Introduction to Syndicated Lending
ⓘContent enriched:New structure and revised (Docs 2.0)
A syndicated credit is usually a large facility made to a borrower(s) or, by a group of banks headed by a lead bank which usually takes a percentage of the facility to itself, syndicating the rest to other banks and financial institutions. The credit can be either fund based or non-fund based. Syndicating loans or spreading debt among a number of investors helps lenders manage their portfolios by reducing risk, improving returns, and increasing fee business. A syndicated facility is structured and priced by the lead arranger or agent, who sells portions of the deal to other lenders, or investor groups as per the terms negotiated by the agent.
Syndication clearly has become more complex over the last several decades. In addition to commercial banks and financial institutions, today's investors include finance companies, insurance companies, securities firms etc., with commercial banks and financial institutions remaining the largest investor category. With a diverse investor base, it is often required that the facility is structured to meet the needs of the market. Often structuring involves revolvers (short term facility) and term loans (long term facility) with the investors being different for these two segments.
The Syndicated Lending (SL) module has been designed keeping in view the complex facility structures prevailing in the market and the need for automated administration of such facilities with flexibility, which is a key feature of Temenos Transact. The Syndicated Lending module also supports fronting bank features.
The module automates the business of administering syndicated facilities where the bank is either the lead manager or lead participant or agent or a mere participant. It handles basic to complex multi-lender, multi-tranche, multi-product, multi-currency, and multi-borrower facilities, from application stage to maturity, based on a workflow approach with rigorous condition checking.
Understanding Syndicated Lending
The system handles the workflow in the following stages:
This stage starts with recording the terms of the mandate and ends with recording the final terms of the credit agreement. Information that can be recorded includes:
- Nature of the facility sought
- Details of the banks, to which an information memorandum is circulated, and their response
- Details of underwriters with underwriting fee and the participation brought in by each one of them.
- Details of final allotment to participants with the commitment fee at participant level
- Details of the participants available for fronting.
Wherever necessary, collection and distribution of an underwriting fee and accounting for underwriting is handled at this stage.
This is a line of credit or a facility granted to the borrower. The administration of the facility is broadly based on:
- Product type,
- Nature of credit (revolving or non-revolving),
- Tenor
- Currency of the facility.
The commitment fee calculation method and its collection frequency is defined at this stage. Tranches can be defined under a facility to phase out disbursements, with each tranche having its own set of terms and conditions for drawdown management. The list of participants that is defaulted from the pre-syndication stage and is available for fronting can be modified at the facility stage.
This is a drawdown against a facility. Multiple loans can be drawn against a facility until it has been fully utilised. Features such as the default of interest rates from the facility and rollover or merger or split of loans are also available.
Apart from the above, interim events that are supported by the system include, rollover or merger or splitting of loans, loan trading, etc.
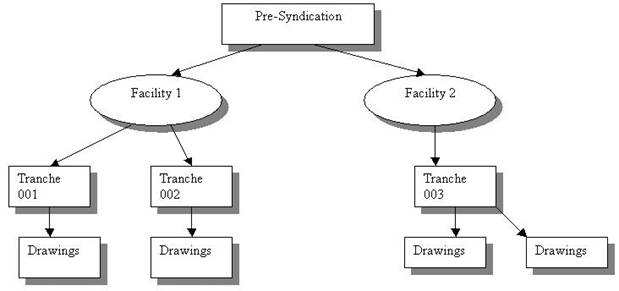
The diagram below represents one of the structures supported by the module.
From the diagram, it is understood that:
- In the pre-syndication stage, details pertaining to 'Facility 1' and 'Facility 2' can be recorded.
- Facility 1 can be further broken down into 'Tranche 001' and 'Tranche 002'.
- Terms and covenants can be recorded at both facility and tranche level.
- The loan processing is linked to the tranche, under which it is drawn, and all terms and conditions stipulated under the respective tranche are validated.
- Information is available at facility or tranche level for an individual participant and at borrower level.
