Enabling Commit Capture
This section shows you how the commit capture feature triggers a data event when a WRITE or DELETE function is performed inside or outside a transaction boundary of configured files and stores the triggered data event in the events table.
Configuring the TAFJ Properties File
You can configure the TAFJ properties file using the following procedure.
- In the .properties file, set the following property to enable commit capture:
temn.tafj.runtime.use.df.cache = true
- Set the following property to write the event to disk whenever the event size exceeds 32K.
temn.tafj.runtime.df.cache.huge.event=true
- Execute the following command from a JBC program to turn on or off the commit capture feature for a file. Internally, the on or off option is set in TAFJ_VOC, hence it will not be reset until it is changed again.
DF_COMMIT_CAPTURE(File_Name, Filter_Mode)
Where, File_Name is the name of the file as in TAFJ_VOC and Filter_Mode is either set as U or Y or by default NULL. Here, NULL indicates that the commit capture feature is turned OFF.
In U mode, the write events are captured whereas in Y mode, both the write and delete events are captured.
The following is the sample command to turn on the commit capture feature for a file:
EXECUTE "DF_COMMIT_CAPTURE('FBNK.CURRENCY','Y')" CAPTURING EXE.OUT
Events Table
The F.DATA.EVENTS table captures the data events. These captured events are constructed with the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Field1 |
Timestamp record created in milliseconds. For example, 1386082891.9949 |
|
Field2 |
Timestamp record processed. (Initially left blank) |
|
Field3 |
Not applicable for TAFJ |
|
Field4 |
Not applicable for TAFJ |
|
Field5 |
Multivalued list of file names. For example, FBNK.STMT.ENTRY]FBNK.ACCOUNT |
|
Field6 |
Sub-valued list of record keys related to the file names. |
|
Field7 |
Sub-valued list of data related to the key or {DELETE} if record deleted. |
|
Field8 |
Sub-valued list of table name. |
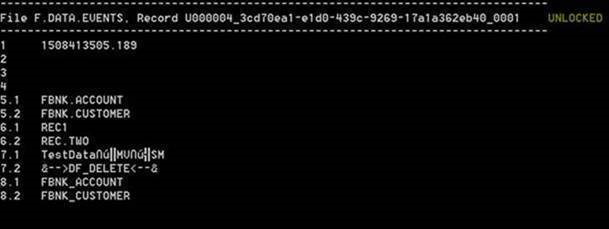
The filter record keys have the following format:
X<Port_No>_<UUID>_<sequence_number>
Where,
X - It is an indicator where, it can hold either the value U for unencrypted or E for encrypted filter records.
Port_No - It is the port number of the process performing the WRITE operation.
UUID - Universally Unique Identifier
sequence_number - Incrementing sequence number for multiple filter records describing a transaction.
In this topic