The following set of files are required to setup Forex (FX):
Account Class
The following list of records require inputs in ACCOUNT.CLASS:
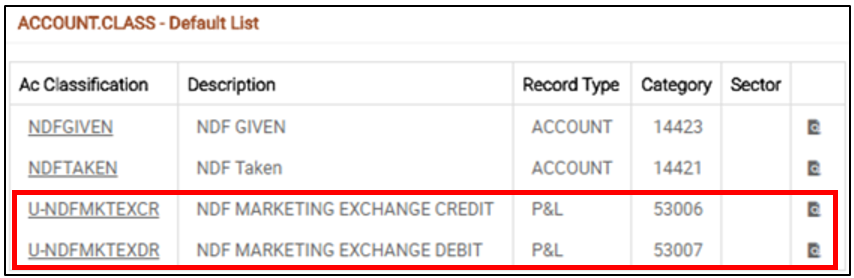
- FXCCYPOS, EXCHADJ, RESFWDCR, RESFWDDR, RESSWAPCR, RESSWAPDR, SUSPFXDR, SUSPFXCR (Suspense accounts used for settlement)
- NETTING (Suspense account for netting)
- BROKER (Suspense account for non-account holder)
- MARKETING (Suspense account for marketing exchange profit)
A sample record in ACCOUNT.CLASS table for SUSPFXDR.
FX Parameter Tables
The FX module supports confirmations, payments, charges, commissions, advices, account entries and updates positions real time. The detailed action that the module takes for a particular FX deal is defined in a series of user-controlled tables.
The following tables are set up to support the entire life cycle of an FX deal:
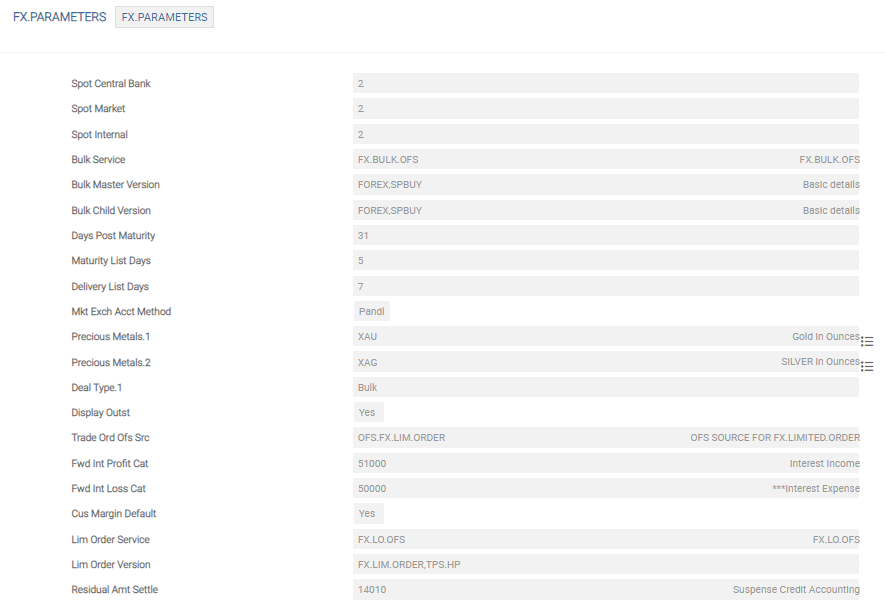
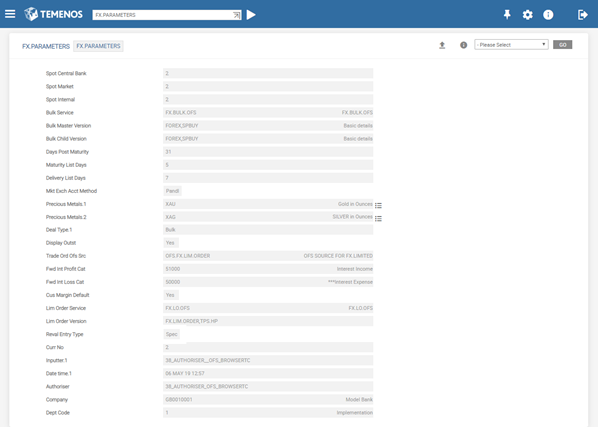
FX.PARAMETERS
The following table describes the mandatory and key fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Spot Central | Local central bank’s rule for the classification of FX transactions between spot and forward. Values are in days. |
| Spot Market | Market practice for the classification of FX transactions between spot and forward. Values are in days. |
| Spot Internal | Bank’s internal rule for the classification of FX transactions between spot and forward. Values are in days. |
| Mkt Exch Acct Method | Determines the accounting of marketing exchange generated from FX transaction. The accounting can either be by posting Internal Suspense account, and Profit and Loss (internal method) or two Profit and Loss entries with DAO of Treasury and Customer, respectively (P and L method). |
| Precious Metal | Defines the currency codes that are considered as precious metals. |
| Cus Margin Default | Determines the default margin automatically applicable to a customer in a FX deal to arrive at the customer rate. |
| Reval Entry Type | Defines whether to use RE.CONSOL.SPEC.ENTRY or STMT.ENTRY methodology for posting revaluation and accrual accounting entries. |
This table defines the parameters that determines the rules by which the system operates.
