Introduction to Interest and Charges
Traditionally, interest and charges are the main sources of income and expense for a retail bank. Interest includes the cost of borrowing funds and the income that accrues to those who deposit funds in a savings account. Interest is calculated as a percentage of the loan or deposit balance, which is paid to the lender by the borrower in the case of a loan and from the financial institution to the depositor in the case of a savings account.
Charge levied is another source of income. A charge is a fee charged for a service provided. For example, arrangement fee for arranging a loan.
Temenos Transact Transact enables locally developed charges and commission to be set-up. It is a collection of a host of individual facilities that a user can use to collect various types of charges.
- It allows different capitalisation frequency to be configured. Frequency for each charge can be set to monthly, quarterly, half yearly or yearly.
- Taxes can be applied on these charges.
- Charges created through generic charge functionality can be set at a group and currency level, or at an account level.
- Interim capitalisation can also be specified for these charges.
Interest and charges are accrued or amortised and capitalised at regular intervals and charged to the bank’s customer account in case of income and paid to bank’s customer account in case of expense.
Accrual – Accrual is the amount of interest earned on a lending, but not yet received. This is also known as interest receivable. Conversely, for deposits, it is an amount of interest that needs to be paid but not yet paid. Also known as interest payable.
Amortisation – Interest can be collected up-front (for example, on a discounted debt instrument where the amount given to customer is less than the face value of the instrument, the difference between accrual and amortization is, with amortisation, interest income is collected upfront) and recognised to P&L over the life of the debt instrument. Charges can be accrued or amortised.
Capitalisation – Capitalisation is when the receivable interest/charge is actually received and the payable interest/charge is actually paid.
The Account module is controlled by high-level grouping conditions. These grouping conditions are used for calculating Interest and Charges.
The system has the flexibility to allow users to apply interest and charges at group level using the grouping conditions or apply interest and charges rules at individual account level.
Components Used in the Calculation of Interest
This section describes the types of calculations and components used in the calculation of interest.
Calculation Type – There are two basic kinds of interest calculation:
- Simple Interest (or flat-rate interest) is calculated as a percentage of a deposit or loan’s principal balance. Interest will be calculated on the original amount, irrespective of how long a depositor keeps money in the bank or a borrower does not repay a debt.
- Compound interest is calculated when interest is added to the principal, thus increasing the principal balance on which interest rate applied. Consider compounding as interest on interest.
Day Basis – Interest is calculated on a day-count convention. The day count convention determines how interest accrues over time. It is often due and payable at shorter intervals, usually a number of months (the interest period). The day count (or 'daycount') convention regulates how the parties calculate the amount of interest payable at the end of each interest or other specific period.
It is commonly expressed as a fraction, for example, 30/365. The numerator will be the convention for the number of days in the period - usually actual or a notional 30. The denominator is the convention for the number of days in the reference period, often annual expressed as 360 or 365 days.
Conventions vary depending on the market type, location and the currency in question. For example, euro-denominated bonds are usually calculated on an actual/actual basis, while fixed rate non-euro denominated bonds are often calculated on a 30/360 basis. The London interbank market, on the other hand, operates on the basis of actual/360, except where the currency is sterling, for which the London interbank convention is actual/365 fixed.
Interest Rate – The interest rate is the rate a bank or other lender charges to borrow its money, or the rate a bank pays its savers for keeping money in an account. The interest rate is typically noted on an annual basis known as the annual percentage rate (APR).
Interest can be fixed or variable and may depend upon a base rate on which an interest spread is added.
Types of Interest Rates – Interest rates can be fixed or variable. Variable is also called floating and is based on a base rate of the jurisdiction the bank is based in. Base rates are normally set by the central bank of each country.
Additionally, a periodic interest rate can be charged on a loan or investment over a specific period of time. Lenders typically quote interest rates on an annual basis but the interest compounds more frequently than annually in most cases. The periodic interest rate is the annual interest rate divided by the number of compounding periods.
Product Configuration
This section covers the product configuration of Interest and Charges.
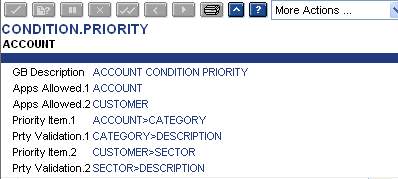
CONDITION.PRIORITY
This application defines the fields from CUSTOMER and ACCOUNT applications to be used for setting various group conditions.
Bank has to decide the criteria required for use (In CONDITION.PRIORITY), particularly for ACCOUNT conditions.
Read Condition Priority in System Tables User Guide for more details.
The following screenshot shows the CONDITON.PRIORITY application.
ACCT.GEN.CONDITION
This application is used to define rules that can be applied to a group of accounts as classified by the bank. For example, a special interest rate is applied to all accounts held by customers under the age of 18 years. This application uses the high-level conditions defined in the CONDITION.PRIORITY application.
Account groups are determined based on customer and account details. The priority data items from CUSTOMER and ACCOUNT applications are specified in the CONDITION.PRIORITY application in the ACCOUNT record. The priority data items which are used in the ACCT.GEN.CONDITION records, are defaulted from the ACCOUNT record in CONDITION.PRIORITY.
