Introduction to Interest Rate Swap
The Interest Rate Swap module helps the users of Temenos Transact system to acquaint themselves with the application features, navigation and the functionality.
This module is intended to the following users or user roles:
| Role | Function |
|---|---|
| Dealer | Executes deals with counterparty and records the deal details in the system |
| Treasury Back office personnel | Ensures authorisation, confirmation and settlement of payments |
| Risk Manager | Enforces and monitors risk limits |
| IT personnel of bank/financial institution | Maintains computing infrastructure and upgrades the computer applications |
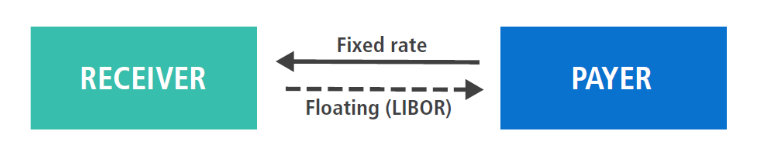
An interest rate swap is a forward contract in which one stream of future interest payments is exchanged for another, based on a specified principal amount. Interest rate swaps involve exchange of a fixed interest rate for a floating rate (or vice versa), to do one of the following:
- Reduce or increase exposure to fluctuations in interest rates
- Obtain a marginally lower interest rate than would have been possible without swap
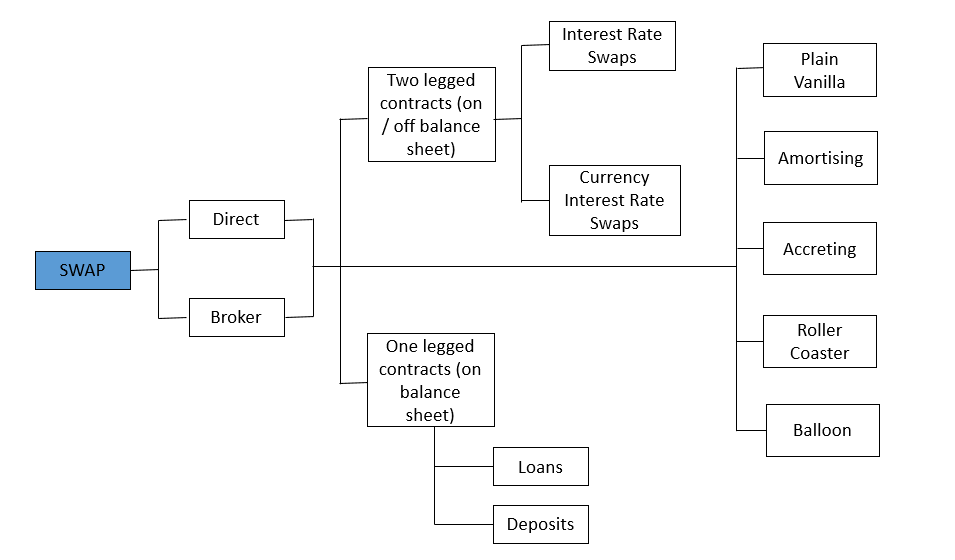
TheTemenos Transact SWAP module supports the recording and administration of both Interest Rate Swaps (IRS) and Currency Interest Rate Swaps (CIRS). It also supports ‘single-leg’ contract types (asset or liability), which are essentially loans or deposits. Additionally, Swaps are incorporated into the Limits, Accounting, Delivery and Position Management modules of Temenos Transact.
The details supporting the swap transaction are held in a single contract. Transaction details stored include the following:
- Counterparty
- Notional principals
- Interest rates
- Schedules for both Swap Legs (interest or premium future payment details - cash flows)
- Payment instructions
All future events, such as Principal Exchange, Interest Payment, Rate Reset, etc., are recorded in SWAP.SCHEDULESand the current and previously processed schedule details are stored in SWAP.BALANCES file. The Temenos Transact SWAP module supports the following products:
| Product Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Vanilla Swap | Exchange of a fixed rate for a floating rate is undertaken. Notional principal is constant throughout the life of the contract |
| Currency interest Rate Swap | Principal is either notional or exchanged but in different currencies |
| Amortizing Swap | Principal is amortised over the life of the contract |
| Accreting Swap | Principal is increased over the life of the contract |
| Roller-Coaster Swap | Principal is subjected to increase and decrease during the life cycle |
| Balloon Swap | Smaller portion of principal amount is amortised while a larger amount is retained until the end of the contract |
| Basis Swap | Both legs of the swap involve floating rate instead of fixed vs floating as seen on vanilla swap |
Product Configuration
This section describes the configuration options the system offers in Interest Rate Swap.