The following are the major functionalities provided in the module:
- Ability to record and process information, from the mandate till the allotment date (Pre-syndication stage)
- Ability to record the information on participants with their share in each facility if the syndication involves multiple facilities
- Monitor the status of the syndicate till the entire line of credit is tied up
- Define various roles and ability to process fee and non-fee based charges for them
- Ability to further breakdown the facility into tranches, and record terms and conditions at facility and tranche level
- Processing drawdown against facility, including all repayment and fees
- Pooling of funds at a central nostro correspondent for disbursement to the borrower
- Rerouting funds repaid by borrower to respective participants – This can either be automated or handled after sighting the credit
- Enable loans to be rolled over in the same or different currency, and ability to merge or split loans
- Handle purchase or sale of participations in the loan or facility
- Delivery messages for the borrower and other members of the syndicate, including SWIFT
- Ability to define repayment schedules at facility or loan level
- Ability to define reducing limit for a revolving facility
- Ability to define and process activity based charges
- Diarise events related to the syndicate and record their outcome
- Availability of information at individual participant level for each event during the life cycle
- Ability to process Bilateral Lending under SL module
- Ability to convert the Bilateral Lending into SL and vice versa
- Ability to record and process risk free rates (RFRs)
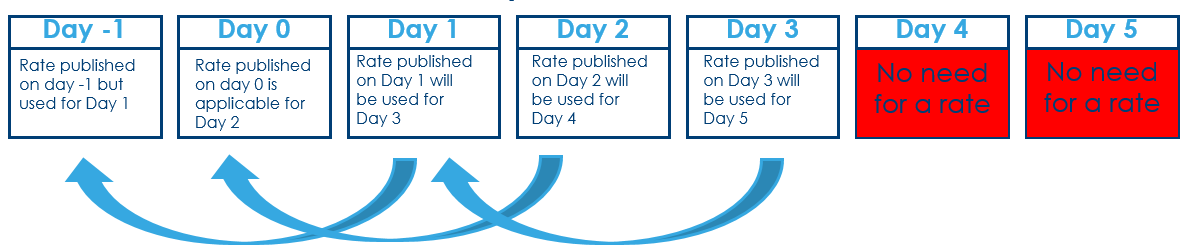
Risk Free rates(RFRs) are alternative rates for Interbank Offered Rate(IBOR) rates that are replacing the IBOR rates. For IBOR rates, the interest rate is fixed for the term at the beginning of the period. Whereas RFRs are overnight, backward-looking rates derived from actual market data for a given business day. They are published each business day with a delay (that is, a rate published this business day is effective for the previous business day). These rates do not have a term structure and a credit risk element.Each major currency has its alternate RFRs as listed below:
- USD – SOFR
- GBP – SONIA
- EUR – ESTER
- JPY – TONAR
- CHF – SARON
The existing PERIODIC.INTEREST table stores the RFRs. The RFR Rate field contains the risk free rate. Banks can set up RFRs for different currencies using this key or create an alternative key in this table. The overnight RFRs are published as a single rate with no bid or offer options.
The SL application follows the lookback market convention to identify the interest rates based on the defined lookback days.
Lookback - For every day in the current interest period, the RFR rate from N days earlier is used.
RFR supports the following lookback types:
- Narrow Definition - Applies the original interest period’s day count to the lookback rate used for the current day, that is, if Wednesday’s rate is used for Friday, applies the Friday’s weight, three days, to the Wednesday’s rate.
- Observation Shift - Applies the original day count of the lookback rate, that is, if Wednesday’s rate is used for Friday, apply the Wednesday’s own weight, one day, and does not use Friday’s day count for it.
The Syndicated Lending module offers banks with the flexibility to use the following interest calculation methods for RFR contracts.
RFRs support the compounding average calculation method where rates must be compounded every day to arrive at a final rate to determine the payment for a particular interest period. This method is accurate for the scenarios where the principal amount remains unchanged during the interest period. The following formula is used to calculate the average RFR compounded rate.
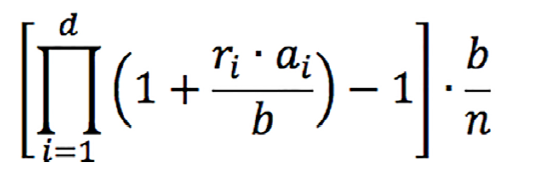
Where:
- n is the number of calendar days from (and including) the start date to (but excluding) the end date
- d is the number of business days in the same period
- b is the applicable day count fraction denominator
- ri is the applicable overnight rate in respect of business day i
- ai is the number of calendar days in the period in respect of which rate ri applies
RFRs support the simple average calculation method where rates have to be compounded every day to arrive at a final rate to determine the payment for a particular interest period. This method is accurate for the scenarios where the principal amount remains unchanged during the interest period. The following formula is used to calculate the simple average RFR rate:
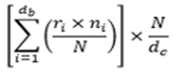
Where:
- db is the number of business days in the interest period.
- de is the number of calendar days in the interest Period
- ri is the rate applicable on the business day i.
- ni is the number of calendar days for which the ri rate applies.
- N is the market convention of quoting number of days in a year.
- i is the series of ordinal numbers representing each business day in the period.
RFRs support the amount calculation method. In this method, contract balance has to be compounded daily instead of rates . The Security Lending module uses the daily RFRs published by the central banks (no rate formula is applied). Use the identified RFR rate on the compounded balance (sum of the outstanding principal and the unpaid accrued amount) to calculate the daily interest accrual. This accrual calculation is accurate with this method when the principal amount changes during the interest period.
RFRs support the NCCR calculation method. It is a variation of the cumulative method which calculates the daily applicable compounded rates (instead of cumulative rates). This method daily annualizes the cumulative compounded rate using calendar days in the schedule period and adjusts the rate daily to calculate the daily compounded rate. It is more accurate for the scenarios where the principal amount changes within the interest period.
The following procedural steps details the NCCR calculation:
- Calculate Annualized Cumulative Compounded Rate (ACR), which is the same as RFR Compounding Average calculation method. ACRi is used in NCCR calculation. The formula to calculate ACRi is,
- db is the number of banking days in the observation period.
- ri is the interest rate applicable on banking day i in the observation period as published on the banking day immediately after the banking day i.
- ni is the number of calendar days for which the ri rate applies (on most days ni is considered as one but on Friday it is considered as three. Generally, the value is greater than one on the banking day before a holiday).
- tni is the total number of ni as of the relevant banking day within the observation period.
- N is the market convention of quoting the number of days in a year.
ACRi =
Where:
- Calculate Unannualized Cumulative Compounded Rate (UCR). UCRi calculation involves unannualizing ACRi (from Step 1) by multiplying with the business day convention, that is, the number of calendar days in the interest period, and divided by the market convention for quoting the number of days in the year (360, 365 and so on). The formula to calculate UCRi is,
- tcni is the total number of cni as of the relevant banking day within the interest period.