Classification of the contracts between spot and forward is dependent on the local central bank and internal reporting rules.
- Definition of the spot default value date.
- Definition of
OFS.SOURCEand versions used for inputting Bulk Orders. - Definition of product and profit or loss categories for neutralisation of forward interest.
- Definition of alternative FX trading holidays.
- Definition of currencies, which is used in all spot date calculations.
- Option to default customer margin rates at contract input level.
- Method opted for marketing exchange profit accounting.
FX.TRANSACTION.TYPE
The FX.TRANSACTION.TYPE table defines parameters for processing different transaction types of FX deals. Configuring transaction types makes the deal capturing process easier, as the details are defaulted from the respective transaction type record defined (such as SP, FW and SW deal types). Hence, any further transaction types to differentiate with in SP, FW or SW needs to have the transaction types of the form SWxx, FWxx or SWxx.
The Activity Code field relates to the codes in FX.ACTIVITY acts as triggers for the associated message types and formats. These are used with multi-rate option deals, which require elaborate confirmations. The other fields describe the rules that needs to be applied to the transaction type. The Transaction Type in the FX record fetches the input automatically using VERSION in operation.
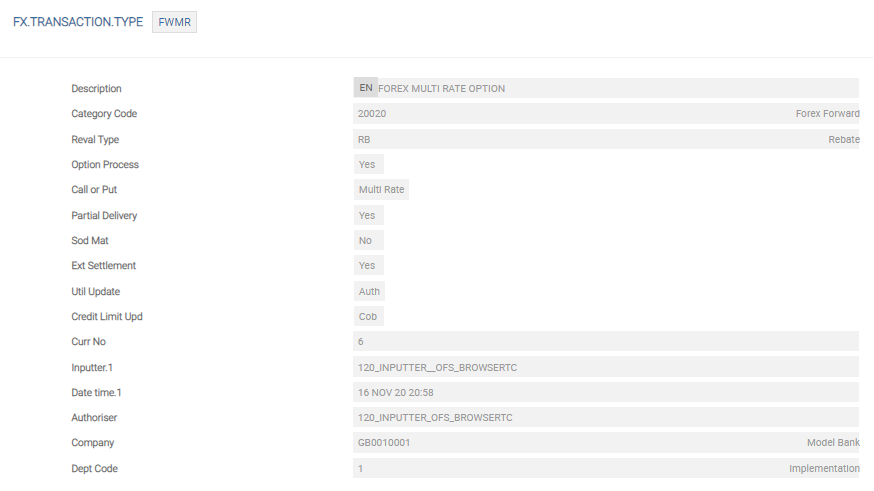
The following table describes the fields in FX.TRANSACTION.TYPE table:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Reval Type | Specifies the revaluation method that can be used for the deal type specified. |
| Max Duration | Specifies a maximum number of days for which a FX option deal can be defined, after which an override is required for entering the deal. |
| Option Type | Specifies whether the deal type is a Single or Multi-rate option. |
| Allow Partial Delv | When set to Yes, partial delivery information can be specified for this particular deal type of FX contract. This is available only with multi-rate options. |
The Transaction Type field defaults to the value of the Deal Type besides other values such as Category Code, Reval Type and SOD Maturity. The VERSION used to input a deal with particular transaction type, needs to default the value in Transaction Type.