Read Parameters and Rules for Groups in System Tables User Guide for more details on XXX.GEN.CONDITION application.
Each general condition record specifies the combination of field values to define one account group. The record ID of the general condition is referred in other parts of the system as the condition group.
Before an account can be opened, a suitable general condition record must exist in order to determine the group to which the account belongs. Also, a capitalisation frequency record, debit and credit interest conditions (in the currency of the account) for that group must be defined.
Whenever an ACCOUNT record is updated, a condition group value is recalculated according to the details held in this table. Amending a record in ACCOUNT or CUSTOMER may result in new interest conditions being applied and possibly an adjustment to interest previously calculated.
If the details of an account match to more than one general condition record, the priority order is used to determine the group. (The higher priority field takes precedence. Priority 1 is the highest priority.)
An overall default condition (no value specified in any field) must be the first record loaded in ACCT.GEN.CONDITION.
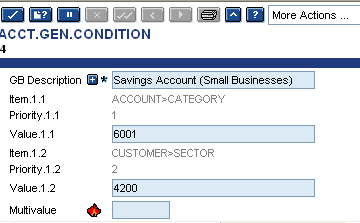
The following screenshot illustrates that the group number four (4) (Savings Account (Small Business)) is defined as any account opened in the system with a category code of 6001, having a customer number whose sector code is 4200.
A base rate is the interest rate that a central bank, such as, the Bank of England or Federal Reserve will charge commercial banks for loans. The base rate is also known as the bank rate or the base interest rate. Floating rate can be derived from a base rate by adding a spread to the base rate.
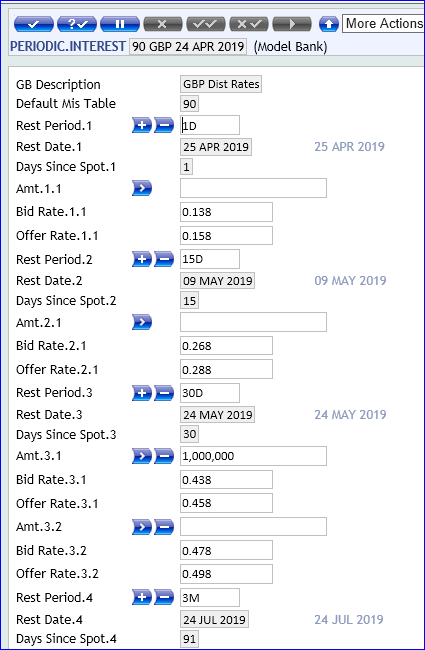
BASIC.INTEREST table allows various frequently used interest Rates, for example, Base Rate, Prime Rate, Overnight Rate and so on, to be defined separately for each currency and stored in a central place where Temenos Transact applications as can access them whenever required.
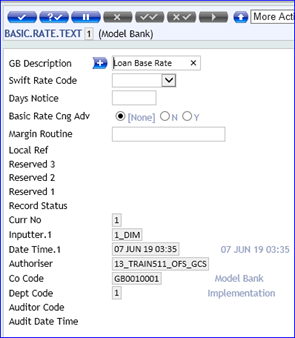
Description for each rate is held in the BASIC.RATE.TEXT table to allow the user to easily identify each ID of the Basic Interest Rate table. For this reason, a description is not included in the input parameters of this table. The BASIC.RATE.TEXT table of descriptions must be defined before creating this table.
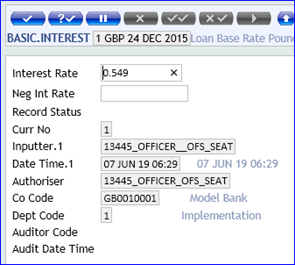
This table defines interest rate for each currency for any time period desired by the user. These periods can be defined either in:
- Months, for example, 1 month, 2 months, 3 months, 6 months and so on.
- Days, for example, 7 days, 15 days, 30 days and so on.
For each period defined by the user, both a Bid Rate and Offer Rate can be entered.
Applications like Foreign Exchange will use PERIODIC.INTEREST to default interest rate on Forward contracts using the Interest Revaluation Method or the Loans and Deposits applications to perform automatic rollover.