- N is the market convention of quoting the number of days in a year.
UCRi =
Where:
- Calculate NCCR, which involves the UCR for that given business day (from Step 2) is subtracted from the UCR of the previous business day, which is then multiplied by the market convention for quoting the number of days in a year (360, 365 and so on) and divided by the day count for the given business day. The formula to calculate the NCCR is,
- cni is the number of calendar days for which the ri rate applies in the relevant interest period.
- BD is banking day for the specific currency only.
- i is the whole number from one to db each representing the relevant banking day in chronological order from, and including, the first banking day in the relevant observation period.
NCRi =
Where:
- Calculate interest accruals using the Simple Interest calculation method. The formula is,
- CAS is Credit Adjustment Spread.
Interest Amount =
Where:
NCCR supports both Narrow Definition and Observation Shift lookback types. The difference between the two types is in the ACR calculation (cumulative compounded rate). During ACR calculation, the Narrow Definition type uses the interest period day count while the Observation Shift type uses the RFR day count. However, UCR and NCCR calculations always use the interest period day count for both Narrow and Observation Shift lookback types.
For Spread-Inclusive Margin treatment, the spread is included as part of the Annualized Cumulative Compounded (ACR) rate calculations (as in Step 1). For Spread-Exclusive Margin treatment, the spread is added at the end of the NCCR calculations (after Step 3). The spread will not have any impact on the UCR or NCCR calculations.
Configuring Parameter Files and System Tables
The configuration required for SL is defined in the below parameter tables.
SL.PARAMETER
This table holds the accrual cycle along with profit and loss(P/L) accounts that are used for various events. It also contains the ID of the Temenos Transact bank (user of SL module) which is the key information as accounting is done only for the Temenos Transact bank. To start with, it is therefore necessary to set up a record in a CUSTOMER table for the Temenos Transact bank.
The accrual cycle can be daily or in multiples of months. The PL category for interest accrual, interest amortisation (in case of discounted loans), commitment fee accrual ,underwriting fee, and, profit or loss on buy or sell transaction are determined from this table. If the bank requires accounting entries to be generated for underwriting, Acct Underwriting field is flagged as Yes.
When a Temenos Transact bank is also acting as an agent, the interest or commitment amount due from the borrower and individual participants’ share in that amount is held in the system. The system calculates the amount of interest or fee (at borrower level) and independently calculates each participant’s share. This can often lead to rounding differences. There could be a situation where the agent bank quotes a rate that differs from the participant quote, which results in skimming of profit.
Any difference in the amount due from the borrower and the amount to be distributed to the other participants is parked in an internal account. The internal account category to be used for this purpose is indicated in the Skim Acc Cat field. A record must exist in ACCOUNT.CLASS table for this category in the Record Type field as Account. The bank can ultimately decide whether the difference in amount is to be credited to its own account or it has to be distributed to the participants.
There are chances that the amount calculated by the system for an individual participant does not actually tally with the amount that is advised by the borrower. This happens when the standard rounding off rules are not decided upfront. In such cases adjustments to the system calculated amount (rounding off) is required, and the system supports in rounding off the amount due to the individual participants. However, in order to avoid input errors at the time of rounding off, the maximum permissible variance is defined in the Max Rounding field.
Maximum back date for early maturity can be restricted using the Max Back Date field.
To enable the processing of Risk-Free Rates (RFRs) in the SL module, the bank has to configure the RFR related fields for rate calculation as per the bank’s preference.
The SL module uses standard calls to the LIMIT module. Whenever a facility or a drawing is entered, the system validates and checks the LIMIT module to see if an approved limit is in place for that product type. If no approved limits exists, a default one is created. Checks are made against the expiry date, available amounts, and, global or sub-product limits, according to the unique limit structure of the bank.
The limit impact is only to the extent of the Temenos Transact Bank’s exposure in the facility and drawing.
A valid LIMIT.REFERENCE record ID with the value IN in the Fx Or Time Band field is to be attached to the Part Limit Ref field of SL.PARAMETER. The system updates this limit for the Participant Bank's share at the time of FACILITY creation and its utilisation.
SL.ROLES
- The various roles in a syndication are user-definable and it is listed in the
SL.ROLEStable. - The ID is a numeric value (up to 99), that is, 99 different roles can be defined.
- Roles are defined in
SL.ROLEStable and assigned to each party involved in the syndication process. - Values (roles) that can be defined in this table are Agent, Agent cum Participant, Participant, Manager, Lead Manager, Underwriter, and Guarantee Custodian, etc.
- This table contains only two fields Description and Short Description (apart from the ID) where the role is defined.
- Short Description field is the description in an abbreviated format that is used for enrichment.
SL.FACILITY
Different types of credit facilities offered by the bank are listed in this table.
- The ID is a numeric value of up to 99.
- The table is user definable, based on individual requirements.
- In the description field the type of loan facility is entered.
- Typical values for this table are TL (Term Loans), PF (Project Finance), GT (Guarantees), etc.
- The table contains only two fields Description and Short Description(apart from the ID) where the type of facility is defined.
- Short Description field is the description in an abbreviated format that is used for enrichment.
SL.PURPOSE
Purposes for which disbursements are made are listed in this table. The ID is numeric and the bank can define up to 99 different purposes based on its requirements.
SL.STATUS
Overall status of the syndication is indicated by values in this table. The ID is numeric, and 99 different statuses can be listed.
