Introduction to Forex
ⓘContent enriched:New structure and revised (Docs 2.0)
The Foreign Exchange (FX) module is designed to meet the needs of dealing operations in the Foreign Exchange Market.
The module offers comprehensive treasury solution starting from the deal capture in the front office to deal processing in back office, covering a wide range of FX products. The module covers entire deal life cycle of FX transactions including features such as recording of limited orders, online limit checking, position updating, revaluation of positions, accounting, brokerage, generation of SWIFT confirmations, payments and print advices. In addition, the module also helps generate reports for audit and risk management.
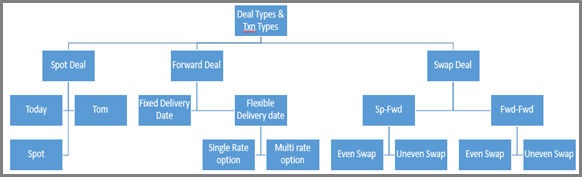
The above image illustrates spot, forward and swap deal types and its associated transaction types supported by the system, which caters to the business needs of Treasury.
Using FX module, a dealer can directly input a deal in the system with key elements, such as currencies, amount, rate, value date and counter-party. This avoids the need for hand-written deal tickets and ensures the real-time update of positions and risk, that is, counterparty’s liability or exposure, exchange position and daily foreign exchange movements reflects the dealer’s system inputted deal.
All elements of FX transactions have default values, except the key information that the dealer provides. Thus, for any given counterparty, payment methods and instructions are loaded automatically from user definable tables. If required, the back office user can confirm or exceptionally amend the deals.
The ability to arrive at intelligent defaults also has another benefit. For example, in a swap, all the default information on the second leg is derived from the first leg. Thus, dealer’s input of information is reduced to the minimum.
After the dealer provides their inputs, the deal slips are printed for the back-office. At the authorisation stage, the system invokes the following:
- Generating and delivering confirmations
- Passing any accounting entries such as brokerage, commissions and charges, and issue of any required pay or receive instructions
Otherwise, there are overnight processes that involve eventual settlement, revaluation and accruals, and exception or maturity reporting.
The FX application is supplied with initial input of the contract details with a few of them requiring any changes during remaining life cycle. Such changes, if any, are generally limited to settlement related. The brokerage calculation and processing of brokerage is handled by using BROKER application.
Product Configuration
This section describes the configuration options the system offers in FX.
FX Build Sequence
Implementation of FX module begins with configuration of various parameter tables.
The following list of files are required for FX main setup, and the mandatory files are suffixed with an *. The dependency tables are marked and stated alongside the parameter tables in their build sequence.
Illustrating Model Parameters
The model parameters consists of the following:
| S.No | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | FX.PARAMETERS
|
The rules that determined the Foreign Exchange (FX) transactions are defined in the following files:
|
| 2 | FX.POS.TYPE
|
Assigns profit centre to the trading position, which can be amended as desired. |
| 3 | FX.TRANSACTION.TYPE
|
Classifies the deal types. A record in this application can control the default value for category codes, revaluation types, and allows delivery and types of options processing. The existing records can be amended and new records can be created. |
| 4 | FX.GEN.CONDITION
|
Identifies a specific group of customers, which can be cross-related to the group condition table, to define conditions applicable to that group. The groups are determined based on customer details such as sector and target. The criteria used and their priority are specified in the Condition Priority file in the record whose ID is FX.MARGIN. |
| 5 | FX.GROUP.CONDITION
|
Defines the spread or margin percentage for a specific customer, group of customers or default group. When a group customer is defined, the FX Gen Condition record needs to exist before any associated group condition is specified. For an individual customer, the ID is C<Customer ID>, whereas, the default group ID is generally assigned as either 99 or 999. |
| 6 | FX.COMM.GROUP
|
Defines spread or margin based on currency, and the amount that falls in a range and is used in FX contracts. The FX Commission Group ID field in SAM is used in FX.BULK.ORDER application, and a reference to SAM is used in FX.GROUP.CONDITION. Hence, the margin is given in absolute terms or referred to FX Commission Group ID (based on which the margin is applied in an FX deal).
|
Illustrating Model Products
The following products are available in the FX module:
| S.No | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | FX Spot | FX Spot is a contract of buying or selling a currency, commodity or security for immediate settlement (payment and delivery) on the spot date at a spot Rprice. |
| 2 | FX Forward | FX Forward is a contract of buying and selling an asset or a currency at a predetermined spot rate at a specified date in the future (which is greater than the spot date). The predetermined rate is called as the Forward Rate. |
| 3 | FX Swap | FX Swap is an agreement between counterparties to exchange currency. The agreement involves swapping of principal and interest payments between two different currencies. |
| 4 | Precious Metal Deal | Precious Metal Deals involve trading in various precious metals such as gold, silver, palladium, platinum and so on, in spot, forward or swap rates depending on the types of deals entered. |
| 5 | Single-rate Option | Single-Rate Option is the deal of exchanging one currency for another. The delivery takes place between two specified dates at customer’s choice without incurring any penalty cost. The option occurs when the customer decides to take delivery of all or part of the transaction before the final value date. |
| 6 | Multi-rate Option | Multi-rate Option is the deal of exchanging one currency for another. The delivery takes place between two different option dates with different rates. The option occurs when the customer decides to take delivery of all or part of the transaction before the final value date. In this, the applied rate depends on the period delivery. |
| 7 | Internal Deals | Internal Deals allow transfers between different positions or dealer desks. Hence, there is no need for accounting entries, payments, advices and so on. The system automatically updates the position, when an internal forex spot or a forward deal is entered. |
| 8 | Broker Deal | Broker Deals are entered when the counterparty is not known. The user needs to enter BR as sub-type and associated brokers deals. Once the counterparty name is known, BR is removed and the counterparty details are entered in the deal. |
| 9 | NDF Vanilla Deal | Non Deliverable Forward (NDF) Vanilla Deals is an hedging strategy, where parties in the contract agree to settle the profit or loss prior to the expiration date of the contract. A vanilla NDF transaction has an agreed rate fixing date, which is two working days before the settlement date. |
| 10 | NDF Exotic Deal | An Exotic NDF Deal allows in setting the fixing date as any date before the vanilla date in the tenure of the transaction. The fixing profit is discounted, if the NDF is fixed and settled early. The discount amount is amortised from the settlement date to the value date of the NDF. |
In this topic