A swap contract input page has the following sections:
- Contract details
- Asset details including schedules
- Liability details including schedules
- Settlement instructions
Most of the fields have default values except for the key elements, such as counterparty, maturity date, agreement type, currencies, fixed interest rate, floating rate index, principal amounts etc. Schedules are entered directly in the contract by using the schedule types, dates, frequencies, amounts and rates. This simplifies the input of a relatively complex swap contract.
All schedules are processed online and at COB, with the exception of the IP and AP schedules, which are due for today. In the latter case, they are processed only at COB.
At input and commit stage, the system checks and updates the credit limits of the customer and Position Management.
At the authorisation stage, the system generates all the necessary accounting entries for various types of schedules including charges and fee, CRF entries, and SWIFT or print trade confirmation messages.
Broker or Customer confirmation is performed using the verify function, and when the contract are confirmed, it is stamped with the terminal number, operator name, time and date. The type of confirmation required is specified as a prefix to the contract number (which is ignored for other functions) with either CU for customer confirmations or BR for broker confirmations.
By using the versions Swap, Customer and Swap, Broker and the default enquiry supplied with these versions, the appropriate prefix is automatically appended to the contract number.
The Temenos Transact SWAP module classifies the deal into IRS, CIRS, Loan and Deposit contracts.
Illustrating Model Parameters
The model parameters consists of the following:
| S.No | Parameters | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Swap Parameters | This table allows the users to define the system lever parameter for processing of Swap contracts. The record ID of this table is 'SYSTEM'. User can also update parameter values for Days post maturity, Maturity Date, Defer online position update and Defer online schedule update. |
| 2 | Swap Reval Parameter | This table allows the user to parameterize the Swap Revaluation setup. The record ID of this table is 'SYSTEM' and consists of parameter values for PL Category, Revaluation Credit Code, Debit Code and setup related to Asset & Liability Short and Long rates selection, Zero coupon rate selection, NPV forward rate, NPV accrual adjustment. |
| 3 | Swap Type Record | This file contains the definition of all types of Swap contracts allowed on the system. It contains details such as Category Codes for Booking Revaluation Entries, Accounting (ON/OFF Balance sheet) and Revaluation Method. |
| 4 | Swap Agreement Type | This file stores the types of agreements that are used in Swap contracts. Each swap contract has to be linked to an agreement type, based on which the validations are performed. The user can modify an existing record and as well create new records. |
| 5 | Swap Activity Record | This file allows the user to define and control the delivery output for Swap module. The records in this file define all the activities that produce delivery outputs. These activities relate to specific events during the life of the contract. If required, the delivery pertaining to each of these events can be produced prior to the event itself. In this case, the number of days in advance of the event that the advices are produced is defined in this file. |
| 6 | Market Rate Text | This table defines descriptions of tradable interest rates that are recognised by SWIFT. The key of the periodic interest table corresponding to the rate described is linked in this file. Floating interest rates defined in Swap Contracts are must also be linked to this file. |
llustrating Model Products
Following products are available under Swap module:
| S.No | Products | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Interest Rate Swap - Trade |
Interest Rate Swap is an agreement between two counterparties to exchange the streams of Interest payments over a period of time. It does not involve the exchange of Principal, and the interests are calculated on the notional amount. The interest rates can be fixed or floating and the payment schedules are either generated from a frequency or can be manually defined. A Trade deal is a speculative transaction without an underlying asset. |
| 2 | Interest Rate Swap - Hedge |
It is an agreement between two counterparties to exchange streams of Interest payments over a period of time and or to lock in a profit or minimize the loss to offset a Loan or Deposit contract on bank book. |
| 3 | Currency Interest Rate Swap - Trade |
It is an agreement between two counterparties to exchange the streams of Interest payments in different currencies over a period of time. Additionally, the principal amount can be exchanged between the counterparties at the beginning and end of the deal. Interest rates can be fixed or floating. The payment schedules can either be generated from a frequency or defined manually. |
| 4 | Currency Interest Rate Swap - Hedge |
It is an agreement between the counterparties to exchange the streams of interest payment in different currencies over a period of time, mainly to lock in a profit (or minimize the loss) to offset a Loan or Deposit contract on banks book. |
In this topic