SL.CHARGE.ACTIVITY
Charges are collected for various events. For example, when a bank grants a facility, the front-end fees can be collected along with the documentation charges, etc.
- Initially the bank must define all the charges and commissions applicable to SL in
FT.COMMISSION.TYPEorFT.CHARGE.TYPEtables. It is possible to group the charges defined inFT.COMMISSION.TYPEorFT.CHARGE.TYPEtable ,and collect them for a particular event. - These charges are then grouped in
SL.CHARGE.ACTIVITYtable for defaulting, when the charges are taken through theSL.CHARGEtable. - The ID of this table is a three character alpha numeric where charges applicable for specific events can be grouped. ID 999 is reserved for taking ad hoc charges (charges not related to any activity) and hence does not accept any
FT.COMMISSION.TYPEorFT.CHARGE.TYPErecord.
It is possible to define the frequency, at which the charges are to be collected, using SL.CHARGE.ACTIVITY table. A user can decide if the charges have to be amortised or not and when it is amortised, the frequency and period of amortisation can also be defined upfront for default purposes. Apart from this, it is possible to define whether the charges are to be shared among all Participants or is applicable only to an Agent.
When charges are taken using SL.CHARGE table , only the ID of SL.CHARGE.ACTIVITY has to be entered while system defaults all the applicable charges. Consider the below example where the front end fees, documentation charges and agency fees have been defaulted. Flexibility has been provided to accommodate charges to be taken at a particular frequency. The frequency, at which the charge has to be applied is indicated in the Charge Frequency field. Agency fees is collected once every year. It is also possible to amortise the charge, and the period over which the charge needs to be amortised can be indicated. The amortisation happens on a monthly basis.
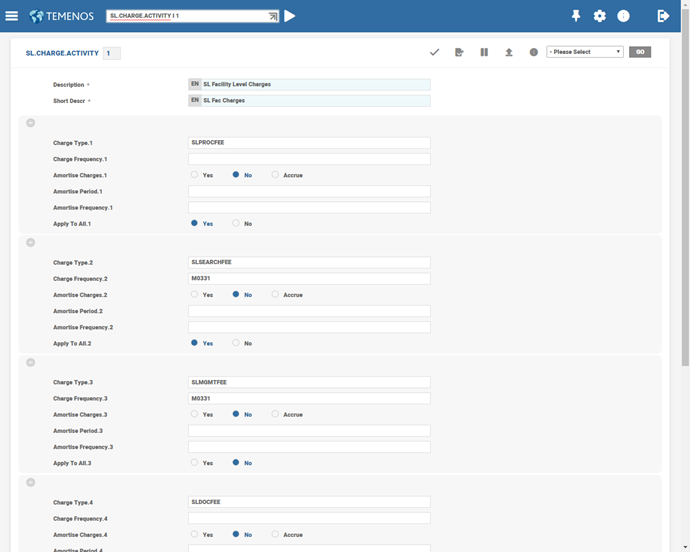
From the agent banks' perspective, some of the charges collected from the borrower has to be distributed to the participants in the ratio of the individual participant’s share in the syndicate. Some charges like agency fees are to not be distributed as they are meant for administration of the facility. If the charges have to be distributed to other participants, then the Apply To All field is flagged as Yes, else the field is flagged to No.
It is also possible to define the base for the calculation of charge if the charge were to be of a percentage type. For example, if the charge were to be collected on a facility, the base amount could either be the original facility amount or the current outstanding. It is also possible for the user to define the base amount manually if the charges were adhoc.
SL.TXN.CODES
The ID of the SL.TXN.CODES is SYSTEM. This table is to list out the transaction codes that are to be used in STMT.ENTRY records for different events.
In syndication, the SL.DIARY is provided in order to record diary events for a facility. The diary events may be recorded at the facility, tranche or drawing level. Specific covenants applicable to a single (or group) participants or a particular borrower can also be defined. Before entering SL.DIARY, it is essential to define SL.DIARY.CODES, which contain the list of standard diary activities or covenants.
SL.FACI.RATES
Drawings under a facility is permitted in any allowed currency. The rate applicable to a drawing in facility currency is captured alone in the facility template. If the rate applicable for a drawing in an optional currency is determined upfront, then that rate is entered in this table. If a drawing is made in the optional currency, then the system defaults the applicable rate.
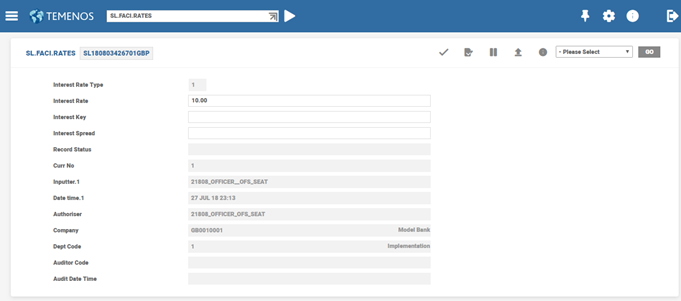
The ID of the record is the facility ID suffixed with the currency. In the above example, for any GBP drawing under this particular facility, Interest Key (1) and Int Spread (2.5%) is defaulted. The interest rate type (fixed or floating) is also stored in this template. For a floating interest type facility the fixed rate is not allowed to be input and vice versa. Similar records can be created for as many optional currencies.
SL.RATES.PART
This table is provided exclusively in cases where differential rates exist. If the rate quoted to individual participants’ is the same and if the same rate is charged to the borrower, then no record need exist in SL.RATES.PART table.