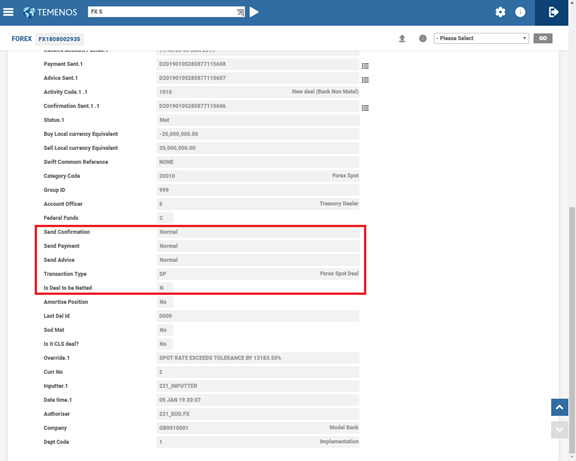
FX.REVAL.TYPE
Using different revaluation methods, the FX deals can raise revaluation of positions. The revaluation types available in the FX application is defined in the FX.REVAL.TYPE table. The system caters for the following different revaluation methods:
This is a straightforward method, which is based (similar to spot revaluation) on the cost or profit attributable to close the position that is, to enter into a deal at today's rates to cover each deal at its maturity (buy back approach).
In forward deals, the rate varies not only because of a change in the market factors (demand and supply) but also over time. The rate to cover forward deals converges with spot rate over time, that is, closer to maturity, until it is eventually covered at spot rate.
- Interpolation
- Next available rate
- Rate at closest date
Interpolation of FX Rates
- The user can define the rates in
FORWARD.RATEStable for any period required.
- The forward rates applied for actual date = Reporting date + 2 working days + number of months
- If this date is not a working day, then the next working day is used.
- When a rate is required for a date that falls between the dates of two rates on the table, then it is calculated by linear interpolation.
If a yield on GBP is 12%, which is on USD is 14% with a spot rate of 1.25. Then, in 12 months
- GBP 1000 would yield GBP 120 interest.
Similarly, if exchanged (@1.25)
- USD 1250 would yield USD 175 interest.
Thus, in order not to sustain a loss, the 12 months forward USD sell rate should be USD 1425/GBP1120 or 1.2723, that is,
- USD 1425 / 1.2723 = GBP 1120
In practice, one of the amounts on the forward deal is held at the same value as for the spot deal. So, in this example, if the forward deal is also for GBP 1000 the USD amount is USD 1275, which is, USD 1250 plus 2% interest differential thereon of USD 25.
Therefore, the discount on the forward USD 12 months rate is to offset the 2% USD interest premium prevailing at the time of the deal. This exchange of profit or loss is accrued over the life cycle of the forward deal, that is, the straight line method, except the profit and loss interest entries are now booked for both the currency bought (credit to Interest Received Exchange) and sold (debit to Interest Paid Exchange).
Using the Same Example
A loan of USD 1250 yields USD 175 in 12 months. In the same time, a debit (revaluation) accrual is made of USD 25 (that is, USD 1250 * 2%). Thus the net result is interest received of USD 150.
As proof that this is correct, GBP 1000 at 12% would have given rise to GBP 120 interest, which converted at spot of 1.25 is also USD 150.
The effect of this accrual (to discount the forward premium or discount) is to value the position at spot rate, therefore, it is necessary to perform spot revaluation every day.
This method is appropriate for swap transaction type, where an actual loan and deposit is booked with a spot and forward deal and real interest rates are used on the forward leg. Hence, to render the deal entirely neutral, that is, the forward accrual eliminates the difference between interest paid and received and the spot deal is cancelled (as the effect of spot revaluation of the forward leg).
As mentioned above, there is a difference between spot and forward rates. In this method, the difference is the amount in local currency is isolated as profit or loss at the start of the contract and then amortised over the life cycle of the deal as a daily accrual between the appropriate interest profit and loss category code (Interest Paid Exchange or Interest Received Exchange) and the exchange reserve adjustment account.
