Introduction to Legal Entity Identifier
Legal Entity Identifiers (LEIs) are assigned to legal entities that are based primarily in the US and Europe where regulations require the use of LEIs to uniquely identify counterparties to transactions in regulatory reporting. Public authorities in these jurisdictions rely on the LEI to,
- Evaluate risk
- Take corrective steps
- Minimise market abuse, if required
- Improve accuracy of financial data
LEI is a 20 digit alphanumeric code that connects to key reference information, which enables clear and unique identification of companies participating in global financial markets. This global standard meets the 2012 specifications of the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO 17442:2012).

The fundamental rule that entities eligible for LEIs are identified under MiFID II with a LEI follows from Article 26(6) MiFIR, Article 5 of Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2017/590 of 28 July 2016 supplementing Regulation (EU) No 600/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to regulatory technical standards for the reporting of transactions to competent authorities, and Annex I .
It is also unequivocally underlined by the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) in Guidelines Transaction reporting, order record keeping and clock synchronisation under MiFID II, 10 October 2016, ESMA/2016/1452 (p. 24).
Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID II)
The MiFID II is a European regulation regarding the financial market, which offers greater protection for investors and injects more transparency into all asset classes from equities to fixed income, exchange traded funds and foreign exchange.
The category of entities eligible to obtain LEI is broad and includes each legal entity
- Partnerships
- Societies
- Associations
- Wealth clients
- Funds
- Sub-funds (sub-funds cannot share an LEI - each sub-fund must get its own LEI)
- Subsidiaries (subsidiary cannot rely on a parent LEI)
The MiFID II framework requires not only trading parties but also all reporting parties, which includes brokers, central counterparties and beneficiaries, to report valid LEI.
The European Securities and Market Authority (ESMA) lists the entities required to be identified through the LEI under MiFIR:
- Investment firms – executes transactions in financial instruments
- Clients (buyer, seller) – executes transactions, when the client is a legal entity, through investment firm
- Trading venue – reports as per MiFIR artile 25(5) on behalf of the client, especially when the client is a legal entity
- Decision maker – acquires the financial instrument, when this person is a legal entity e.g. investment managers acting under a discretionary mandate on behalf of its underlying clients
- The firm – transmits the order
- The entity – submits the transaction report (i.e. trading venue, ARM, investment firm)
- The issuer – lists and/or traded on a trading venue any financial instrument
The above entities are identified with LEI even if they had no previous legal obligation to obtain one and regardless of where they are operating or legally based (Briefing Legal Entity Identifier (LEI), 09 October 2017, ESMA70-145-238, p. 3).
Configuring Legal Entity Identifier
The following table is required to configure Legal Entity Identifier:
Configuring LE.PARAMETER
Use this parameter table to define rules to identify a customer as an individual customer, an entity or a sub fund customer. The table allows determining the identifier to be validated for its presence.
- Either an API or a Temenos Transact Rules Engine can be attached to this parameter to define the criteria.
- There is also option available to define number of days to notify in case of expiration of an identifier.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | The ID of the record must be a valid Temenos Transact company and ihould be a customer company. The rules defined in this record is applicable company wide. |
| Entity Rule | Rules can be defined using the Temenos Transact Rules engine. Once the rule is defined, the ID of a valid EB.RULE.GATEWAY can be captured in this field. Usage of Entity Rule and Entity API fields are mutually exclusive if defined. |
| Entity API | Where rules are handled via an API, a valid routine name listed in EB.API application is specified in this field. If you try to update both Entity Rule and Entity API fields, an error “Either Rule or API must be defined and not both” is displayed. One of the fields is mandatory, as it is necessary for the KYC process to identify the type of customer. |
| Notify Exp Days | 1–999 days
Specify the number of days ahead of expiry of LEI by when system can raise a warning for renewal. This warning or override message is raised only if there is any transaction initiation for the customer in which case during the LEI transaction control system can check for approaching next renewal date of LEI in use. The override message notifies the end user when an LEI is due for renewal up to XXX days prior to next renewal date.