SL.RATES.PART – Single participant rate
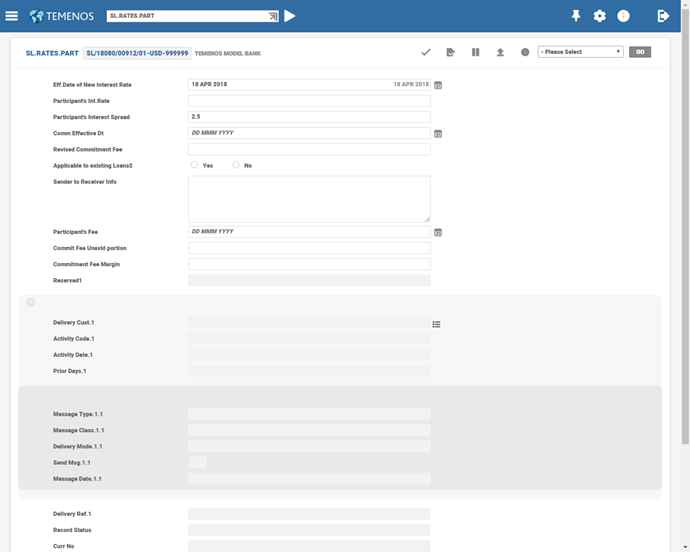
The ID of the record is the facility ID suffixed with currency and the customer ID the of Participant. In the above example a Part Int Spr of 2.5% applicable to the bank is applied for any drawing in GBP. For the other participants, if no record exists in this table then the spread input in the drawing is applied.
SL.RATES.PART – Rate for all participants
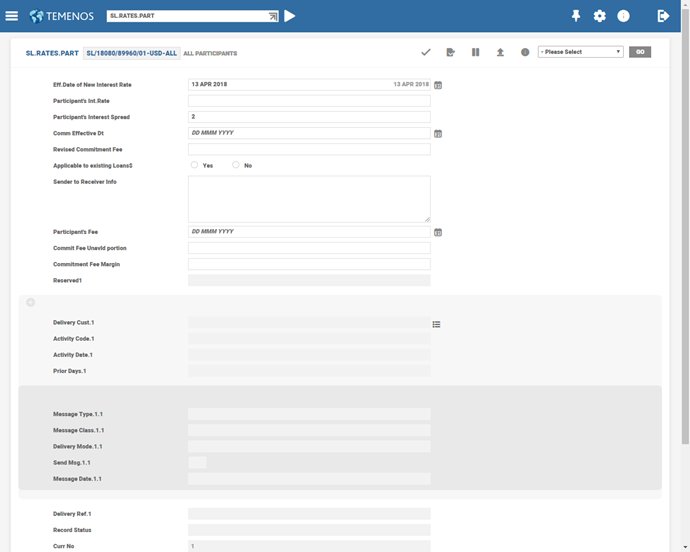
In large syndications, the number of participants can be many. In some situations, the rate quoted by only a few of them can be different, and for the rest the same rate is applicable. In such situations, a weighted average rate is quoted to the borrower that is input at the time of drawing. For the rate applicable to the individual, a Participant’s record must exist in this table. However, to minimise the input, one record can be created with a suffix of ALL indicating that the rate is applicable to all participants. To exclude only the few participants for whom a different rate is applicable, records can be created for these participants alone.
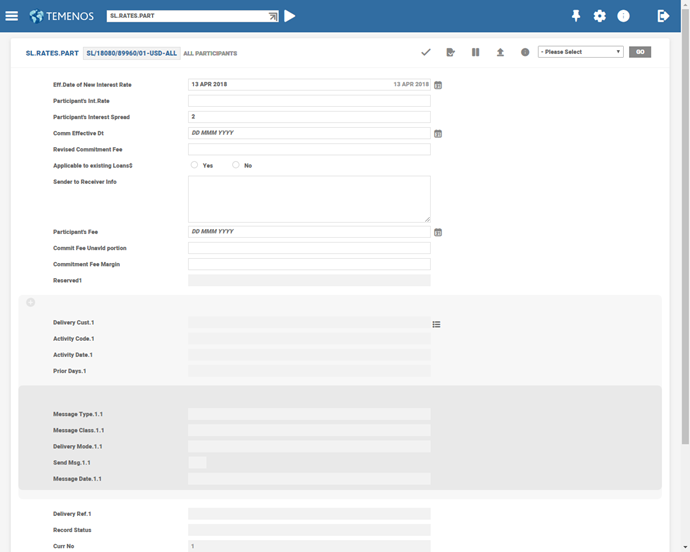
If the above record were to exist, then for any drawing in GBP a spread of 2% is applied to all Participants. If the above record and that for AFRIBANK were to exist, a spread of 2% is applied to all participants except AFRIBANK. A spread of 2.5% is applied to AFRIBANK. The spread applied to the borrower is always picked up from the drawing template (SL.LOANS).
Creating Model Products
SL Module supports the below features:
| Product Name | Product Attributes |
|---|---|
| Pre-Syndication |
|
| Facility |
|
| Drawings |
|
| Rollover/Merger/Split of Loans |
|
| Buying and Selling Transactions |
|
| Diary of Events | Record diary events for a facility recorded at the facility level, Tranche level or drawing level |
Setting up Delivery Advices/Swift Message
SWIFT Message types are the format or schema used to send messages to financial institutions on the SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) network. It is a messaging network that financial institutions use to securely transmit information and instructions through a standardized system of codes.