The following ACCOUNT.CLASS records are used to obtain the internal account category:
| RESFWDCR | Forward deals credit |
| RESFWDDR | Forward deals debit |
| RESSWAPCR | Swap deals credit |
| RESSWAPDR | Swap deals debit |
Effectively this deal is now being carried at spot rate (since the forward discount or premium is being accrued) and therefore, it is necessary to revalue this every day as if it was a spot deal (by using the technique described in spot revaluation). The rate at which it is re-valued is the Reval Rate (if specified on the CURRENCY table), otherwise uses Mid Reval Rate.
This method is primarily for the swap contract type and similar to the SL method except that the premium or discount of a swap is amortised over the contract period in the currency in which the premium or discount arises (that is, the currency, which differs in amount between the legs of the deal).
Similar to interest method, the revaluation type considers the difference in the interest yields of the contract currencies. However, the interest calculation of interest or hedge method is not based on the contractual amounts of the deal but on a notional principal amount on each side (buy and sell).
The notional principal amount is the present value (PV) of the contractual amounts. In other words, the notional principal amount, when applied the interest rates applicable to each currency of the contract, yields the contractual amounts of the deal over the contract term. This means, the deal amounts are effectively split into a principal and interest element and it is this interest element, which is accrued on each side of the deal over its life.
The difference between the interest and interest or hedged methods are illustrated below:
In all cases, the USD interest rate is 14% and GBP interest rate is 12%. The spot rate of exchange between the two currencies is 1.25. The forward rates refer to 12 months forward contract.
- 1 – Illustrates the figures that are described in the interest method of revaluation.
- 2 – Shows a similar deal by using the interest or hedged method.
- 3 – Compares the results of trading a round GBP deal amount, method IH, against the original example, method IN.
| Revaluation Type | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IN | IH | IH | |
| USD Principal | N/A | 1,250 | 1,116 |
| GBP Principal | N/A | 1,000 | 893 |
| USD Interest yield | 178.5 | 175 | 156 |
| GBP I5nterest Yield | 120 | 120 | 107 |
| USD Deal Amount | 1,275 | 1,425 | 1,272 |
| GBP Deal Amount | 1,000 | 1,120 | 1,000 |
| USD/GBP Forward Rate | 1.275 | 1.2723 | 1.2723 |
This method of calculating interest yields associated, with a forward contract is appropriate to a hedging situation where a forward foreign exchange deal is made in cover of balance sheet items.
Since the notional principal amounts correspond to an actual spot transaction and are not the same as the resultant forward contract amounts, this revaluation type is not available for use on first leg of the swap contracts, if the swap is a SP-FWD.
DEALER.DESK
The DEALER.DESK table allows the bank to specify to the system how their dealing room activity is organised.
POSITION file. This enables the bank to view their currency position by dealer desk (if required), and book the revaluation Profit or Loss at dealer desk level.
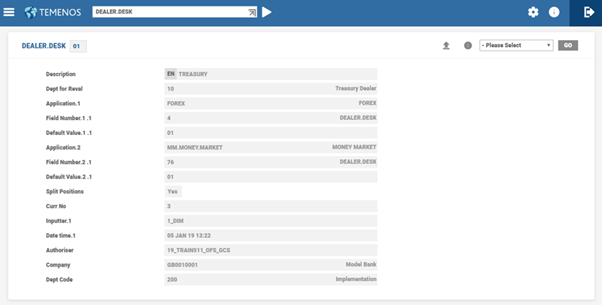
The following table describes the fields in DEALER.DESK table:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Dept. for Reval | Identifies the department to which profits or losses have to be allocated for this dealer desk. This field is used during the revaluation process. |
| Cr. Reval Categ | Category code to hold PL Category for Asset and Liability Credit revaluation. |
| Dr. Reval Categ | Category code to hold PL Category for Asset and Liability Debit revaluation. |
| Split Positions | For FX transactions in cross currencies, the position records are generated online. On the value date, these records are split and position records are created for buy or sell currency against local currency. |
BROKER
The BROKER table allows the bank to identify its authorised brokers.
