. It is possible to store other replies sent by other bank systems, which are acting as an intermediary systems before the messages sent to SWIFT network. |
| 5. | DE.DLN.REQUIREMENTS
|
Allows the bank to define the rules to request a positive or overdue delivery notification. In this way, the bank has the option to request a positive delivery notification and overdue warning (Optional). It is not possible to request only overdue warning. |
| 6. | DE.ALT.CHARS
|
This table helps to parameterise the alternate characters (defined in ASCII.VAL.TABLE) for the local unsupported characters. Various rules are defined to replace the alt chars based on the position of the unsupported character in the message string. A default alternate character is defined if alternate character is not defined for an unsupported character. |
| 7. | DE.MSG.CHARS.RULE
|
This parameter table defines the character set rules for each carrier and message type. |
Illustration Model Products
Model Products are not applicable for this module.
In this topic