Configuring Delivery Advices/Swift Message
This topic deals with how swift messages are configured.
EB.ACTIVITY
The generation of messages is activity based. The activities are defined in the EB.ACTIVITY file. The ID of the record is <the application ID followed by a four-digit code separated by a hyphen>. For example, SL-2102.
The four digits are derived as given below:
The first digit indicates the application for which the activity has been generated. Currently for Temenos Transact release, G13.1.0 the system would recognize three values for the first digit as follows:
- 1 = PRE.SYNDICATION.FILE
- 2 = FACILITY
- 3 = SL.LOAN (with a scope for addition in future releases)
The second digit indicates the operation done under each application. Currently the system would recognize six values as follows:
- 0-OTHERS
- 1-INPUT
- 2-AMENDMENT
- 3-NOTICE
- 4-CONFIRMATION
- 5-REVERSAL (with a scope for future addition)
The third digit indicates the components for which the message is being generated viz. Principal or Interest or Commitment fee etc. Currently the system would recognize five values as follows:
- 0-OTHERS
- 1-PRINCIPAL
- 2-COMMITMENT FEE
- 3-INTEREST
- 4-CHARGES (with a scope for future addition)
The fourth digit indicates the recipient of the message. At present the system recognizes three values as follows:
- 1-PARTICIPANT ONLY
- 2-PARTICIPANT and BORROWER
- 3-BORROWER ONLY (with a scope of addition in future)
A typical EB.ACTIVITY record for SL-2102 is appended below:
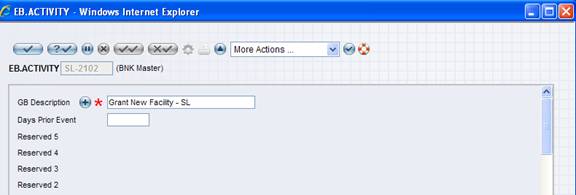
EB.ADVICES
The messages required to be generated for each EB.ACTIVITY is defined in this file. The ID of this file is the same as EB.ACTIVITY file.
The mapping key to be used, the print format to be used (for print messages) and the EB.MESSAGE.CLASS file to be looked at are defined in this file. A typical EB.ADVICES file for SL-2102 is appended below.
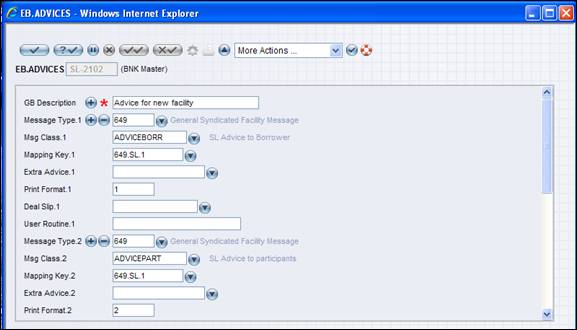
In order to cater to the Tags 28 and 29 in Syndication messages, SL.PART.DELIVERY.DTLS table has been introduced. This enables capturing information relating to Account Officer, Department, Phone, Telex and Fax numbers. The ID of this table would be that of Customer.
The SL.PARAMETER (system) record has to be set up properly for triggering soft delivery. A typical set up are detailed below:
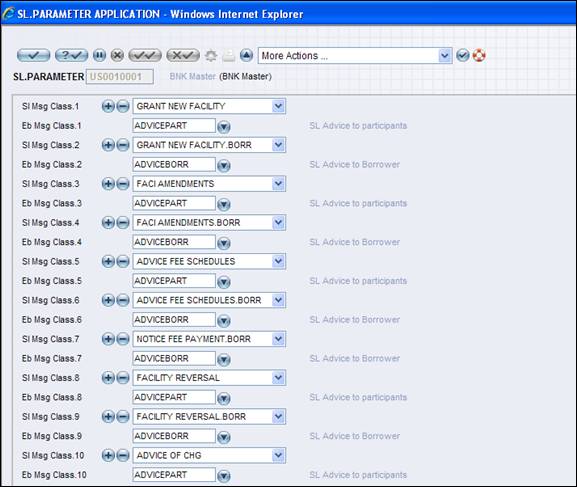
Here theSl Msg Class is the class identified by the program internally for the activity generated by the system. Eb Msg Class is the message class attached to a particular message in the EB.ADVICES file. On determination of the EB.ACTIVITY code, the system identifies the EB.ADVICES to be triggered. From there the messages to be generated are picked up along with theEb Msg Class record. Then theEb Msg Class is compared with the parameter settings and the appropriateEb Msg Class is identified by the program and used.
The following table details the messages that would be generated from individual applications along with the respective DE.MAPPING or DE.FORMAT.PRINT or DE.FORMAT.SWIFT records that are used.