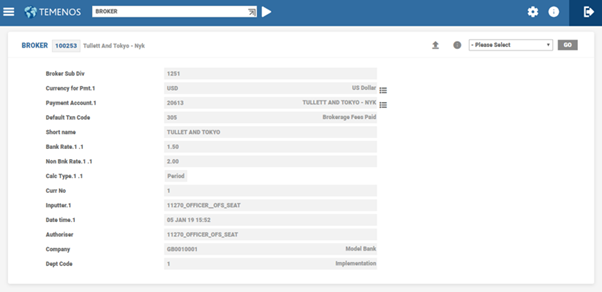
The following table describes the fields in BROKER table:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Ccy For Payment | Identifies the valid currencies for payment allowed for the broker. |
| Payment Account | Account in which the funds needs to be paid to the broker. |
| Bank Rate | Rate used for brokerage calculations, if the customer of the deal is a bank type customer. |
| Non-Bank Rate | Rate used for brokerage calculations, if the customer of the deal is a non-bank type customer. |
| Calc Type | Defines whether the brokerage calculation is Fixed or Period or Present value basis. |
The bank pays a brokerage to the brokers, when deals in interbank are done by them. The BROKER table allows definition of the brokerage payable based on amounts and period or tenor of the deals undertaken.
FX.DEAL.METHOD
FX deals are initiated in multiple ways. It can be through an intermediary such as a broker (defined in BROKER table) or other means such as Reuters or Bloomberg dealing systems, telex or telephone. The FX.DEAL.METHOD table allows the users to define which deal methods are applicable and to use this information on advices.
FORWARD.RATES
The FORWARD.RATES table stores the forward premium or discount Pips for a currency against local currency and by market. It can also store the premium or discount for ON (overnight) and TN (Tomorrow next), which are useful in deriving today’s and tomorrow’s rate. These are denoted by a negative sign before the value in the Rest Date field, that is, -2 and -1. Forward periods are defined either in days (7, 15 and 30) or months (1, 2, 3, and 12 ). Premium is denoted with no sign while the discount is denoted by a minus or negative sign.
The system refers to this table during revaluation of forward contracts with RB method and in case of tolerance check while inputting a deal. In both the cases, the forward rate derived by system consists of mid-reval rate or reval rate from CURRENCY record together with the premium or discount from this table.
The FORWARD.RATES table is used for forward revaluation (Rebate Method) and also for the purpose of tolerance checks, on input of a forward FX transaction.
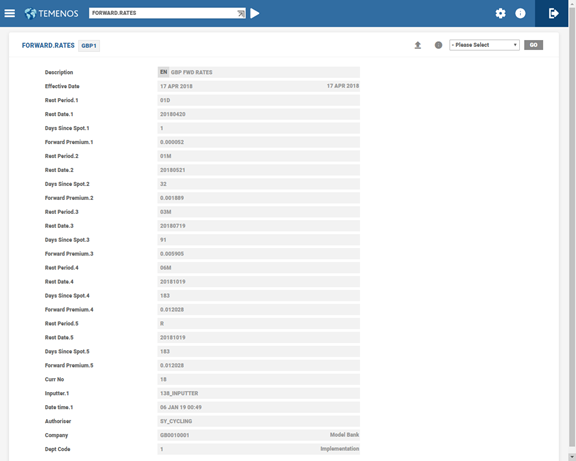
The rest date calculation is based on the holiday set up of the local and other country currencies. However, if the system has to calculate the rest date with some other country’s holiday set-up, instead of local country, then is done using the ST.RATE.PARAMETER table.
Rest date calculation is from the spot date, which is unlike the PERIODIC.INTREST table, where it starts from the system date.
FX.TEXT
The FX.TEXT is a table of advice texts that are printed on advices or confirmations when settlement information for a counterparty is not known. It is used where the counterparty has not specified settlement details and entries are posted to an internal account (if the settlement details are not completed by the value date).
There are nine options in the table, which has unique text printed on the advice confirmation. The user chooses the text to be printed by keying a number between 1 and 9 at the appropriate account field when loading a contract.
One record is used for payments (credits) and other for receipts (debits). Each may be posted to the same or different suspense accounts (as defined in ACCOUNT.CLASS) by currency. Accordingly, use of text 1 defaults a different advice text if used in both the buy and sell account fields.
Based on what text message needs to populate in the SWIFT deal confirmation message, the user selects a value from 1 to 9, while the suspense account 14205 defaults in Setlmnt A/c for Ccy Buy field.
In this topic