|
Illustrating Model Parameters
This section covers the below model products for the Legal Entity Identifier (LE) module.
| S.No | Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | LE.PARAMETER
|
|
| 2. | LE.ELIGIBILITY.PARAM
|
|
| 3. | LE.DIRECTORY
|
|
| 4. | OC.CUSTOMER
|
|
Illustrating Model Products
This section covers the below model products for the Legal Entity Identifier (LE) module.
| S.No | Product Name | Features |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | LE.PARAMETER,INPUT | This version is accessible to the Administrator to create or amend a record and to set the appropriate criteria that differentiates a private person (NCI) from entity (LEI) respectively during KYC and as well as during transaction execution. |
A record with Entity API is defined. The purpose of the API option is to provide flexibility to the bank user to classify the customers by whatever criteria considered relevant.
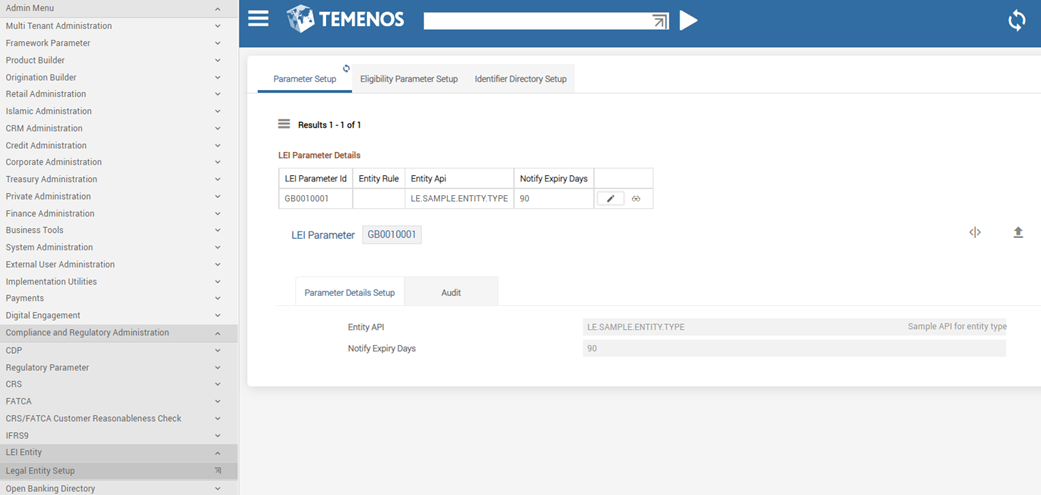
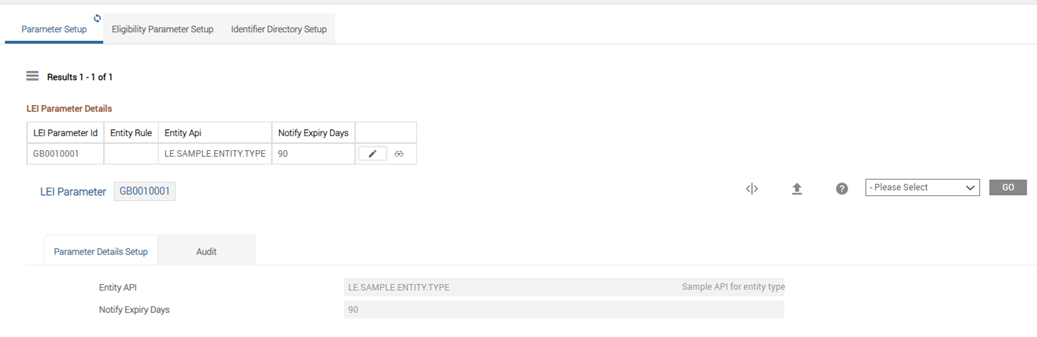
The below screenshot displays the LE.PARAMETER, which displays a record with Entity Rule defined:
In this topic