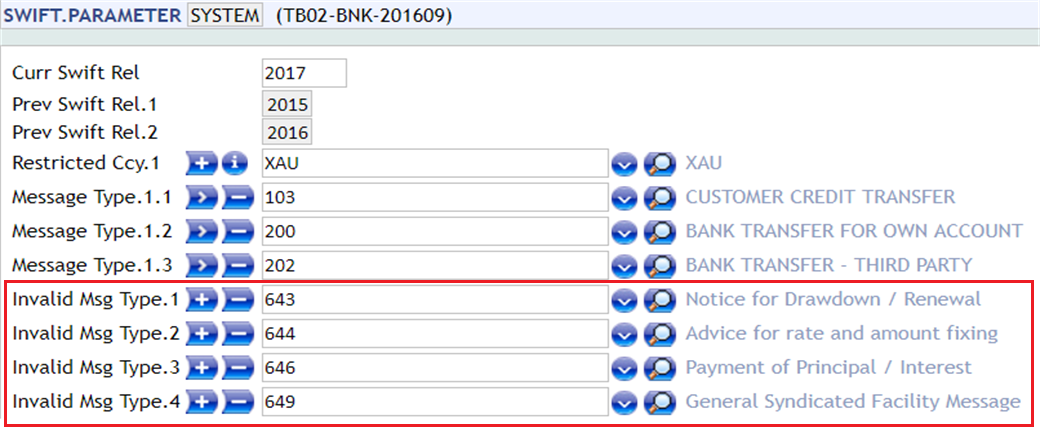
The SWIFT.PARAMETER has a multi-value Invalid Message Type field, where user can define the message types that are made as invalid and not supported by SWIFT. It must be a valid message type in DE.MESSAGE application. If the SWIFT message is of the type defined in this field, system would write the message in repair stating 'Invalid SWIFT Message Type'.
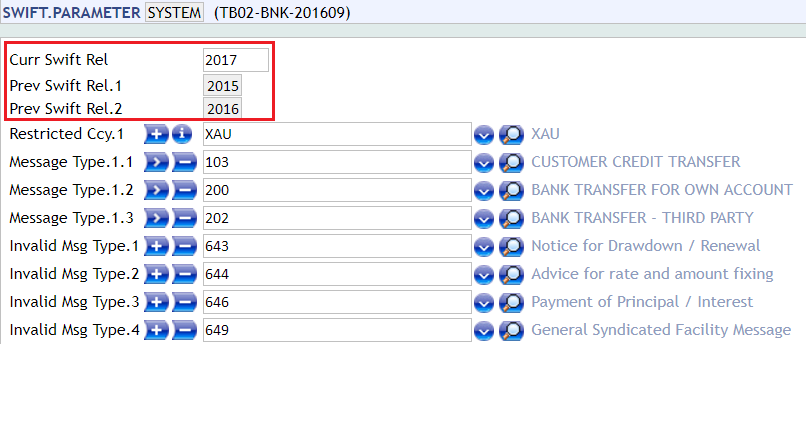
SWIFT.PARAMETER – Curr Swift Rel
The SWIFT 2017 rule book changes are effective only from the time when theCurr Swift Rel field in SWIFT.PARAMETER is updated as 2017. The Prev Swift Rel field is updated automatically with the old value ofCurr Swift Rel field.
SWIFT.PARAMETER – Invalid Message Type
SWIFT comes up with the message types that are no longer supported by SWIFT in their annual rule Book. These unsupported messages should be defined in theInvalid Message Type field in the SWIFT.PARAMETER, as shown below. It must be a valid message type in DE.MESSAGE.
Implementing Delivery Advices/Swift Message
The following messages are generated in the circumstances defined.
Summary of Messages:
| Type of Deal/operation | Message | Recipients |
|---|---|---|
| Grant of New Facility | 649 | Advice to Borrower |
| Amendment to a Facility | 649 | Advice to Borrower |
| Reversal/Cancellation of a Facility | 692 | Participants & Borrower |
| Notice of Commitment fee due | 645 | Borrower |
| Advice of Commitment fee collection | 690 | Participants & Borrower |
| Actual Loan Draw Down | 643 | Borrower |
| Amendment to a Loan | 643 | Advice to Borrower |
| Reversal/Cancellation of a Loan | 692 | Participants & Borrower |
| Notice of Interest Payment | 691 | Borrower |
| Confirmation of Interest/Principal payment | 646 | Advice to Borrower |
| Notice of Charge due | 691 | Borrower |
| Advice of Charge collection | 690 | Participants & Borrower |
The following table details the settings of the Swift messages generated by each area. (The details are the same as described in the Swift Message above.)
