Introduction to Financial Risk Management
The FRM application is built on Analytics and Transact Data Hub (TDH) platform. It is integrated with Transact and is available as a pre-packaged and upgradeable risk management software. It enables the user to,
- Navigate complex regulatory and compliance landscape.
- Run sophisticated risk models.
- Ensure profitability and risk-informed decisions for greater efficiency and transparency.
The below diagram depicts the FRM modules.
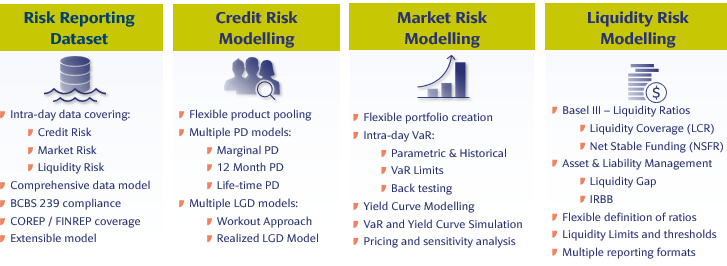
Liquidity Risk Overview
Following the failure of many banks to adequately measure, manage and control their liquidity risk in 2007 and in subsequent years, the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) introduced two liquidity standards as part of the Basel III post-crisis reforms.
- Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) - Enhances banks' short-term resilience.
- Net Stable Funding Ratio (NSFR) - Aims to promote resilience over a longer time horizon by creating incentives for banks to fund their activities with more stable sources of funding on an ongoing basis.
LCR is designed to ensure that the bank holds a sufficient reserve of High-Quality Liquid Assets (HQLA) to allow them to survive a period of significant liquidity stress lasting 30 calendar days. LCR seeks to promote short-term resilience of a bank's funding profile by ensuring that it has sufficient liquid assets to cover possible short-term liquidity outflows. Under the requirements, the bank is required to maintain an LCR requirement of at least 100%.
The LCR has two components:
- Value of the stock of High-Quality Liquid Assets (HQLA) in stressed conditions
- Total net cash outflows
The NSFR is the amount of available stable funding relative to the amount of required stable funding. This ratio must be equal to at least 100% on an ongoing basis.
The NSFR has two components:
- Available Stable Funding (ASF) - The portion of capital and liabilities expected to be reliable over the time horizon considered by the NSFR, which extends to one year.
- Required Stable Funding (RSF) – A function of the liquidity characteristics and residual maturities of the various assets held by that institution and those of its Off-Balance Sheet (OBS) exposures.
In this topic