Introduction to Financial Risk Management (FRM)
The FRM application is built on Analytics, Transact Data Hub (TDH) and Temenos Data Lake (TDL) platforms. It is integrated with Temenos Transact and delivered as a pre-packaged and upgradeable risk management software. It enables the clients to:
-
Navigate complex regulatory and compliance landscape
-
Run sophisticated risk models
-
Ensure profitable and risk-informed decisions for greater efficiency and transparency
The FRM application consists of three modules and they are:
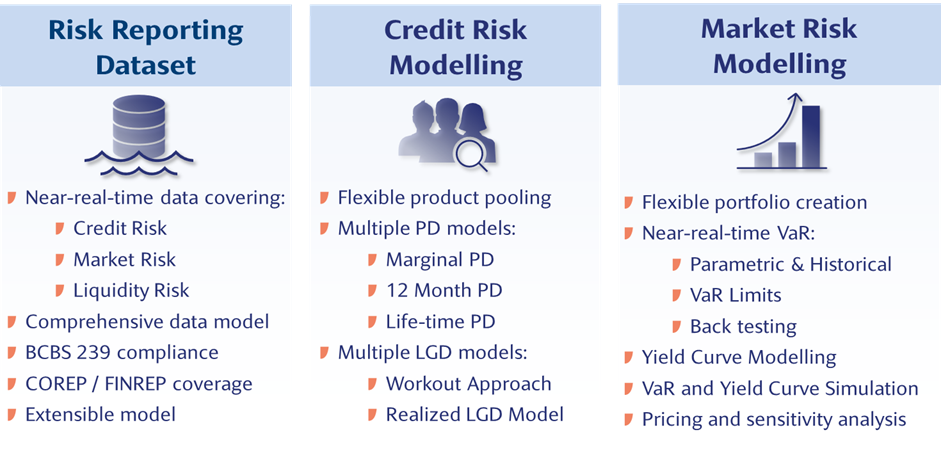
IFRS9 - PD/LGD Modelling Overview
There are various Credit Risk models available for Banks to compute Probability of Default (PD) and Loss Given Default (LGD) based on the nature of its business operations and portfolio complexity. It can range from simple scoring-based models to a complex statistical default model. Financial institutions are free to choose the model as long as it is consistent, auditable and flexible.
FRM utilizes one of the most commonly used models for PD:
- Macro-Economic Model
For LGD:
- Realized LGD and
- Workout Approach
These models effectively provide forward-looking PD and LGD required for International Financial Reporting Standard – 9 (IFRS9) Expected Credit Loss provisioning.
Credit Risk Modelling offers a comprehensive analytical computation capability to assess counterparty credit risk profile in bank’s lending. It has a pre-configured interface with Temenos Transact using Data Event Streaming (DES) and Temenos Data Engineering (TDE) components. This model also provides advanced PD and LGD modelling capability using various models as per IFRS9 requirements.
The various PD and LGD calculated in the system are shown in the below screenshot.
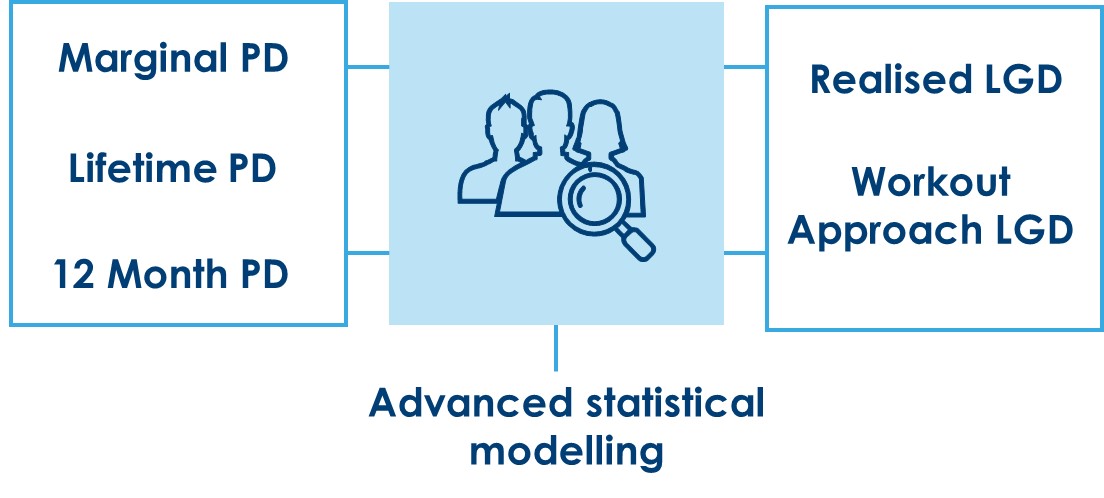
PD is usually calculated as a forward-looking estimate of the realized Default Rate (DR) over a 12-month horizon. DR is calculated as observed number of defaulted contracts/accounts during the period compared to active contracts/accounts at the start of period.
- Marginal PD (Conditional PD) is the probability of defaulting at time ‘T’ given survival up to that point. Specifically, P [default during period n | survival until start of period n]
- Life-time PD (Unconditional PD or Cumulative PD) is the probability of defaulting at any time during the residual maturity of the account. It requires long term perspective on macro-economic parameters and overview of economic cycle over long term. Time series analysis is carried out to arrive at a PD term structure.
- 12-month PD is Point-in-Time PD with 1-year time horizon. That is basically Conditional PD over a 12-month period.
- Realised LGD approach uses actual recovery rate for each contract/account that is calculated by discounting the recoveries using EIR. This is then scaled up at the portfolio level to calculate portfolio LGD.
- Workout Approach classifies all defaulted contracts/accounts under three categories:
- Cured,
- Restructured and
- Recovery
LGD is then derived as probability weighted recovery rates under each classification.
In this topic