FACILITY
| S.No | MSG.CLASS | EB.ADVICES | DE. MSG | DE. MAPPING | DFP | DFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GRANT NEW FACILITY (ADVICEPART) GRANT NEW FACILITY.BORR (ADVICEBORR) | SL-2102 | 649 | 649.SL.1 | 649.1.1.GB(B) 649.2.1.GB(P) | 649.1.1 |
| 2 | ADVICE FEE SCHEDULES (ADVICEPART) ADVICE FEE SCHEDULES.BORR (ADVICEBORR) | SL-2122 | 690 | 690.SL.3 | 690.1.1.GB(B) 690.2.1.GB (P) | 690.1.1 |
| 3 | NOTICE FEE PAYMENT.BORR (ADVICEBORR) | SL-2323 | 645 | 645.SL.1 | 645.2.1.GB (B) | 645.1.1 |
| 4 | FACI AMENDMENTS (ADVICEPART) FACI AMENDMENTS.BORR (ADVICEBORR) | SL-2202 | 649 | 649.SL.1 | 649.3.1.GB(B) 649.4.1.GB(P) | 649.1.1 |
| 5 | FACILITY REVERSAL (ADVICEPART) FACILITY REVERSAL.BORR (ADVICEBORR) | SL-2502 | 692 | 692.SL.1 | 692.1.1GB(P&B) | 692.1.1 |
SL.LOANS
| S.No | MSG.CLASS | EB.ADVICES | DE. MSG | DE. MAPPING | DFP | DFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | LOAN DD.BORR (ADVICEPART) | SL-3102 | 643 | 643.SL.1 | 643.2.1.GB(B) | 643.1.1 |
| 7 | NOTICE OF LOAN DD (ADVICEPART) | SL-3302 | 643 | 643.SL.1 | 643.1.1GB(P) | 643.1.1 |
| 8 | LOAN AMENDMENTS (ADVICEPART) LOAN AMENDMENTS.BORR (ADVICEBORR) | SL-3202 | 643 | 643.SL.1 | 643.3.1.GB(B&P) | 643.1.1 |
| 9 | ADVICE RATE AND AMOUNT FIXING (LOAN.RATE.CHANGE) | SL-3231 | 644 | 644.SL.1 | 644.1.1.GB | 644.1.1 |
| 10 | LOAN REVERSAL (ADVICEPART) LOAN REVERSAL.BORR (ADVICEBORR) | SL-3502 | 692 | 692.SL.2 | 692.3.1.GB(P&B) | 692.1.1 |
| 11 | NOTICE OF INT PAYMENT.BORR (ADVICEBORR) | SL-3332 | 691 | 691.SL.2 | 691.1.1.GB | 691.1.1 |
| 12 | CONFIRM INT PAYMENT (ADVICEPART) CONFIRM INT PAYMENT.BORR (ADVICEBORR) | SL-3432 | 646 | 690.SL.2 | 690.3.1.GB (B) 690.4.1.GB (P) | 690.1.1 |
The SWIFT messages relating to deal confirmation (MT320) for RFR contracts does not have the actual interest rate as the final rate applicable, for the interest period is not available at the contract initiation. During contract maturity, the final rate applicable is available and the maturity confirmation (MT320) for RFR contracts have the actual interest rate.
SL.CHARGE
| S.No | MSG.CLASS | EB.ADVICES | DE. MSG | DE. MAPPING | DFP | DFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | ADVICE OF CHG (ADVICEPART) ADVICE OF CHG.BORR (ADVICEBORR) | SL-2143(P) SL-3143(L) | 690 | 690.SL.1 | 690.5.1.GB(B) 690.6.1.GB(P) | 690.1.1 |
| 13 | NOTICE OF CHG.BORR (ADVICEBORR) | SL-2343 SL-3343 | 691 | 691.SL.1 | 691.2.1.GB | 691.1.1 |
SL.BUY.SELL
| S.No | MSG.CLASS | EB.ADVICES | DE. MSG | DE. MAPPING | DFP | DFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | TRANCHE AMENDMENTS (PARTICIPATION) TRANCHE AMENDMENTS.BORR (PAYMENT) | SL-2202 | 649 | 649.SL.2 | 649.5.1.GB(B) 649.6.1.GB(P) | 649.1.1 |
SL.REPAYMENT.SCHEDULES
| S.No | MSG.CLASS | EB.ADVICES | DE. MSG | DE. MAPPING | DFP | DFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | NOTICE OF INT PAYMENT.BORR (ADVICEBORR) | SL-3332 | 691 | 691.SL.2 | 691.1.1.GB | 691.1.1 |
| 16 | CONFIRM INT PAYMENT (ADVICEPART) CONFIRM INT PAYMENT.BORR (ADVICEBORR) | SL-3432 | 646 | 690.SL.2 | 690.3.1.GB (B) 690.4.1.GB (P) | 690.1.1 |
SL.ROLLOVER
| S.No | MSG.CLASS | EB.ADVICES | DE. MSG | DE. MAPPING | DFP | DFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | LOAN DD(ADVICEPART) | SL-3002 | 643 | 634.SL.2 | 643.4.1.GB | 643.1.1 |
| 18 | ADVICE RATE AND AMOUNT FIXING(LOAN.RATE.CHANGE) | SL-3231 | 644 | 644.SL.1 | 644.1.1.GB | 644.1.1 |
SL.RATES.PART
| 19 | ADVICE RATE AND AMOUNT FIXING(LOAN.RATE.CHANGE) | SL-3231 | 644 | 644.SL.1 | 644.1.1.GB | 644.1.1 |
Invalid Message Types
The messages MT 643, MT 644, MT 646, and MT 649 are being removed from the FIN Network, as there has been no FIN traffic for them. Hence, SWIFT MT does not support them from 2017. However, this removal from FIN network have no impact on messages that are used on proprietary networks or any other non-FIN network or messaging service.
The system has the ability to prevent a particular message type being sent to SWIFT. The user is able to define these invalid message types in the Invalid Message Type field in SWIFT.PARAMETER. If any message comes to the formatting queue with the invalid message type defined in the SWIFT.PARAMETER, the system sends it to REPAIR with the message “Message Type xxx is Invalid”, thereby preventing the message from being sent to Swift.
The following swift messages to the participants are suppressed from being sent to the SWIFT channel.
- MT643 is generated at the loan drawdown stage and the loan amendment stage
- MT644 specifies the interest rate and, if applicable, the exchange rate, for the next interest period
- MT646 is the advise of payments and/or prepayments of principal and/or of interest with the same value date.
- MT649 is the message that is generated at the Facility creation stage.
- The Invalid Message Type field must be one of the above mentioned messages that are not supported by SWIFT but still exist in the
DE.MESSAGEfor use in any non-FIN network or messaging service.
In this topic