Illustrating Model Parameters
The high-level configurations available in the Model Bank are given below:
| S.No | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CONDITION.PRIORITY
|
Allows the user to define the fields from CUSTOMER and ACCOUNT to be used for setting various group conditions. |
| 2 | ACCOUNT.ACCRUAL
|
At company level, it provides the system with information on how and when to process accrual of interests and charges on customer accounts. The accrual process can be specified at Account Category and Account Group for which the associated interest accrual parameters are defined. |
| 3 | ACCOUNT.CREDIT.INT
|
Allows the user to define special credit interest conditions when the corresponding group credit interest conditions are not suitable. Credit interest rates can be specified for different balance levels, which can apply either to the entire balance or the gap balance amount between the two balance levels. |
| 4 | ACCOUNT.DEBIT.INT
|
Allows the user to define special debit interest conditions when the corresponding group debit interest conditions are not suitable. The user can define interest to be calculated on daily average using value-dated balance and also can define interest rate to be fixed or linked to basic rates with margin. |
| 5 | GROUP.CREDIT.INT
|
Allows the user to specify the calculation method of credit interest for a group of accounts. The user can also specify second interest on the account with different capitalisation frequencies. |
| 6 | GROUP.DEBIT.INT
|
Allows the user to specify the calculation method of debit interest for a group of accounts and provides the link to the GENERAL.CHARGE application, where the charges applicable to the same group of accounts are specified. The user can also specify negative interest and tax on interest. |
| 7 | ACCT.CAPITALISATION
|
Allows the user to specify the next date and subsequent frequency of application of debit and credit interest capitalisations for a specific account. |
| 8 | GROUP.CAPITALISATION
|
Allows the user to specify the next date and subsequent frequency of application of debit and credit interest capitalisations for a group of accounts. |
| 9 | ACCT.INTERIM.CAP
|
Allows the user to request interim interest capitalisation on particular ACCOUNT records without affecting the normal application cycles. |
| 10 | ACCT.GROUP.CONDITION
|
Allows the user to define the rules for accounts belonging to a group and specific currency mentioned in the table. Some examples for rules defined are notice withdrawals, account violations, deferring interest and charges, rounding rules for interest and premium interest, automatic IBAN (International Bank Account Number) generation and others. |
| 11 | GROUP.CONDITION
|
Allows the user to define group-level conditions for the calculation and application of interest and charges. |
| 12 | TABLE.CAPITALIS.CORR
|
Allows the user to request recalculation of previously applied interest. |
| 13 | DEBIT.INT.ADDON
|
Allows the user to specify a supplementary flat percentage charge to be applied to the overdraft interest amount calculated by the system on the capitalisation date. |
| 14 | HIGHEST.DEBIT |
Allows the user to specify a percentage charge based on the highest debit balance recorded on an account during the application period for debit interest or during the application of the ledger fee charges. |
| 15 | GOVERNMENT.MARGIN
|
Allows supplementary flat percentage charge to be calculated on overdraft balances by the system on the capitalisation date and collected on behalf of the government. |
| 16 | BALANCE.REQUIREMENT
|
Allows the user to define a fixed account charge to be applied if the specified balance is not maintained. |
| 17 | NUMBER.OF.CREDIT
|
Allows a fixed charge to be specified for each chargeable credit entry that is passed over an account during the capitalisation period. |
| 18 | NUMBER.OF.DEBIT
|
Allows a fixed charge to be specified for each chargeable debit entry that is passed over an account during the capitalisation period. |
| 19 | NUMBER.OF.TXNS
|
Allows a default charge based on the number of transactions in an ACCOUNT record. |
| 20 | TRANSACTION.CHARGE
|
Allows a charge, determined by the TRANSACTION code, to be specified for each entry that is passed over an account during the capitalisation period. |
| 21 | TURNOVER.CREDIT
|
Specifies a percentage charge on the total value of chargeable credit entries that is passed over an account during the capitalisation period. |
| 22 | TURNOVER.DEBIT
|
Specifies a percentage charge on the total value of chargeable debit entries that is passed over an account during the capitalisation period. |
| 23 | INTEREST.STATEMENT
|
Specifies a flat fee that is levied at the time of capitalisation of debit interest. |
| 24 | GENERAL.CHARGE
|
Specifies the group of accounts for which charges are to be levied and the type of balance overrides that are allowed. |
| 25 | GROUP.ACCRUAL.PARAM
|
Defines the options for the bulk accrual of accounts and reduces the number of accrual accounting entries, with entries being posted at consolidated levels such as application, currency market, account officer and category. |
| 26 | AC.PENDING
|
Holds information related to debit interest and charges pending for posting to the actual account. This application can be used to make adjustments to the existing interest or charges. |
| 27 | AC.VIOLATION
|
Holds information related to violations in an account within a statement period. |
| 28 | ACCT.SUSP.SETTLE
|
Allows the user to request settlement of interest or charges that have been captured in suspense account.'', that is, stored in a Suspense Amount field in the ACCOUNT record instead of being booked to profit and loss. |
| 29 | TEST.ACCRUAL
|
Allows the user to test and demonstrate the Temenos Transact accrual process. It allows the user to enter sample contracts along with interest rates and principal movements with their effective dates. The user can also enter keys in the EB.ACCRUAL.PARAM application so that the principal amounts and dates can be manipulated by the core accrual process. |
| 30 | IC.CHARGE
|
Allows the user to define the generic charging structure for accounts or group of accounts in a particular currency. |
| 31 | IC.CHARGE.PRODUCT
|
Allows the user to define the basic charging information of generic charges set for accounts. |
| 32 | ACCT.STATEMENT.CHARGE
|
Holds details of charge amounts and defaults related to statement charges. |
| 33 | ACCT.INTERIM.CHG
|
Allows the user to define a series of accounts where an interim capitalisation is required. |
| 34 | REBUILD.TRAN.CHARGES
|
Allows the user to define the transaction-level charges to be rebuilt for an account, a group of accounts or all accounts. |
Illustrating Model Products
Model Products are not applicable for this module.
In this topic